摘要
创新是推动长期社会发展和经济增长的最为有效的动力,更是一个企业生存和发展的灵魂。如何促进企业创新,正在成为越来越重要的社会议题,因此,研究企业创新的影响因素有着重要意义。
另一方面,随着企业间生产经营联系的日益紧密,越来越多的企业高管在外部机构兼职。CEO 作为企业的重要决策者,通常具有良好的技术知识、管理经验和生产实践经验,因此,外部机构通常青睐聘任其他企业的 CEO 作为兼职人员,CEO 在外兼职已经成为普遍现象。
本文试图分析 CEO 的在外兼职是否会对原企业的创新绩效产生影响。基于中国 A 股市场 2005-2014 年的面板数据,本文利用行业-年份-区域固定效应模型,研究了 CEO 在外兼职对原企业创新绩效的影响,以及 CEO 外部兼职机构的行业、地区、类别特征对于提高原企业创新绩效的作用。
首先,本文对 CEO 外部兼职对企业创新绩效的影响进行了总体研究,由于 CEO 在外兼职有利于知识的溢出与转移,因而有可能会促进原企业创新。研究结果表明,具有外部兼职的 CEO,对原企业创新绩效具有显著的促进作用。其中,CEO 在外兼职的数量也是重要因素,CEO 在外兼职数量越多,越有利于提高原企业的创新绩效。
其次,由于 CEO 的外部兼职机构具有较大的差异性,其行业属性、地区属性和类别属性也会成为影响溢出和转移的知识质量的关键因素,从而影响知识溢出对于企业创新绩效的提升作用。因此,本文进一步研究了 CEO 外部兼职机构的行业属性、地区属性和类别属性,对于企业创新绩效的影响,结果表明:
(1) CEO 在与原企业不同行业的外部机构兼职,相比于在与原企业同行业的外部机构兼职,更有利于提高原企业的创新绩效;
(2) CEO 在与原企业同地区的外部机构兼职,比在不同地区的外部机构兼职,对原企业创新绩效的提升作用更强;
(3) CEO 在一般企业类、行业协会类和科研院所类外部机构的兼职对原企业创新绩效具有显著的促进作用,而 CEO 在政府部门和其他外部机构的兼职对原企业的创新绩效没有显著影响。
因此,本研究认为,在企业聘任 CEO 的过程中,注重创新产出的企业应该更多地考虑聘任具有外部兼职较多的 CEO,同时,CEO 的主要外部兼职机构最好是与原企业同地区、不同行业的机构,并且最好是在一般企业、行业协会和科研院所兼职。
对于外部投资者而言,如果被投资企业的 CEO 具有较多的外部兼职,并且主要外部兼职机构为与原企业不同行业、同地区的一般企业、行业协会和科研机构,则可以预期被投资企业会具有较好的创新产出水平。
关键词:创新;CEO 在外兼职;兼职机构类别
Characteristics of CEO outside Multiple Appointments and Firm Innovation Performance
ABSTRACT
Innovation is the most effective factor in promoting long-term social development and economic growth, as well as the soul of enterprises’ survival and development. It has been a more and more important social issue that how to promote enterprises’ innovation, therefore, researching on the determinants of enterprises’ innovation is very meaningful.
Meanwhile, as there is increasingly closer links in production and investment among companies in the market, more and more executives have multiple appointments in outside institutions, including in firms, government departments, industry associations, academic institutions, and so on. CEOs are the most important decision makers in firms, they usually have excellent technical knowledge, management skills and production experiences, therefore, CEOs are better preferred to be appointed as a member by outside institutions, CEOs’ outside multiple appointments have become a common phenomenon recently.
This paper aims to study whether CEOs’ outside multiple appointments will have influence to their home firms’ innovation. Based on the panel data of Chinese A-share market from 2005 to 2014, using industry-year-region fixed effect model, this article studies the influence from CEOs’ outside multiple appointments to their home firms’ innovation performance, and the moderating effect of outside institutions’ industrial, regional and classification characteristics toward home firms’ innovation.
Results have shown that, CEOs who have outside multiple appointments will significantly improve their home firms’ innovation performance. Besides, results also shown that the more outside multiple appointments a CEO has, the greater promoting effects he/she will bring to the home company’s innovation performance.
In addition, since the industrial, regional and classification differences of outside insititutions are also key factors affecting the quality of knowledge outflow and transfer, thus influencing innovation, this paper further studies the industrial, regional and classification characteristics of CEOs’ outside multiple appointment institutions toward innovation, results are as follows:
(1) Comparing with CEOs’ multiple appointments in the same industry, CEOs’ multiple
appointments in different industries have greater improvement to home firms’ innovation performance;
(2) CEOs’ multiple appointments in the same region can better promote home firms’ innovation performance, comparing with different region multiple appointments;
(3) CEOs’ multiple appointments in other firms, industry associations and academic institutions all significantly promote home firms’ innovation, while multiple appointments in government departments and other institutions do not have significant effects.
Therefore, this paper suggests that in the process of appointing new CEOs, enterprises which value more on innovation output should consider hiring CEOs who have more outside multiple appointments. At the same time, it would be better if the majority of CEOs’ outside multiple appointment institutions are general enterprises, industry associations and academic institutions, and are of different industry and same region to the home firms.
For outside investors, if the invested enterprise's CEO has more outside multiple appointments, and the majority of outside institutions are enterprises, industry associations and academic institutions that are of different industries and same region to CEOs’ home firms, then investors can generally expect the enterprise to have good innovation performance.
KEY WORDS: Innovation; CEO outside multiple appointments; Association type
表目录
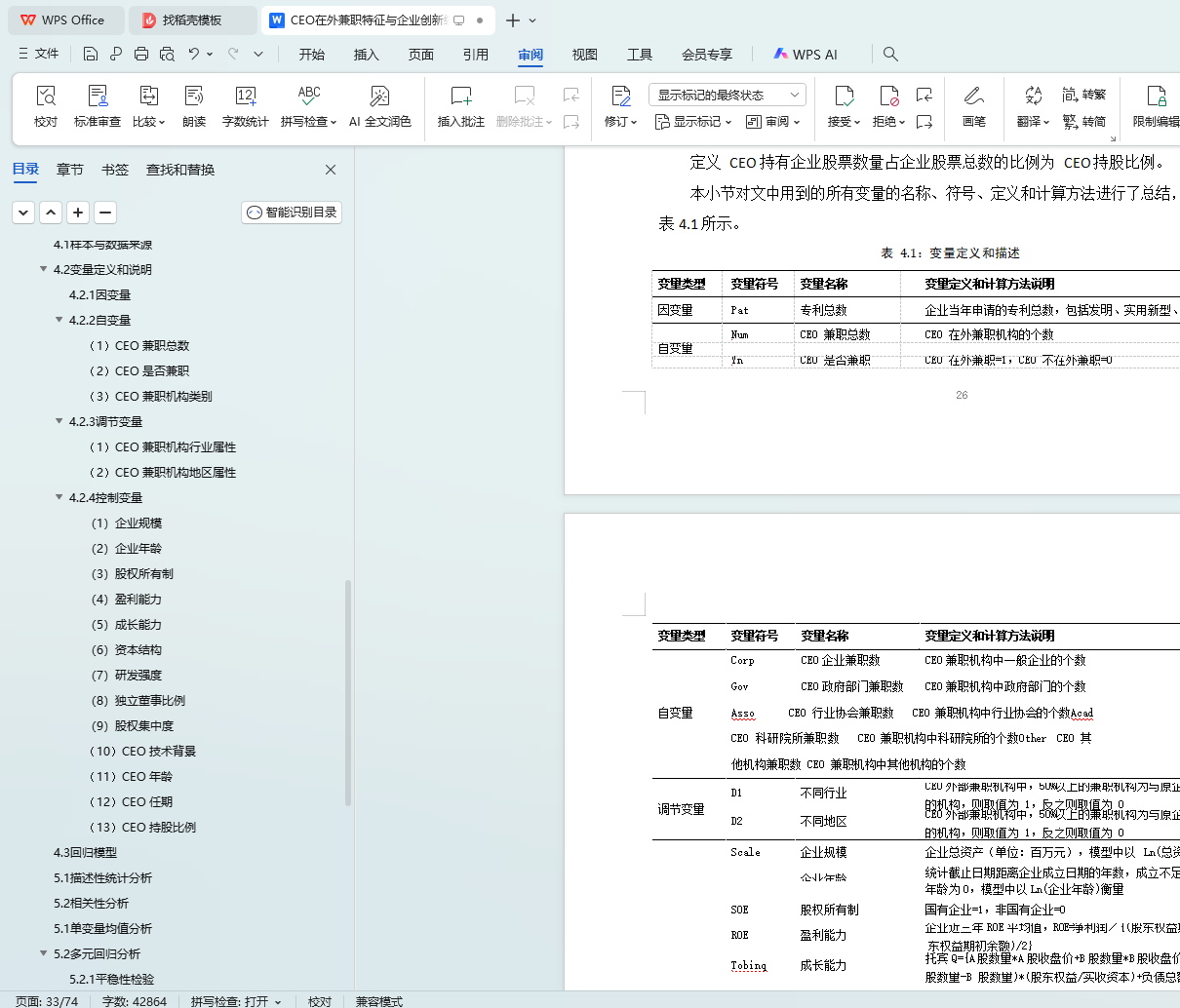
表 4.1:变量定义和描述 24
表 5.1:变量统计描述 28
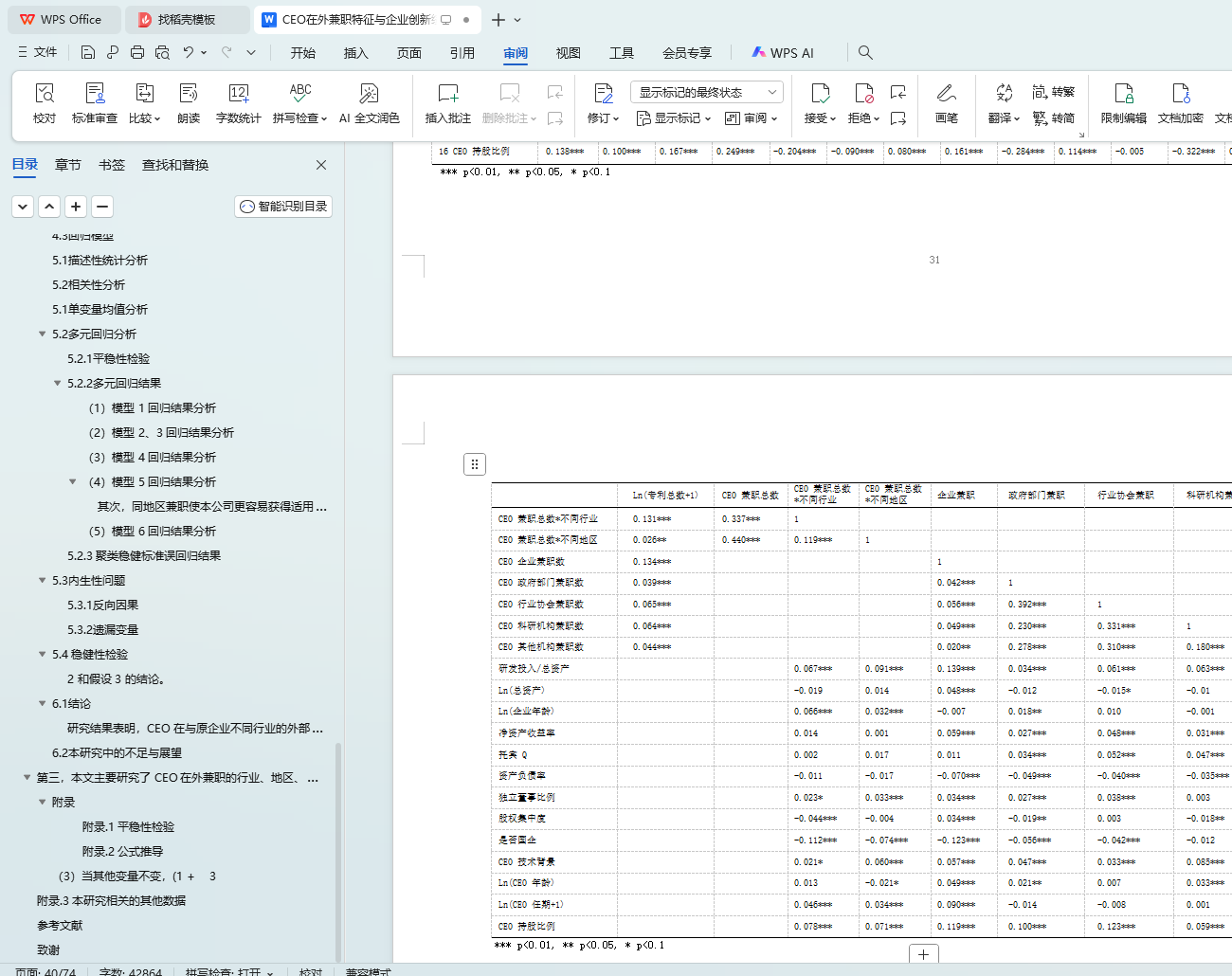
表 5.2:相关性分析 31
表 5.3:单变量均值分析 33
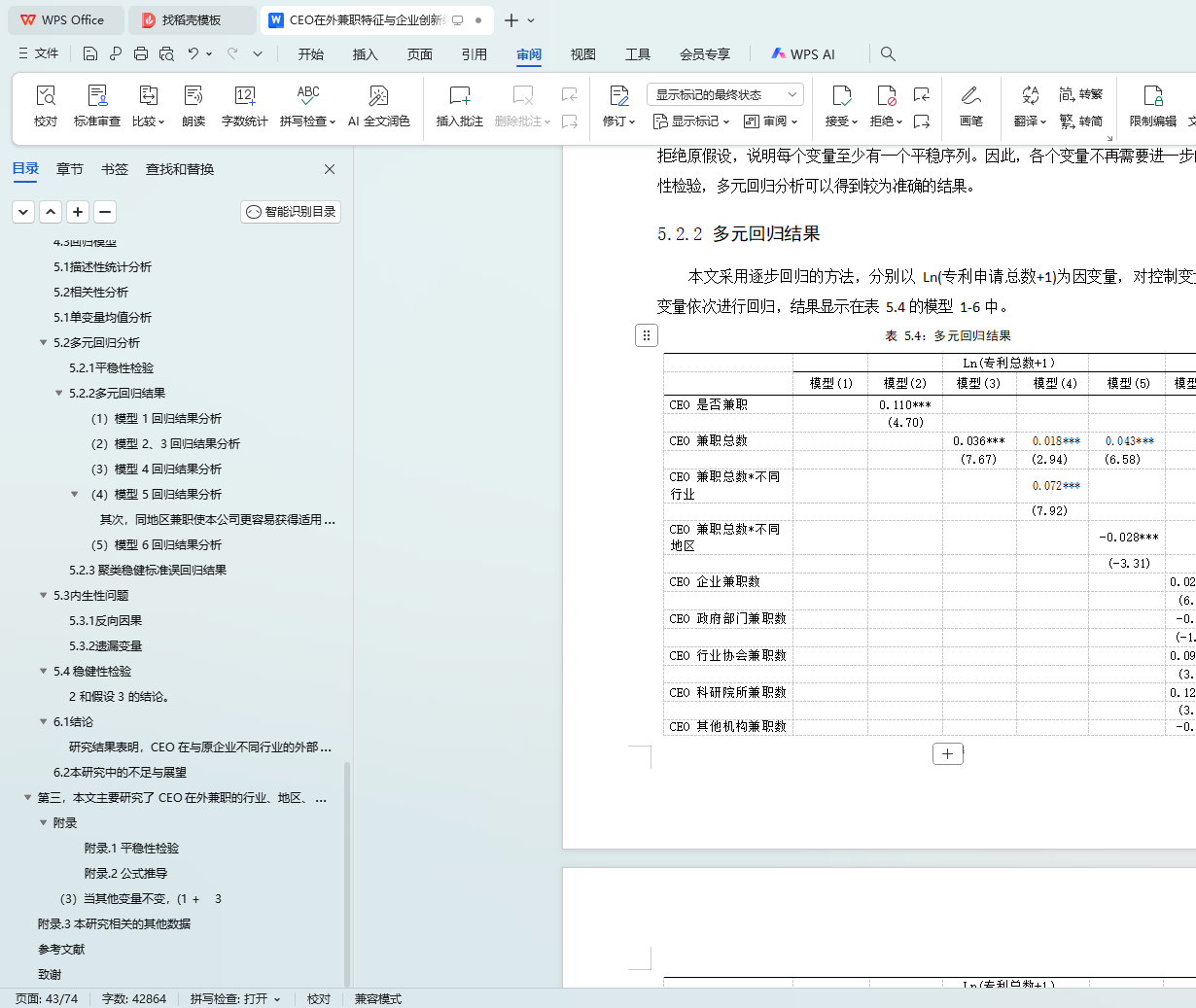
表 5.4:多元回归结果 34
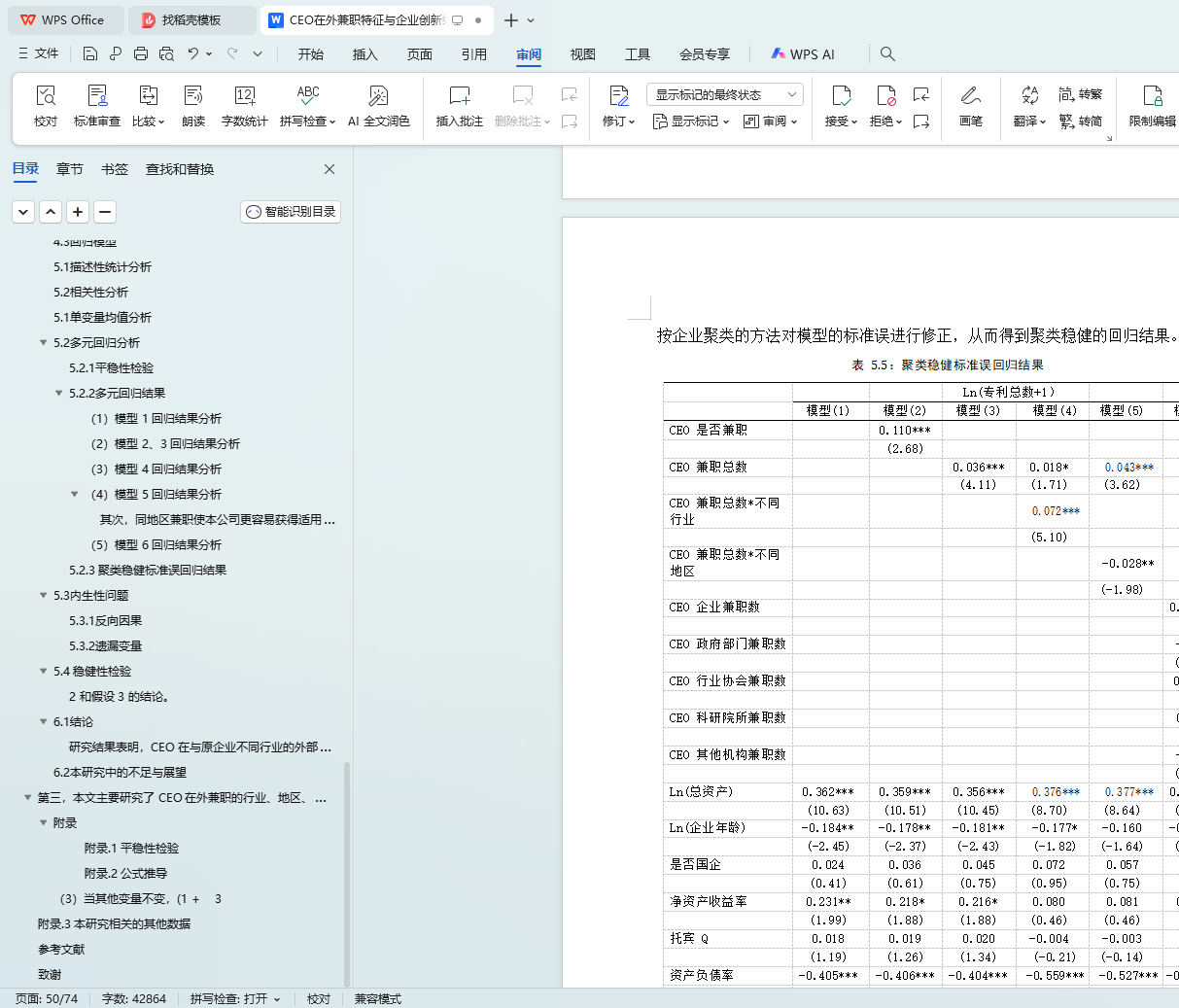
表 5.5:聚类稳健标准误回归结果 42
表 5.6:联立方程和工具变量回归结果 45
表 5.7:稳健性检验回归结果 47
表 附录.1:平稳性检验 54
表 附录.2:CEO 兼职、专利数量年度统计 56
表 附录.3:CEO 兼职、专利数量分行业统计 56
表 附录.4:方差膨胀因子(VIF) 56