摘要
随着我国金融业市场化改革的逐步深入,2003年后我国逐渐出现了非金融企业参股金融企业的现象,特别是银行业,由于监管严格,体量庞大,对投资资金需求较高,对于参股股东的资金实力要求严苛。上市公司一般均是行业龙头,雄厚的资金实力使其成为银行增资扩股过程中极为青睐的对象。对于银行持股企业,在我国情况较为复杂,监管尺度几经调整,参股来源和形式多样,形成较为复杂的局面。
2015年以来,随着经济下行压力逐渐增大,关于新一轮“债转股”和“投贷联动”的政策消息频出,使得银行与企业的股权关联再一次成为焦点。预计随着详尽政策的陆续出台,未来我国银企股权关联形式会更多样,也会更紧密。
本文研究了银企股权关联与企业风险承担之间的关系。此前的文献并没有严格区分企业参股银行以及银行持股企业二者对企业风险承担影响差异,本文认为二者的主动发起者和动机均不相同,因此影响路径和结果不能混为一谈。通过对1999~2014年我国沪深两市的上市公司进行研究,发现企业参股银行对国有企业和非国有企业具有不同影响,仅对非国有企业的风险承担水平具有显著提高,而对国有企业并没有这一特征。另一方面,银行持股比例与风险承担之间具有“U”形特征。由于我国银行持有企业股份比例普遍较低,高持股比例现象主要集中于国有企业,总体来看银行持股将降低企业风险承担水平。对国有企业,持股比例与风险承担水平“U”形关联显著;对非国有企业,持股比例与风险承担水平呈负关联。
自此,我们认为,银企股权关联作为一种重要的非正式制度,在新兴市场中,银行主动参与企业的股权投资在低比例时并不具有正面影响,在高比例时的影响也存在一定不确定性;而企业参与银行股权投资对非国有企业风险承担水平的提高具有一定改善作用,对国有企业影响不显著。
本文在参考前人研究方法后,系统研究了银企股权关联与企业风险承担之间的关系。通过理论推理提出企业参股银行与银行持股企业对企业承担不同的影响,并通过实证检验获得经验数据的支持。对现实具有一定的指导意义。
关键词:银企股权关联,企业参股银行,银行持股企业,企业风险承担
Effects of Bank-firm Equity Connection on Corporate Risk Taking:Evidence from China
Jiao Xue (Finance)
Directed by Wei Cen
ABSTRACT
With the gradual deepening of the financial market reform. Since 2003, there have been financial enterprises ownerships held by firms, especially banks. For the reason that banks are strictly supervised and large, they need a lot of investing capital funds with demanding requirement for the shareholders. Listed companies are usually top in their fields and become favorable objects in the process of bank increasing investments. For firm stakes held banks, it’s more complex both for the source and forms, and the situation is much more complicated.
Since 2015, under increasing pressure of downward economy, the government has published intensive measures about the second round of “Debt for equity swap” reform and linkage of equity and loans, which made the Bank-firm Equity Connection (BFEC) once become the focus. It’s expected that with te implement of those policies, BFEC will be closer and diversified in the future.
This paper studied the relationship between BFEC and corporate risk taking. There is no strict distinction of the different impacts on corporate risk taking between firm stakes held by banks and bank stakes held by firms. This paper argued that the motivation and operating access are not same and can not be confused, so that the influence and transmitting channels are distinguising. Based on the date from 1999 to 2014 of China's Shanghai and Shenzhen listed companies, we found that bank stakes held by firms have different impacts on SOEs and non-SOEs. The holding behavior can significantly improve the level of firms’ own risk taking for non-SOEs. And it’s not significant for SOEs. On the other hand, the impact of corporate risk taking is associated the shareholding ratios of firm stakes held by banks and relationship is “U”-shaped. Overall, bank ownership could reduce the corporate risk taking level. For SOEs, it’s significant for reason that the high ratio holding behavior happened on them. For non SOEs, the relationship is negatively related.
Since then, we believe that BFEC as an important informal institutions in emerging markets, the impact of firm stakes held by banks is uncertain, and bank stakes held by firms indeed improve the level of risk taking for non-SOEs.
In this paper, on the basis of previous research methods, we systematically studied the relationship between BFEC and corporate risk taking. We proposed the different influence of those two types on theoretical reasoning, and it’s supported by the empirical test of the data. It’s meaningful for the guidance of the reality.
KEY WORDS: Bank-firm Equity Connection,Bank stakes held by firms,Firm stakes held by banks,Corporate Risk-taking
目录
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景和问题的提出
1.2 研究基本框架
1.3 研究贡献和创新之处
第二章 国内外研究情况及文献综述
2.1 企业风险承担相关文献综述
2.1.1 外部环境对企业风险承担的影响文献评述
2.1.2 内部特征和治理机制对企业风险承担的影响文献评述
2.1.3 管理者个体特征对企业风险承担的影响文献评述
2.2 银企股权关联文献综述
2.2.1 企业参股银行文献综述
2.2.2 银行持股企业文献综述
2.3 银企股权关联与企业风险承担文献评述
2.4 本章小结
第三章 银企股权关联的发展
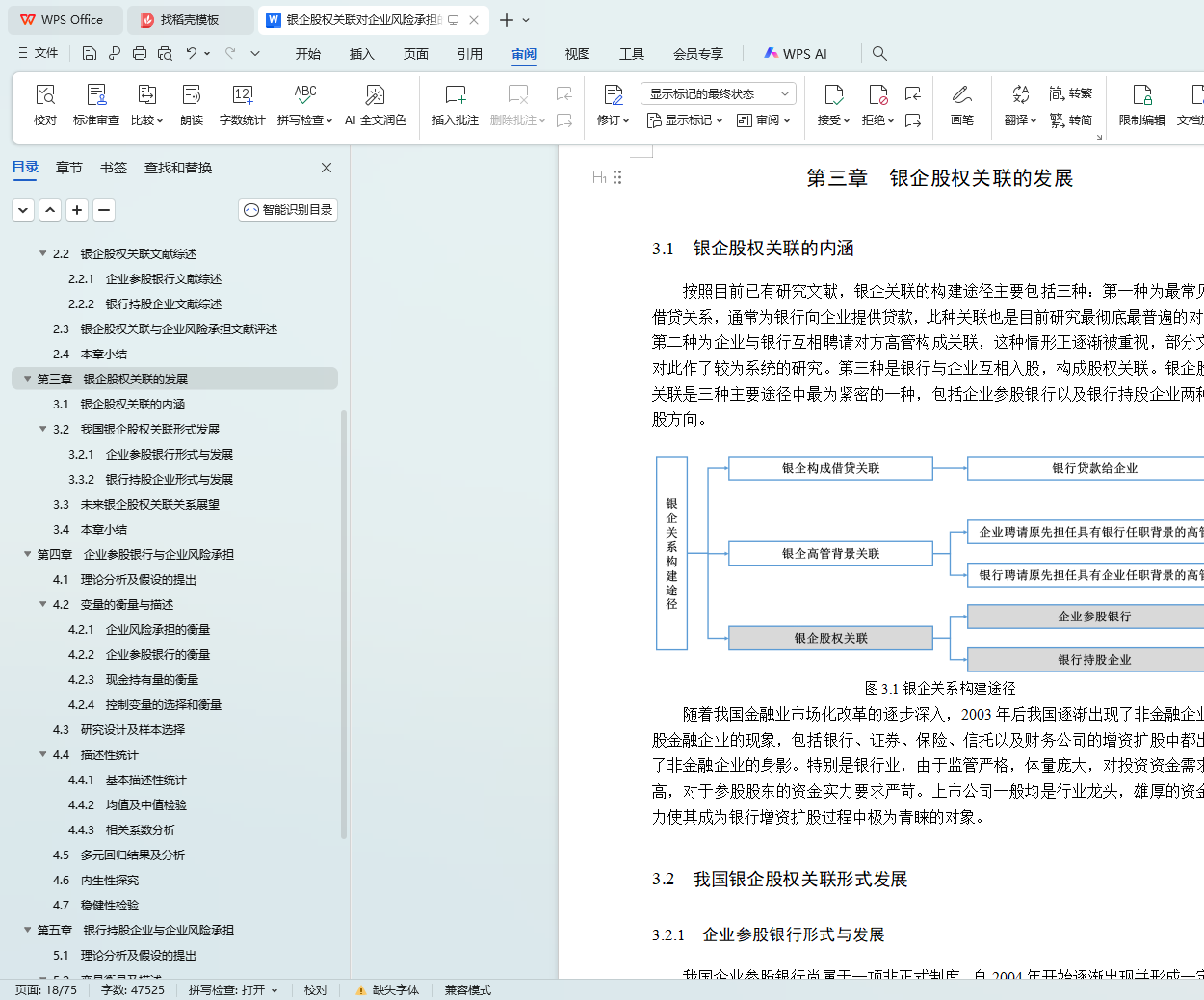
3.1 银企股权关联的内涵
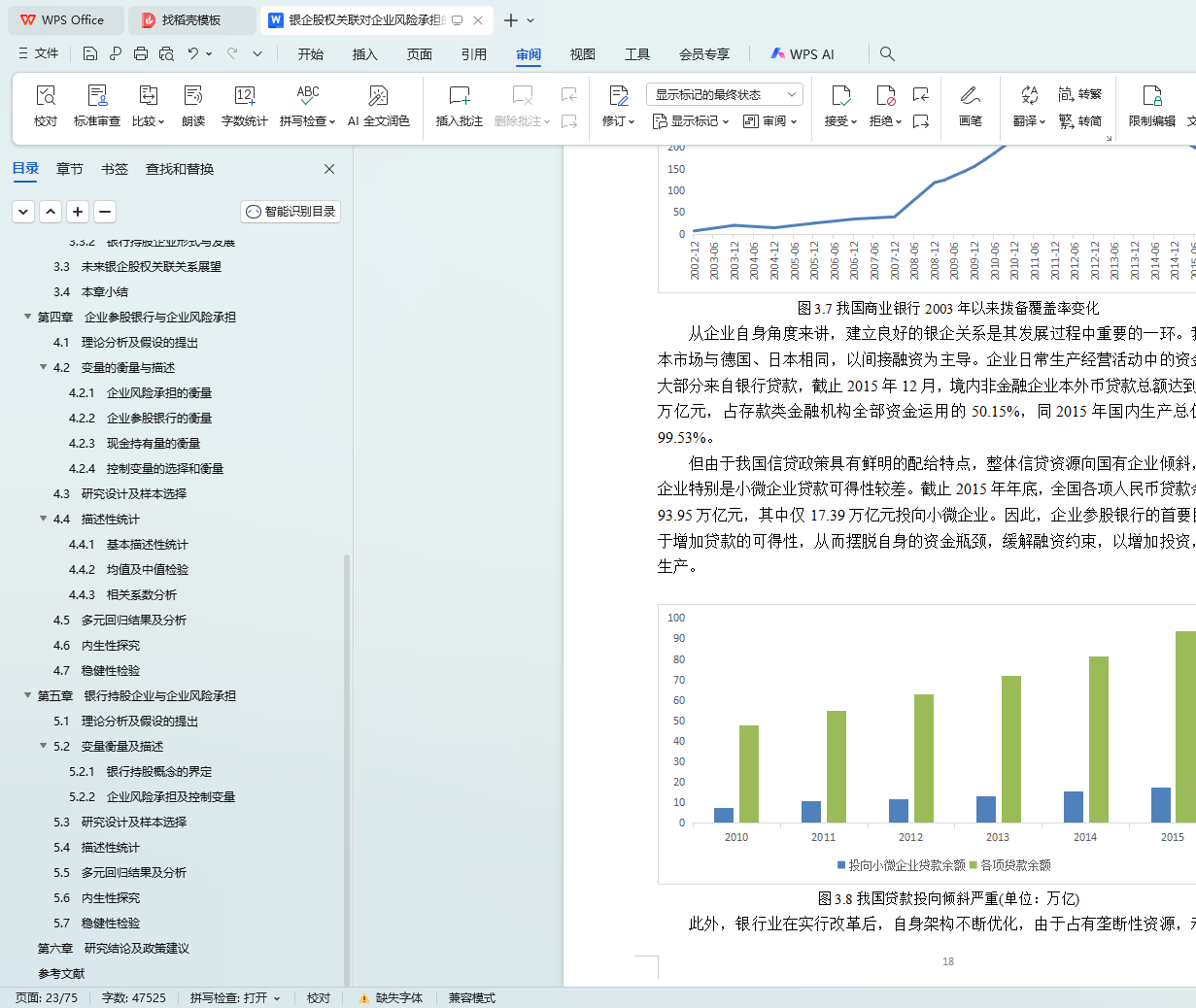
3.2 我国银企股权关联形式发展
3.2.1 企业参股银行形式与发展
3.3.2 银行持股企业形式与发展
3.3 未来银企股权关联关系展望
3.4 本章小结
第四章 企业参股银行与企业风险承担
4.1 理论分析及假设的提出
4.2 变量的衡量与描述
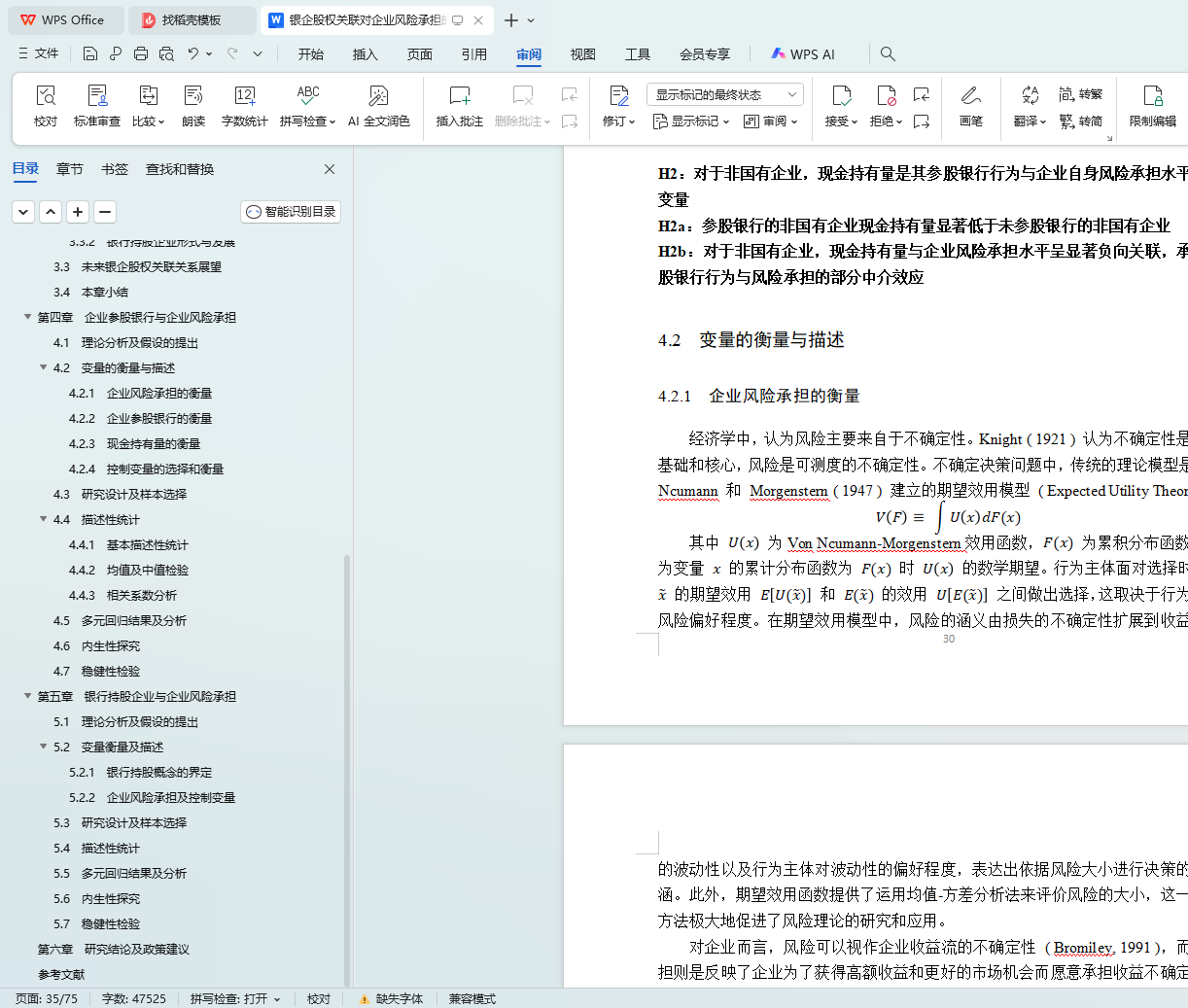
4.2.1 企业风险承担的衡量
4.2.2 企业参股银行的衡量
4.2.3 现金持有量的衡量
4.2.4 控制变量的选择和衡量
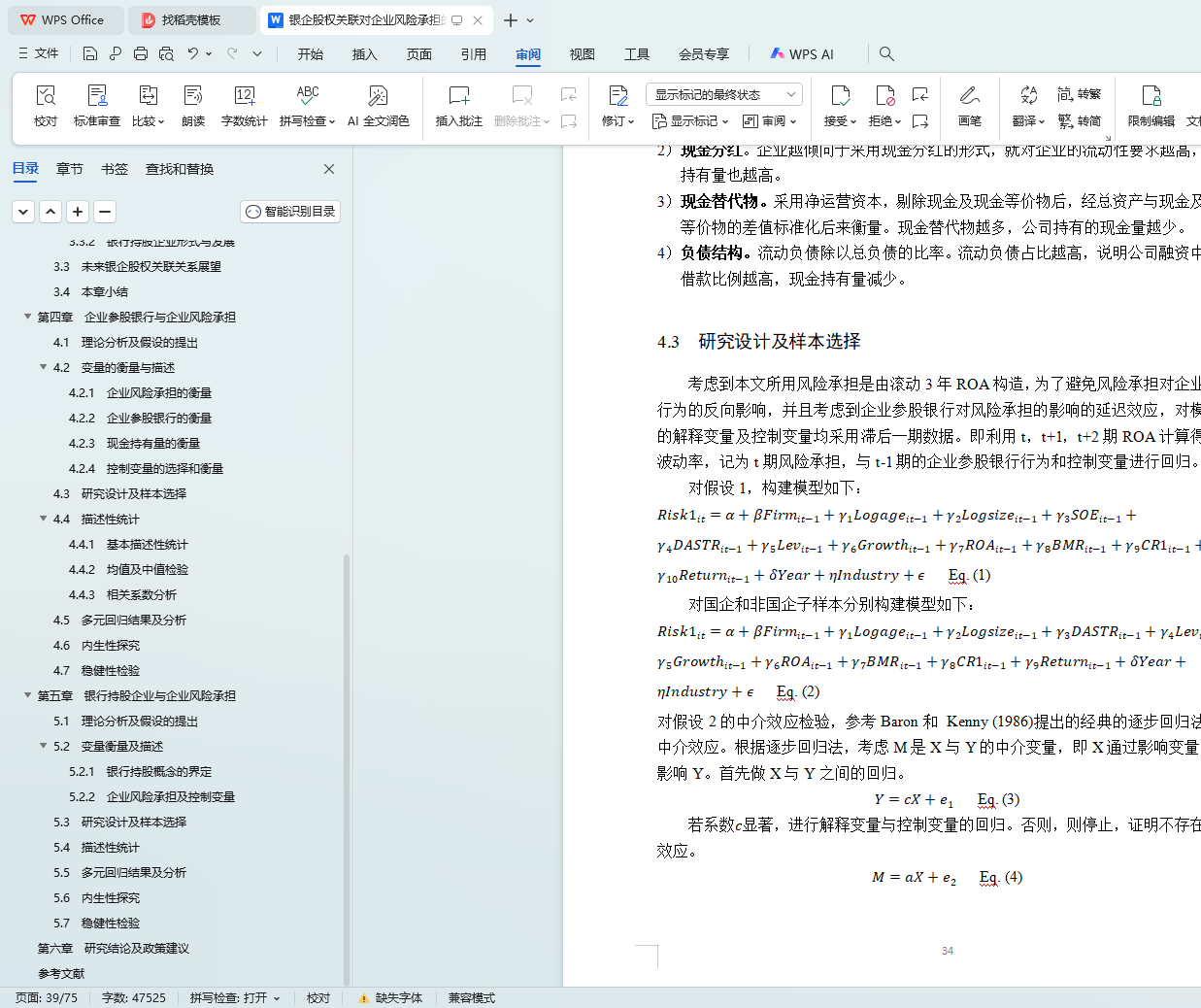
4.3 研究设计及样本选择
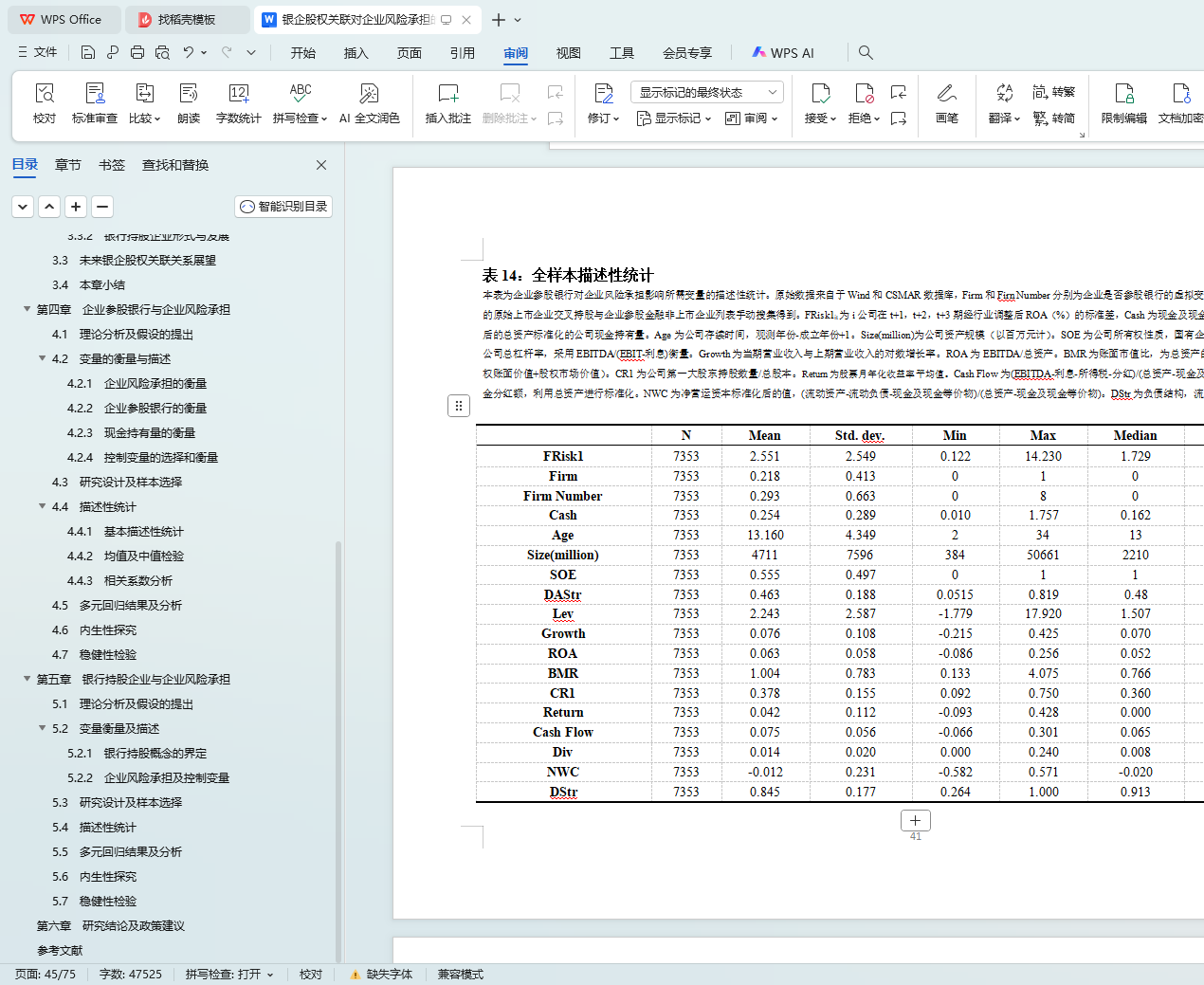
4.4 描述性统计
4.4.1 基本描述性统计
4.4.2 均值及中值检验
4.4.3 相关系数分析
4.5 多元回归结果及分析
4.6 内生性探究
4.7 稳健性检验
第五章 银行持股企业与企业风险承担
5.1 理论分析及假设的提出
5.2 变量衡量及描述
5.2.1 银行持股概念的界定
5.2.2 企业风险承担及控制变量
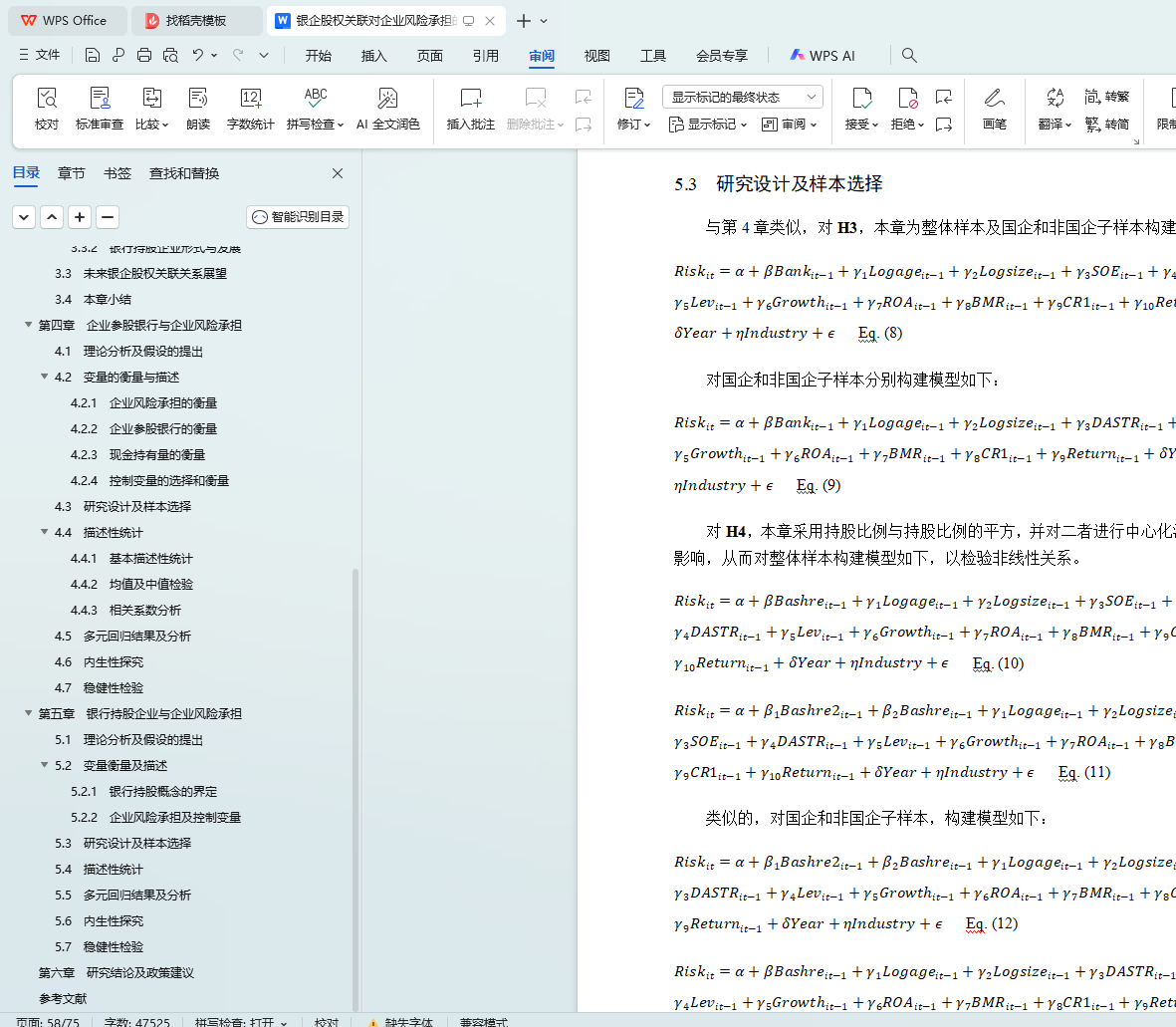
5.3 研究设计及样本选择
5.4 描述性统计
5.5 多元回归结果及分析
5.6 内生性探究
5.7 稳健性检验
第六章 研究结论及政策建议
参考文献
致谢