摘要
截至2015年底,中国国有企业约占沪深A股所有公司的35%,是中国证券市场的重要组成部分。国有企业治理问题的特殊性在于,国有企业高管兼具企业家和准官员双重身份。任职国企高管,可能只是国有企业CEO仕途之上的一种晋升方式。因此,研究政治晋升对公司的影响这一问题很有意义。我们关心,国有企业高管的准官员身份会不会对国有企业的信息透明度和股票收益率产生影响。本文研究国企CEO的政治晋升和股价暴跌风险之间的关系,以及这种关系是否会受到CEO年龄的任期的影响。
本文选取2004-2015年中国A股所有国有企业为样本,采用混合的OLS模型和Ordered Logistic模型对股价暴跌风险进行多元线性回归。本文研究了国有企业CEO的政治晋升对股价暴跌风险的影响,以及CEO年龄、任期和公司信息透明度对该影响的作用。我们发现(1)国有企业CEO政治晋升增加了股价的暴跌风险。(2)这一效果在公司信息透明度较低时显著。信息透明度较高时CEO政治晋升对暴跌风险的影响会减弱(3)在CEO年龄较小时,任期较短时,晋升动力更强,对暴跌风险的影响显著。本文结果表明,政治晋升激励增强了国有企业CEO隐藏坏消息的动力,从而增加了股价的暴跌风险。
关键词:政治晋升,暴跌风险,国有企业
Political Promotion of SOE Executives
and Stock Price Crash Risk
Hao Yang ( Finance )
Directed by Wei Cen
ABSTRACT
About 35 percent of A-shares listed companies are Chinese SOEs until the end of 2015. Chinese SOEs is an important part of Chinese security market. Unlike private enterprises, CEOs have dual occupations as both entrepreneurs and quasi-officials. Working as CEOs in Chinese SOEs may be one way to achieve political promotion for them. Therefore, it is meaningful to research the impact of political promotion of CEOs on Chinese SOEs. We are wondering whether being a quasi-official will affect information opacity and distribution of stock price return of firms. We mainly study the relationship between political promotion and stock price crash risk.
Using sample of A-shares listed Chinese SOEs from 2004 to 2015, we make multiple linear regression by pooled OLS model and Ordered Logistics model. The results show that (1) The political promotion of CEOs in Chinese SOEs significantly increases stock price crash risk of firms; (2) In firms with higher degree of information opacity, the impact is significant; (3) for younger CEOs and CEOs with shorter tenure, incentives for political promotion are stronger, thus increase stock price crash risk. We find that political promotion motivates CEOs to withhold bad news, and to increase the stock price crash risk.
KEY WORDS: Political promotion, crash risk, SOEs
目录
摘要
ABSTRACT
目录
第一章 引言
1.1 研究背景
1.2 研究动机和贡献
1.3 研究内容和结构
第二章 文献综述
2.1 股价暴跌风险
2.1.1 股价暴跌风险的定义和衡量方式
2.1.2 国外对暴跌风险的研究
2.1.3 国内对暴跌风险的研究
2.1.4 导致暴跌风险的其他机制
2.2 政治晋升激励
2.2.1 政治晋升的定义和衡量方式
2.2.2 地方政府官员的政治晋升
2.2.3 国有企业高管的政治晋升
2.3 本章小结
第三章 研究设计
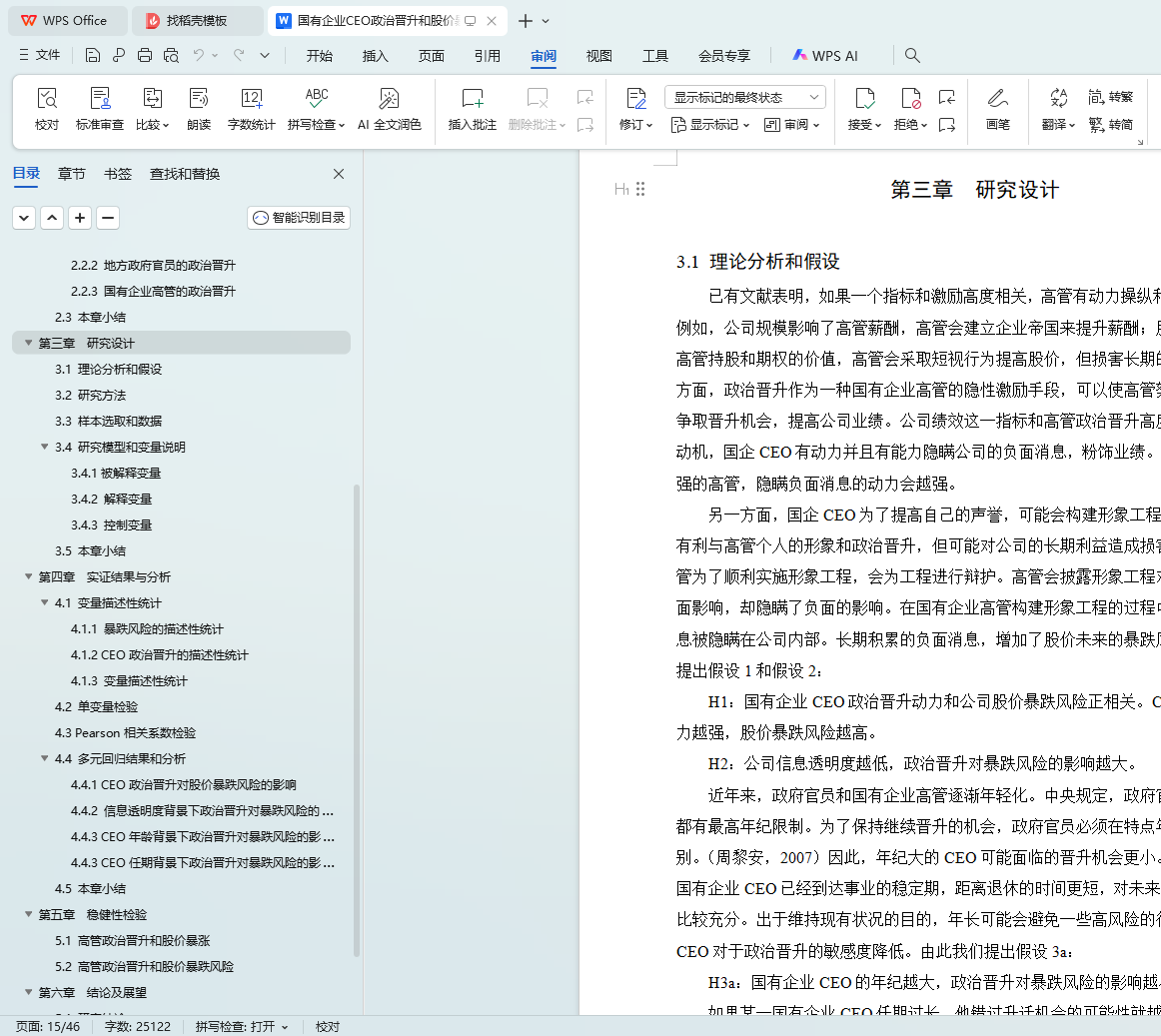
3.1 理论分析和假设
3.2 研究方法
3.3 样本选取和数据
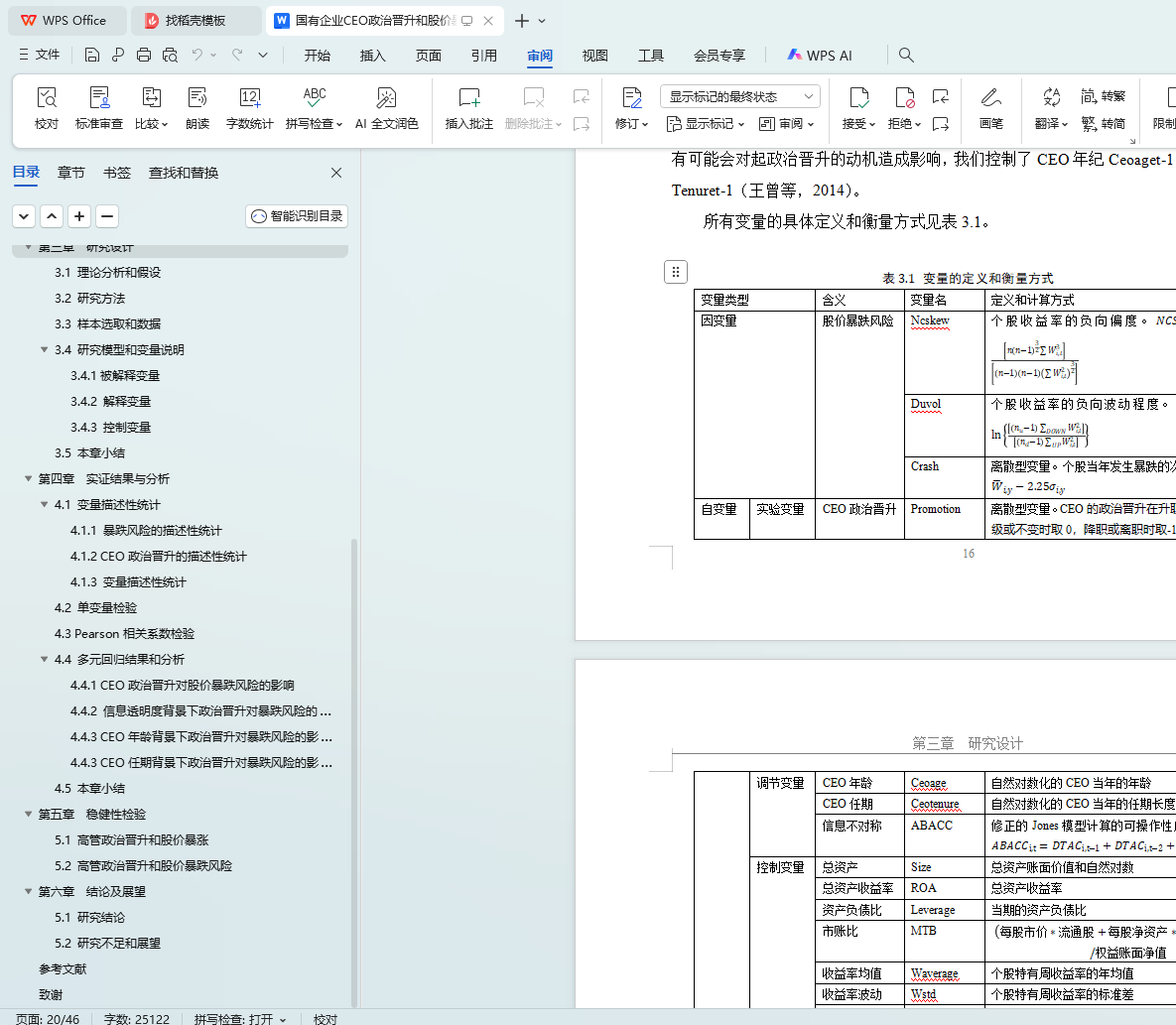
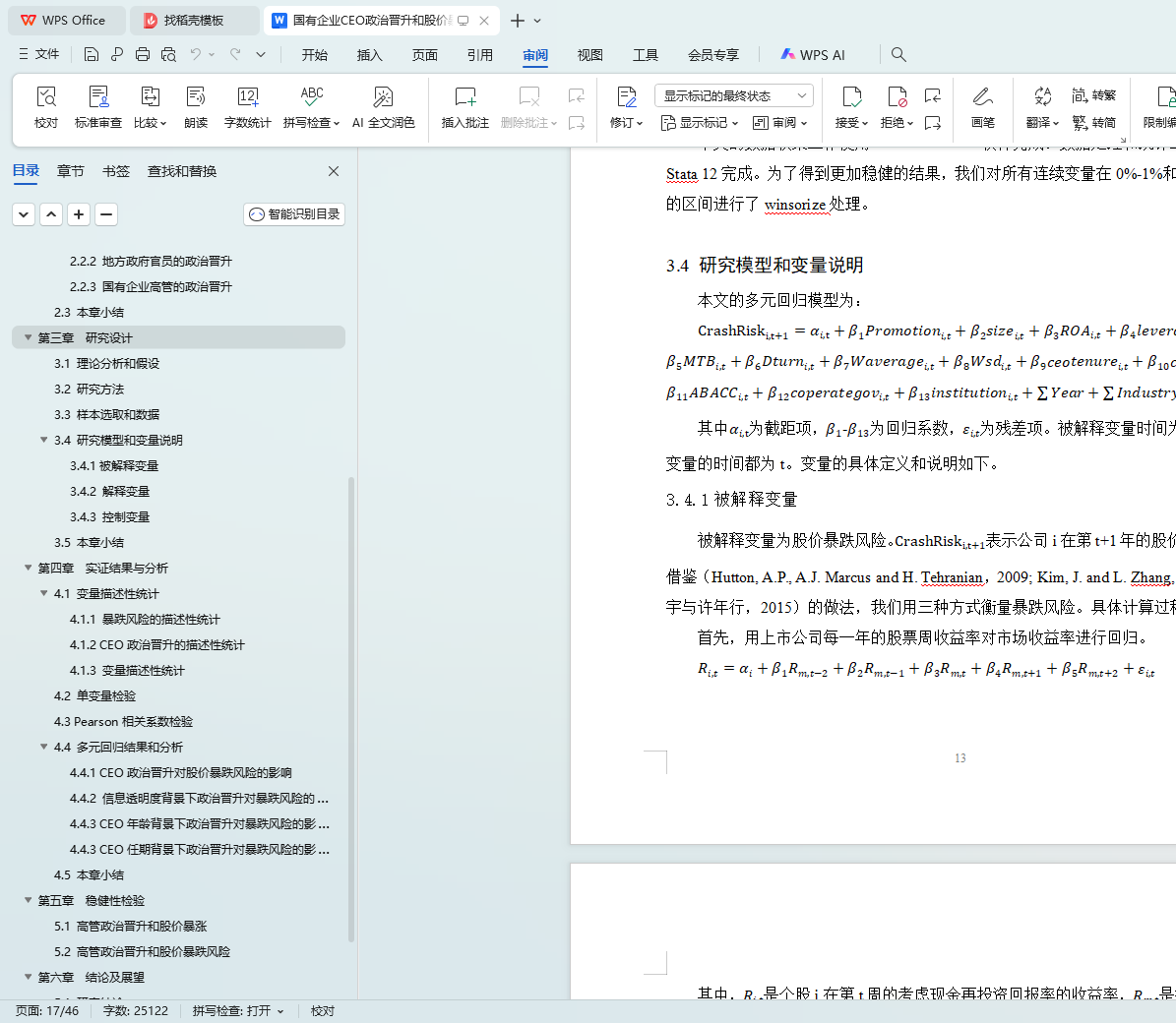
3.4 研究模型和变量说明
3.4.1被解释变量
3.4.2 解释变量
3.4.3 控制变量
3.5 本章小结
第四章 实证结果与分析
4.1 变量描述性统计
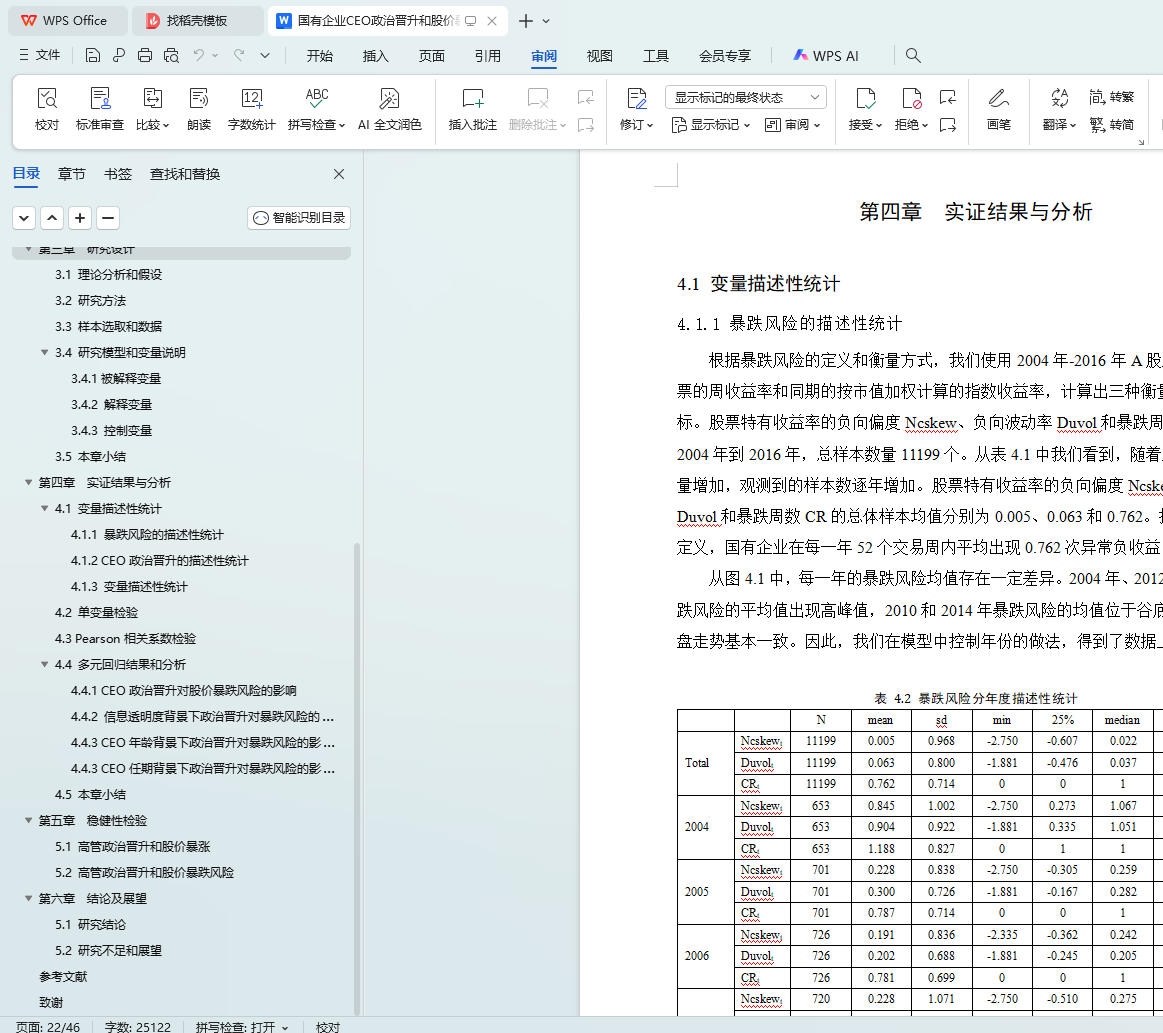
4.1.1 暴跌风险的描述性统计
4.1.2 CEO政治晋升的描述性统计
4.1.3 变量描述性统计
4.2 单变量检验
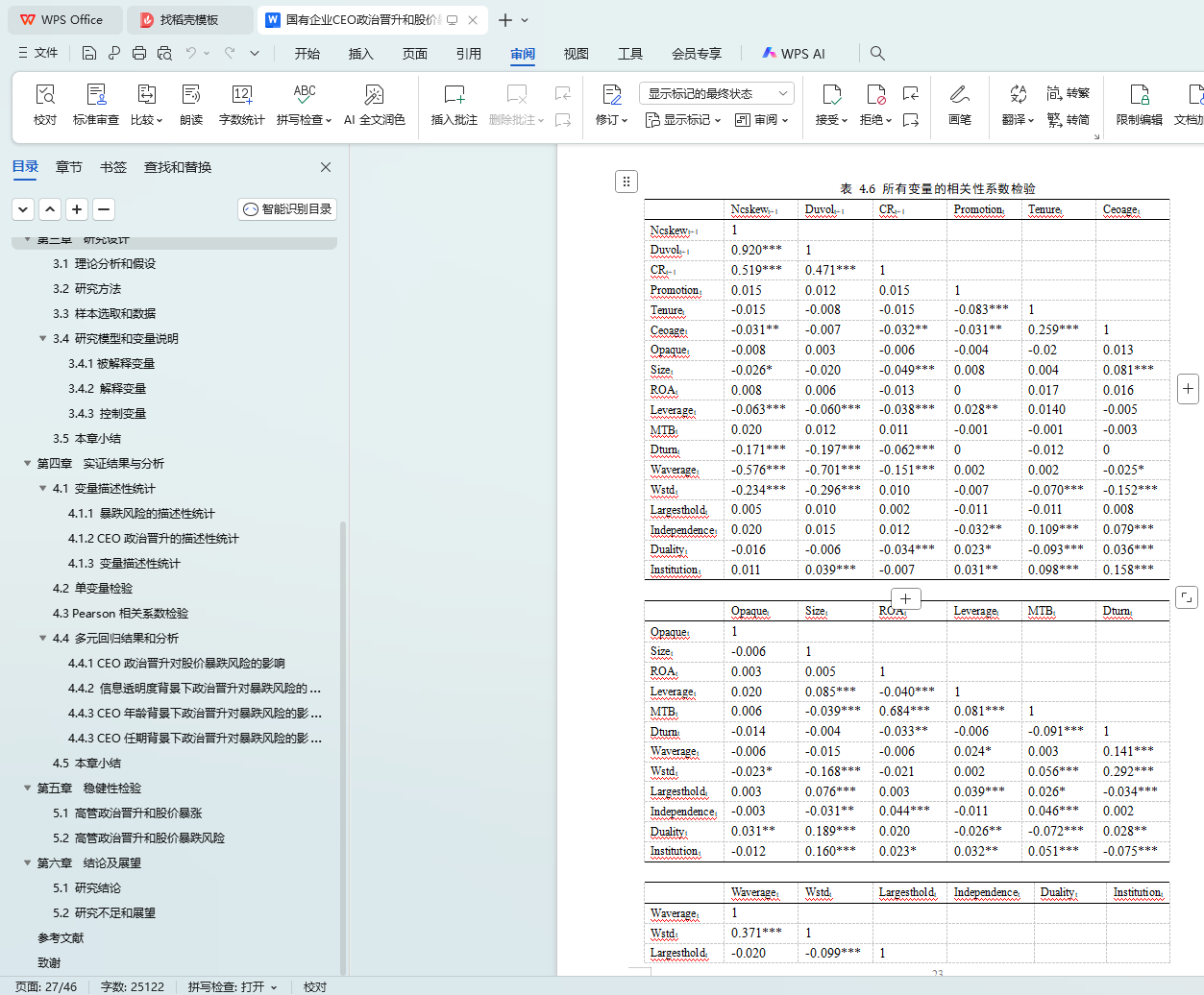
4.3 Pearson相关系数检验
4.4 多元回归结果和分析
4.4.1 CEO政治晋升对股价暴跌风险的影响
4.4.2 信息透明度背景下政治晋升对暴跌风险的影响
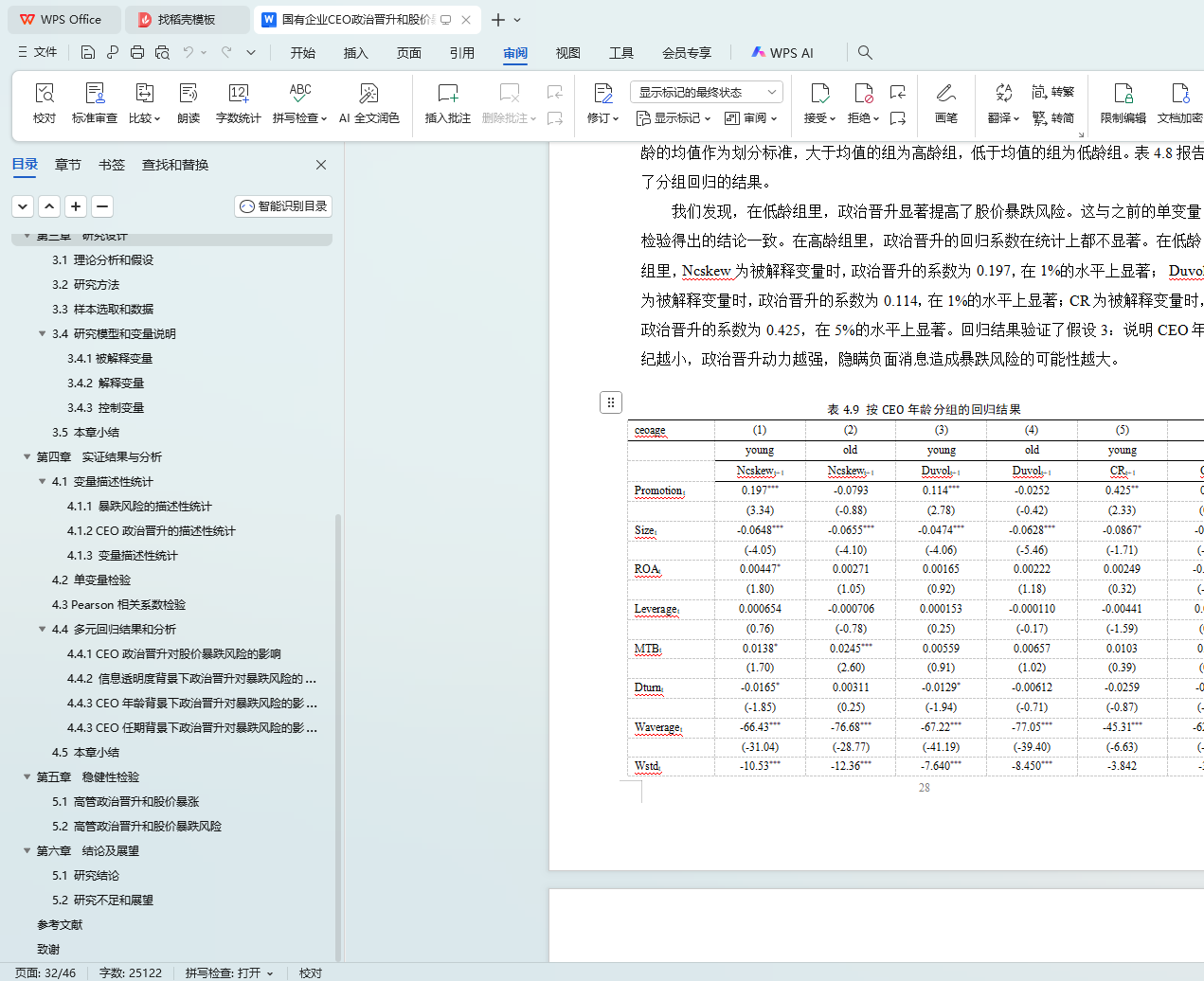
4.4.3 CEO年龄背景下政治晋升对暴跌风险的影响
4.4.3 CEO任期背景下政治晋升对暴跌风险的影响
4.5 本章小结
第五章 稳健性检验
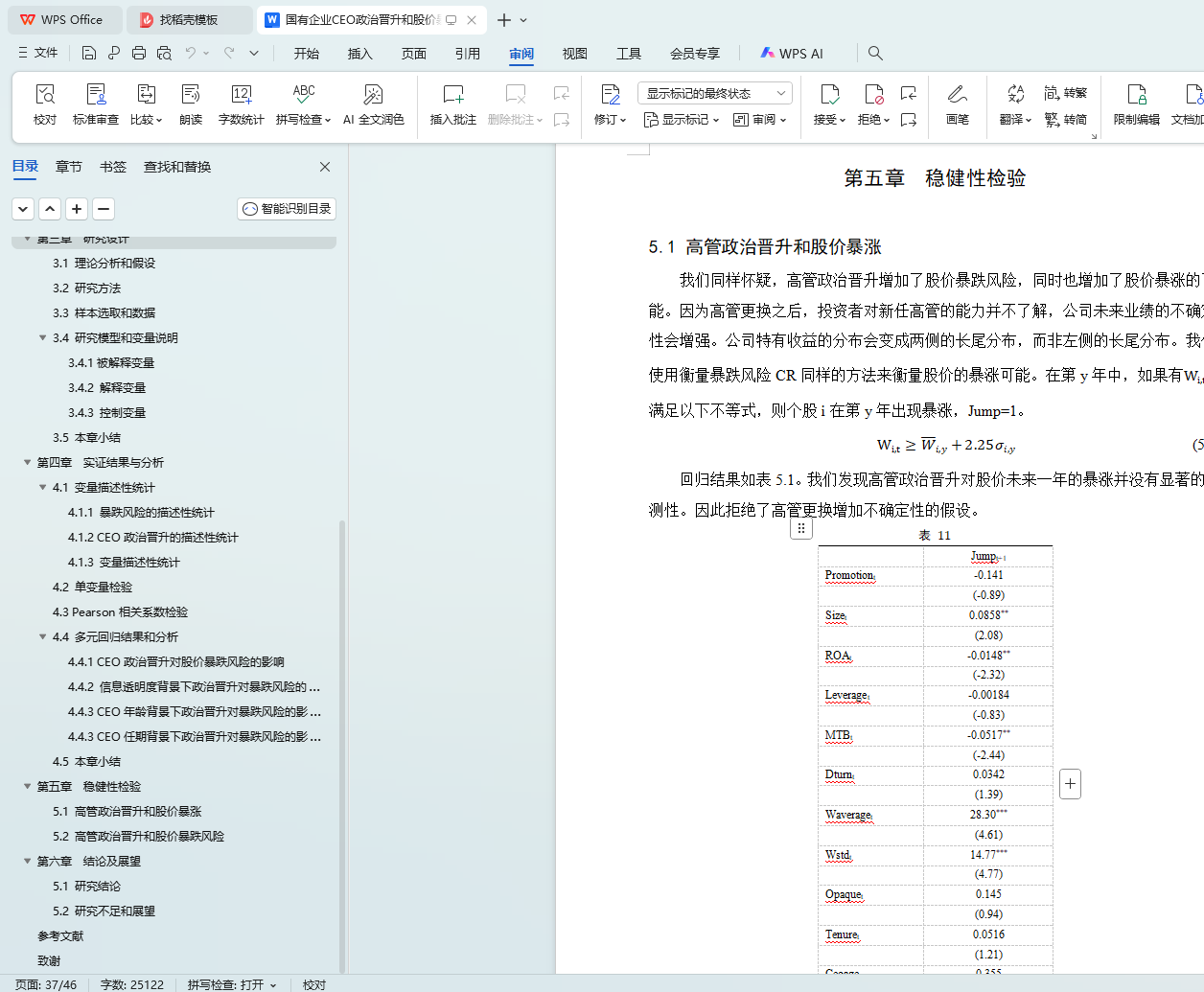
5.1 高管政治晋升和股价暴涨
5.2 高管政治晋升和股价暴跌风险
第六章 结论及展望
5.1 研究结论
5.2 研究不足和展望
参考文献
致谢