摘要
本设计采用模块化设计,以便根据要求选择和定制配置,并在需要的时候方便更换和添加其他模块,而且给出了两种移动方式的设计方案,即履带式移动方式和轮式的设计,两者都有各自的特点,但主要以研究设计履带式为主,它具有良好的机动性,在越障、跨沟、攀爬方面具有明显优势。该机器人的最大优点是具有良好的越障性能、环境适应性能、防摔抗冲击性能并具备全地形通过能力。而轮式探测机器人则机动性能比较好。除了设计探测机器人的总体结构外,还给出了移动控制方案。
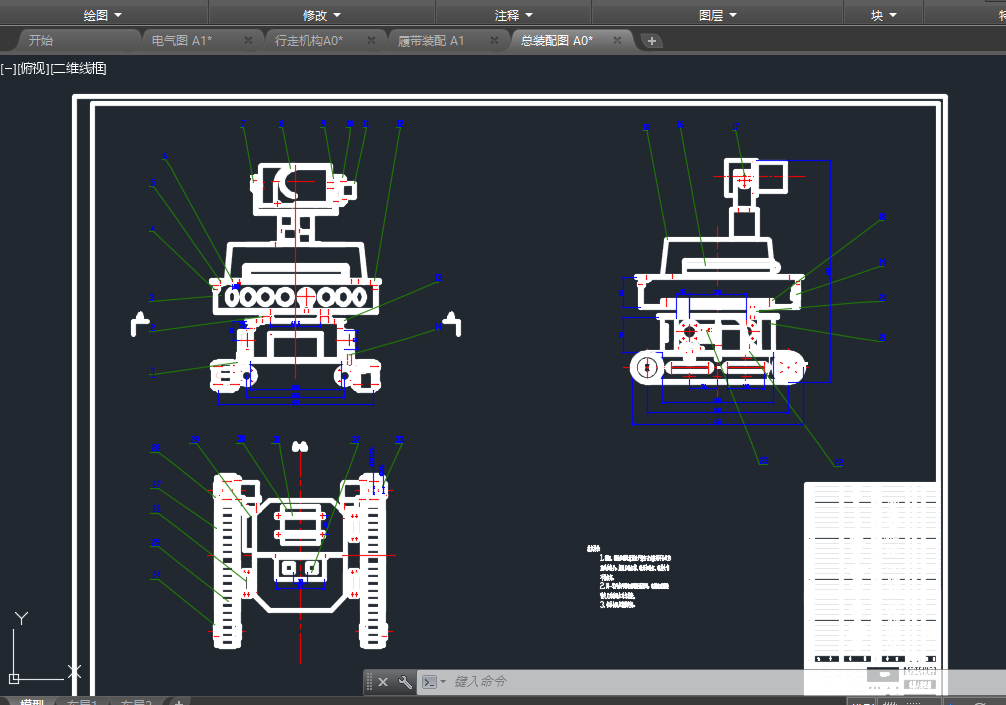
机器人最重要的机构是运动底盘的设计,即使软件设计的再好,移动方式没有设计好,那么机器人也不会很好的执行任务。轮式,腿式,履带式的移动方式在设计过程中已经给出,
可以根据自己设计的要求进行选择如果地形比较平缓,或是有沟壑的地形,可以选择履带的移动方式;如果是平缓没有沟壑的地形,就选用轮式的移动方式;如果地形成阶梯状,而且地形比较复杂,最好选用腿式的方法。
本设计可以采用两种控制系统,即通过上位机直接通过总线对机器人进行控制或是通过无线电台对机器人进行控制。
关键词: 探测机器人; 模块化设计; 履带移动方式; 机器人的控制系统;
Abstract
The design is modular in design so that in accordance with requirements of options and custom configuration, and when needed to facilitate the replacement and add other modules, and is given two mobile forms of design options, that is, tracked and wheeled mobile way of design , Both have their own characteristics, but mainly to crawler-based research and design, it has good mobility in the barrier, the inter-ditch, climbing has obvious advantages. The robot is the greatest advantage of the barrier has a good performance, adapt to environmental performance, Fangshuai impact resistance and have all-terrain capacity. The wheeled robot will detect mobility is better。In addition to detecting robot design the overall structure, but also gives a mobile control ways。
Robot is the most important bodies of the sports chassis design, even the best software design, mobile design means no good, then the robot will not be very good mission. Wheeled, legged, tracked the movement of way in the design process has been given, Can be designed in accordance with the requirements of their own choice if the relatively flat terrain, or a gully of the terrain, can choose to track the movement; If the gully is not flat terrain, on the choice of wheeled mobile way, if formed ladder, and More complex terrain, the best choice legged approach。
This design uses two types of control systems, through the PC directly through the bus to control the robot through the radio or to control the robot。
Keywords: Detecting robot; modular design;tracked mobile; robot's control system;
目 录
摘要 ――――――――――――――――――――――――I
Abstract――――――――――――――――――――――II
第一章 概述――――――――――――――――――――――――4
1.1 机器人的应用范围――――――――――――――――――――――4
1.2 探测机器人的先状及发展趋势―――――――――――――――――4
1.3 研究内容――――――――――――――――――――――――――5
第二章 机械系统的设计―――――――――――――――――――7
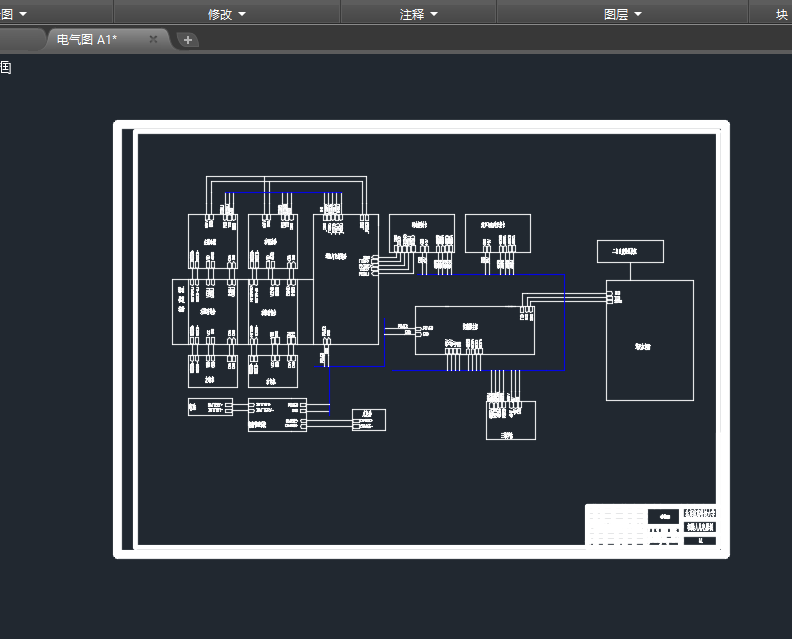
2.1 计算机模块的设计――――――――――――――――――――――7
2.2 传感器模块的设计――――――――――――――――――――――8
2.3 电源及驱动模块的设计――――――――――――――――――――8
2.4 底盘运动模块的设计―――――――――――――――――――――8
2.5 各模块的连接――――――――――――――――――――――――11
第三章 能源驱动的设计选择―――――――――――――――――14
3.1 能源的供给―――――――――――――――――――――――――14
3.2 电机的选择―――――――――――――――――――――――――14
3.3 电机驱动的选择―――――――――――――――――――――――15
第四章 传感器系统的设计――――――――――――――――――17
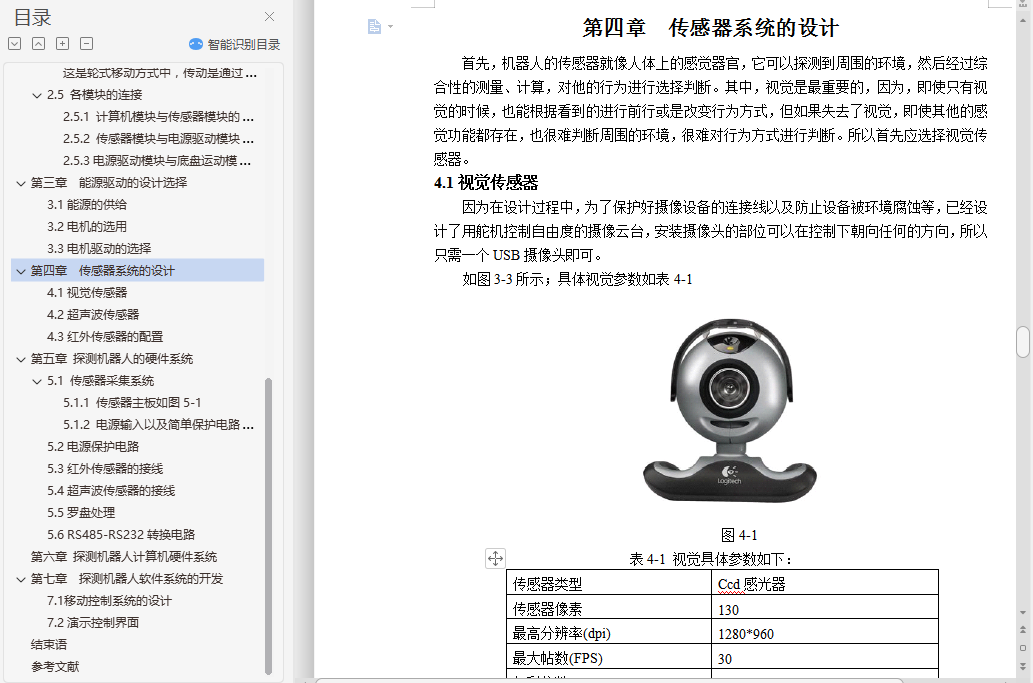
4.1 视觉传感器―――――――――――――――――――――――――17
4.2 超声波传感器――――――――――――――――――――――――17
4.3 红外传感器―――――――――――――――――――――――――19
第五章 探测机器人的硬件系统――――――――――――――――20
5.1 传感器采集系统―――――――――――――――――――――――20
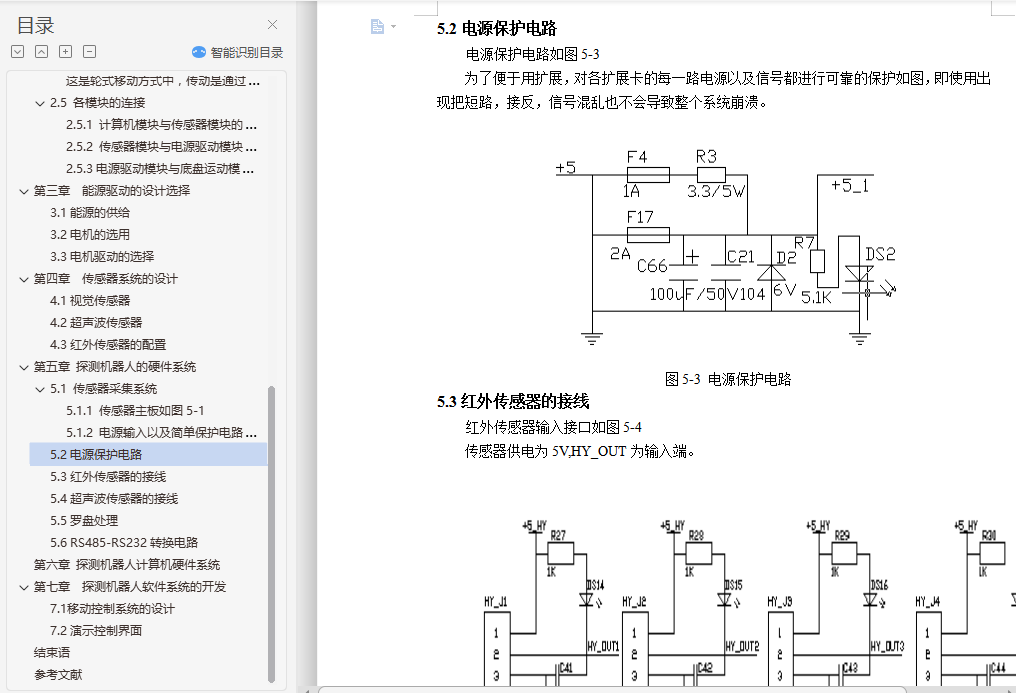
5.2 保护电路――――――――――――――――――――――――――20
5.3 红外传感器的接线――――――――――――――――――――――21
5.4 超声波传感器的接线―――――――――――――――――――――21
5.5 罗盘处理流程――――――――――――――――――――――――21
5.6 RS485-RS232转换电路――――――――――――――――――――22
第六章 探测机器人计算机硬件系统――――――――――――――23
6.1 无线电台通讯系统――――――――――――――――――――――23
6.2 电子罗盘――――――――――――――――――――――――――23
第七章 探测机器人软件系统的开发――――――――――――――25
移动控制系统的设计―――――――――――――――――――――25
演示控制程序――――――――――――――――――――――――25
结束语 ―――――――――――――――――――――29
参考文献 ―――――――――――――――――――――30