|
New Roman"; font-size: 12pt;'>51
5.2.3 集成分类方法实验 54
5.3 本章小结 55
第6章 总结与展望 56
6.1 工作总结 56
6.2 研究展望 57
致谢 59
参考文献 60
附录 67
, 摘要
运动功能障碍是多种脑损伤疾病的重要表现,如癫痫疾病、脑卒中等。对患者运动功能的检测与评估是进行疾病诊断和康复治疗的重要方法。同时,脑电信号(Electroencephalogram,EEG)是直接反映大脑活动情况的电生理表现形式。通过对EEG的分析,可以发现大量的生理、病理信息。本文希望通过对EEG的分析处理,对脑受损疾病患者的运动功能障碍进行评估。而对EEG的有效处理分析是一项复杂的工程。
本文选取具有运动功能障碍表现的典型疾病—癫痫患者作为本课题研究的实验对象,主要通过利用EEG分析方法对患者的癫痫特征进行提取与识别。本文着重研究EEG分析处理算法,其中包括:EEG的消噪方法、特征提取方法以及模式分类识别算法。主要研究内容和创新点包括以下几个方面:
(1)提出一种基于降噪源分离的EEG消噪方法。降噪源分离是盲源分离中一种新方法,可以根据待处理信号的特点具有针对性地设计合适的降噪函数,进行源分离处理而获得源信号。本文首先设计仿真实验,选择适合癫痫患者EEG的降噪函数,再根据该降噪函数进行源分离处理和消噪处理。通过仿真实验与实际EEG处理结果表明,降噪源分离的EEG消噪算法的消噪效果优于基于独立成分分析的盲源分离算法的消噪效果。
(2)提出一种基于多种熵融合的EEG特征提取方法。由于单一的一种熵值只能表达信号某一方面的复杂度,往往缺少对信号的整体度量。为了对EEG从多个角度实现更加全面的信息表达,提出一种基于多种不同物理意义的熵融合的EEG特征提取方法,提高了EEG特征的完整表达能力。这一创新性方法已经在Neural Computing & Applications(SCI源刊)发表。研究工作首先分析四种不同测量方法的熵在EEG中的物理意义及表现,然后通过实验分析多种熵融合对EEG分类效果的提升。
(3)提出一种基于极限学习机的集成分类器设计。极限学习机是一种较为新型的分类器,是近年来EEG分类器设计的研究热点之一。本文针对常规极限学习机泛化能力差、分类结果不稳定的缺陷,利用集成分类的思想,根据Bagging和Adaboost两种集成方法,将多个极限学习机集成为一个强分类器。实验分析证实,本文所设计的分类器在取得较好的分类结果的同时,也改善了极限学习机分类结果的稳定性。
关键词:运动功能障碍,脑电信号,癫痫,降噪源分离,熵理论,特征融合,极限学习机,集成学习
ABSTRACT
Motor function disorders is an important manifestation of various brain injury diseases, such as epilepsy, stroke and other diseases. The detection and evaluation of motor function in patients is an important method in the process of diagnosis and rehabilitation. At the same time, the EEG signal is a biological signal that directly reflects the activity of the brain. Through the analysis of EEG signals, we can obtain a lot of physiological and pathological information. The aim of this paper is to evaluate the motor function of patients with brain injury by analyzing EEG. However, it is a complex project for analyzing EEG signals efficiently.
In this paper, we choose epilepsy patients with motor function impairment as the subject in this study. The main purpose of this study is extracting and identifying the epileptic features of the patients in the EEG signals. In the process of the study, this paper focuses on the algorithms of EEG signal processing, including the denoising method, feature extraction method and pattern recognition algorithm of EEG signals. The main contents of this paper include the following aspects:
(1) This paper proposes a denoising method of EEG based on Denoising Source Separation (DSS). DDS is a new method in Blind Source Separation, which can design exclusively a suitable denoising function according to the characteristics of the EEG. After the signals are processed by DSS, we can obtain the source signals. In this paper, firstly we design a simulation experiment to select the denoising function of DDS based on the epilepsy EEG. Then, source separation processing and denoise processing are performed by the DSS. The results of simulation and real EEG signal processing show that the denoising effectiveness of proposed method is superior to that of the method using the Independent Component Analysis.
(2) A novel feature extraction method of EEG using multiple entropies fusion is proposed. Since a single entropy only can express the complexity of signal from one view and often lack the overall measurement. In order to achieve more comprehensive expression from multiple perspectives, an EEG feature extraction method based on entropies fusion of different physical meanings is proposed to improve the expression of EEG features. This innovative approach has been published in Neural Computing & Applications (SCI journal). This paper firstly analyzes the physical meaning and expression of four different entropies in EEG. Then we employ the experiment to analyze the improvement of EEG signal classification on different entropies fusion.
(3) This paper proposes an ensemble classifier based on Extreme Learning Machine (ELM). ELM is a new classifier and one of the hotspots of EEG classifier design in recent years. However, conventional ELM has the poor generalization ability and unstable classification results. To solve these problems, in this paper, we design an ensemble classifier that the multiple ELM classifiers are integrated into a strong classifier using Bagging and Adaboost. The experiments’ results show that the classifier designed in this paper can not only obtain better classification results, but also solve the problem of classification instability in ELM classifier.
Keywords: Motor Function Disorders, Electroencephalogram, Epilepsy, Denoising Source Separation, Entropy Theory, Feature Fusion, Extreme Learning Machine, Ensemble
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT III
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 课题的背景和意义 1
1.2 运动功能障碍评估的研究现状 2
1.2.1 基于量表的评价方法 2
1.2.2 基于生物运动力学的评价方法 3
1.2.3 基于生物电信号的评价方法 5
1.3 课题研究面临的问题 6
1.4 研究内容与论文框架 7
1.5 本章小结 8
第2章 课题研究方案设计的前期理论准备 9
2.1 EEG基础理论介绍 9
2.1.1 脑结构与功能 9
2.1.2 EEG的产生原理与特点介绍 10
2.1.3 EEG与运动功能的关系 11
2.2 常见造成运动功能障碍的脑损伤疾病及选择实验对象 13
2.2.1 脑卒中 13
2.2.2 帕金森病 13
2.2.3 癫痫 14
2.3 实验数据 15
2.3.1 CHB-MIT数据采集过程介绍 15
2.3.2 德国波恩大学癫痫数据库的数据采集过程介绍 16
2.4 本章小结 17
第3章 EEG的消噪方法及特征提取方法 18
3.1 基于降噪源分离的EEG消噪方法设计 18
3.1.1 基于小波变换的消噪方法 18
3.1.2 基于盲源分离的消噪方法 18
3.1.3 基于降噪源分离的EEG消噪方法 19
3.1.4 EEG消噪实验 21
3.1.4.1 降噪函数的选取 21
3.1.4.2 仿真消噪实验 24
3.1.4.3 真实信号的消噪分析 25
3.2 EEG的特征提取方法 28
3.2.1 熵理论在EEG中的应用综述 28
3.2.2 基于多种熵融合的EEG特征提取方法 30
3.2.2.1 基于香农熵的幅值复杂度测量 30
3.2.2.2 基于香农熵的相位同步复杂度测量 32
3.2.2.3 小波能量熵 34
3.2.2.4 样本熵 36
3.3 多种熵融合处理 38
3.4 本章小结 39
第4章 基于极限学习机的集成分类方法 41
4.1 EEG分析中常用的分类算法综述 41
4.1.1 K近邻算法 41
4.1.2 支持向量机 41
4.1.3 人工神经网络 42
4.2 极限学习机 42
4.2.1 极限学习机算法原理 42
4.2.2 ELM在EEG中的应用介绍 44
4.3 基于极限学习机的集成分类算法 44
4.3.1 基于Bagging的集成学习方法 45
4.3.2 基于Adaboost的集成学习方法 46
4.4 本章小结 48
第5章 实验结果分析 49
5.1 实验数据处理 49
5.1.1 波恩大学数据集 49
5.1.2 CHB-MIT数据集 49
5.2 实验结果与分析 50
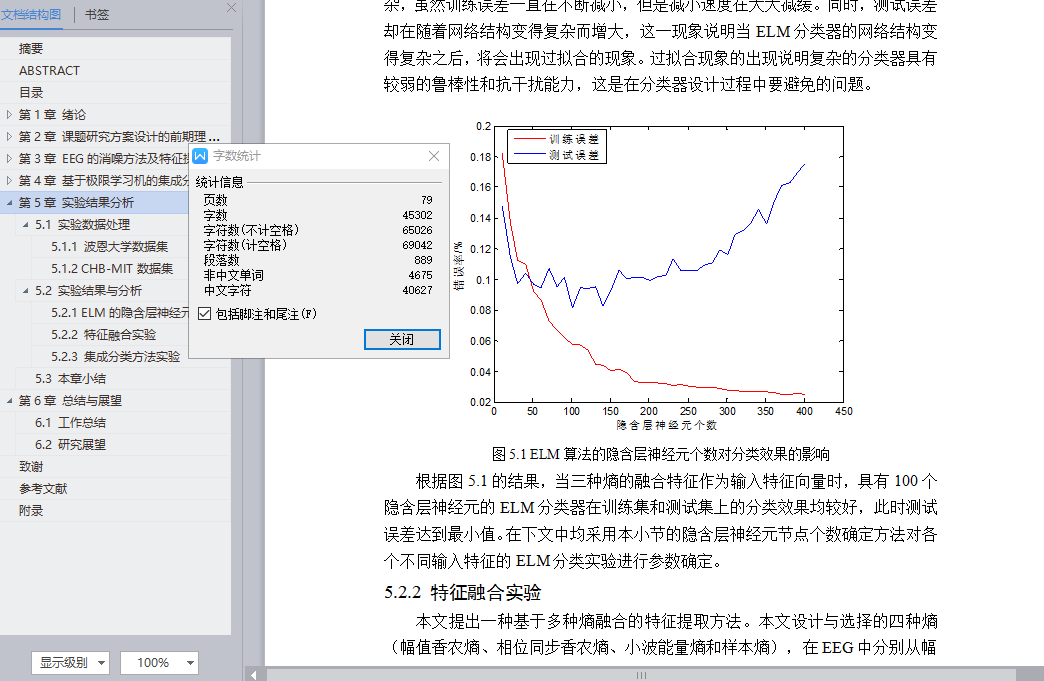
5.2.1 ELM的隐含层神经元个数选择实验 50
5.2.2 特征融合实验
|



