摘要
我国作为农业大国,果蔬年产量可观,且大量果蔬需进行干燥加工处理。然而,当前我国蔬菜干燥加工技术水平相对滞后。鉴于此,本研究创新性地将热泵干燥技术、自动检测技术以及实时监控技术集成应用于蔬菜干燥加工领域,致力于开发一套热泵干燥装置电控系统,以实现对蔬菜干燥加工全过程的精准实时监控。
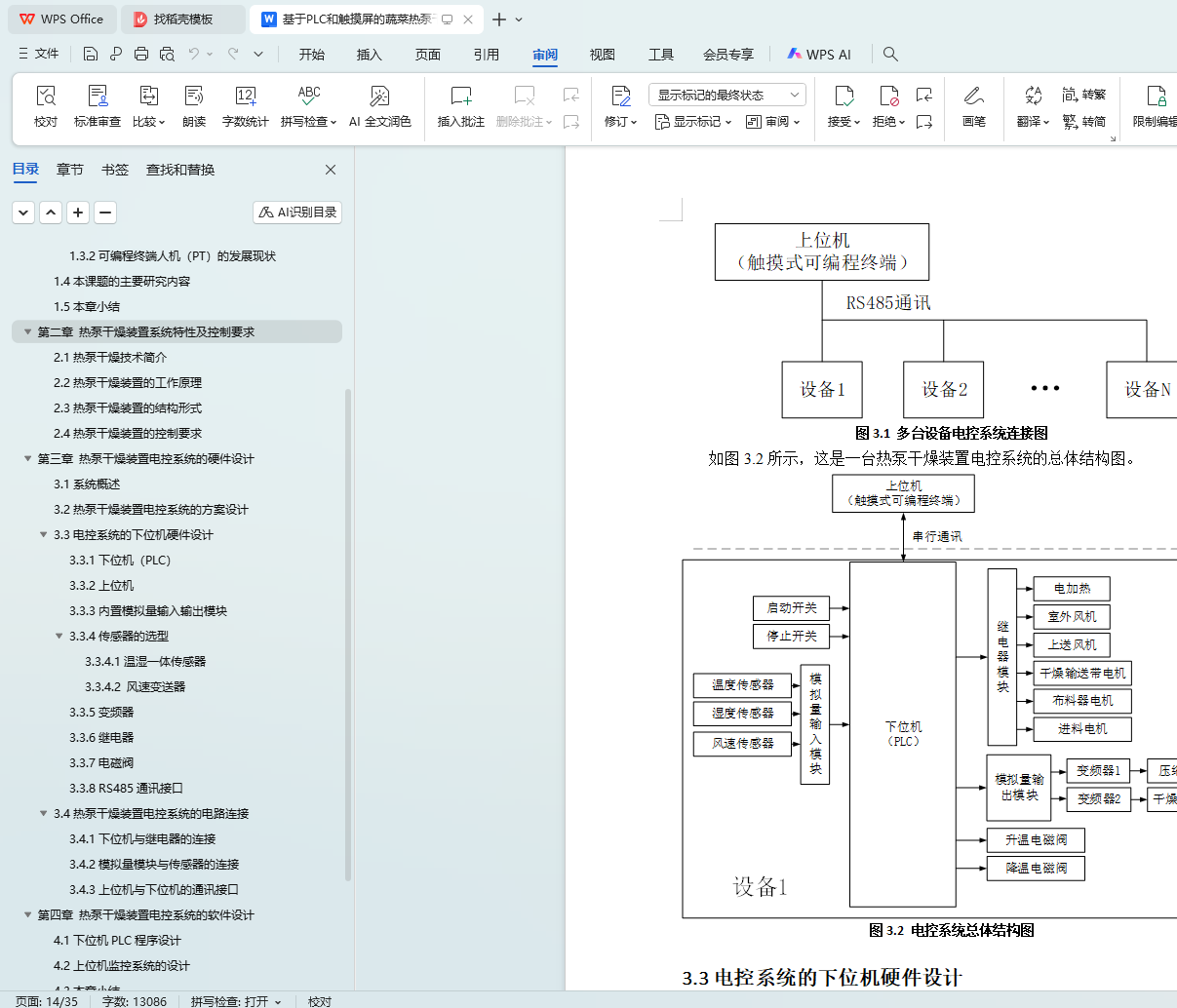
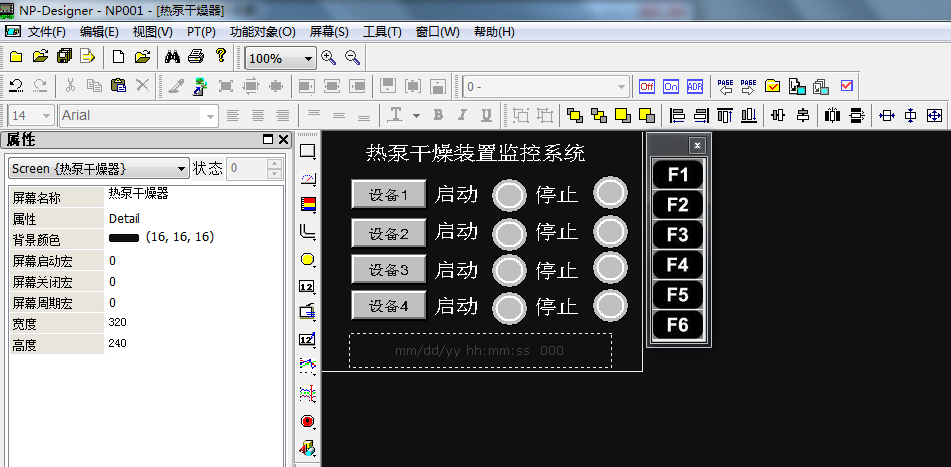
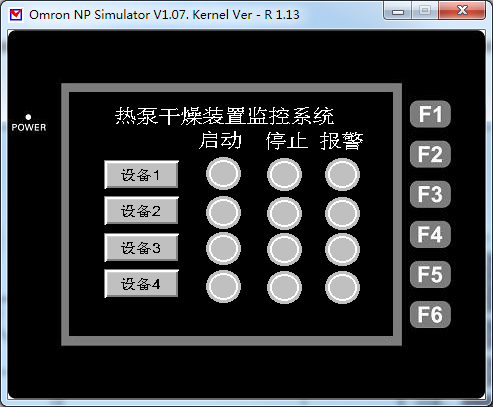
该电控系统主要由热泵干燥装置、下位机控制系统以及上位机监控系统三部分构成。热泵干燥装置的核心组件包括压缩机、冷凝器、蒸发器、膨胀阀以及干燥风机等,它们协同工作以完成干燥任务。下位机控制系统以 PLC 为核心,搭配 PLC 模拟量扩展模块和各类传感器,传感器负责实时采集干燥过程中的温度、湿度、风速等模拟量信号,并将其传输至 PLC 模拟量输入模块进行数字化转换与存储。下位机 PLC 作为现场控制中枢,借助专业编程软件编写用户程序,能够依据热泵干燥系统的工艺要求,精确控制多台设备的多批次启动与停止,实时测量并调整干燥过程中的温度、湿度,有效发散过热能量,及时识别并处理系统故障,同时与上位机进行 RS485 通讯。上位机监控系统采用可编程终端人机触摸屏,通过编写触摸屏自带的组态软件,实现对现场数据的全面实时记录与处理,涵盖运行数据的清晰显示、参数的灵活设定、报警信息的直观显示与便捷查询等功能。
通过本研究设计的电控系统,成功实现了蔬菜脱水加工的自动化,不仅显著降低了操作成本,还大幅提高了产品品质,为蔬菜干燥加工行业的升级发展提供了有力的技术支持。
关键词:蔬菜干燥加工;热泵干燥技术;PLC 控制系统;人机触摸屏监控;过程自动化
Abstract
As a major agricultural country, China boasts a considerable annual output of fruits and vegetables, with a large proportion of them requiring drying and processing. However, the current technological level of vegetable drying and processing in China is relatively backward. In view of this, this study innovatively integrates heat pump drying technology, automatic detection technology, and real-time monitoring technology into the field of vegetable drying and processing, aiming to develop a set of electrical control system for the heat pump drying device to achieve precise and real-time monitoring of the entire vegetable drying and processing process.
The electrical control system mainly consists of three parts: the heat pump drying device, the lower computer control system, and the upper computer monitoring system. The core components of the heat pump drying device include a compressor, a condenser, an evaporator, an expansion valve, and a drying fan, which work together to accomplish the drying task. The lower computer control system takes PLC as the core, equipped with PLC analog expansion modules and various sensors. The sensors are responsible for real-time collection of analog signals such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed during the drying process, and transmit them to the PLC analog input module for digital conversion and storage. As the on-site control center, the lower computer PLC writes user programs with the help of professional programming software. It can precisely control the multi-batch start and stop of multiple devices according to the process requirements of the heat pump drying system, measure and adjust the temperature and humidity in real-time during the drying process, effectively dissipate excess heat energy, promptly identify and handle system faults, and communicate with the upper computer via RS485. The upper computer monitoring system adopts a programmable terminal human-machine touch screen. By writing the configuration software自带 (which can be translated as "bundled" or "included" in this context, here translated as "included" for a more natural expression) in the touch screen, it realizes comprehensive real-time recording and processing of on-site data, covering functions such as clear display of operating data, flexible setting of parameters, intuitive display and convenient inquiry of alarm information.
Through the electrical control system designed in this study, the automation of vegetable dehydration processing has been successfully achieved, which not only significantly reduces operating costs but also greatly improves product quality, providing strong technical support for the upgrading and development of the vegetable drying and processing industry.
Keywords:vegetable drying and processing; heat pump drying technology; PLC control system; human-machine touch screen monitoring; process automation
目录
摘 要
Abstract
第一章 绪论
1.1课题的研究背景和研究意义
1.2热泵干燥的国内外研究现状
1.2.1热泵干燥的国外研究现状
1.2.2热泵干燥的国内研究现状
1.3方案背景技术简介
1.3.1可编程控制器(PLC)的现状与发展
1.3.2可编程终端人机(PT)的发展现状
1.4本课题的主要研究内容
1.5本章小结
第二章 热泵干燥装置系统特性及控制要求
2.1热泵干燥技术简介
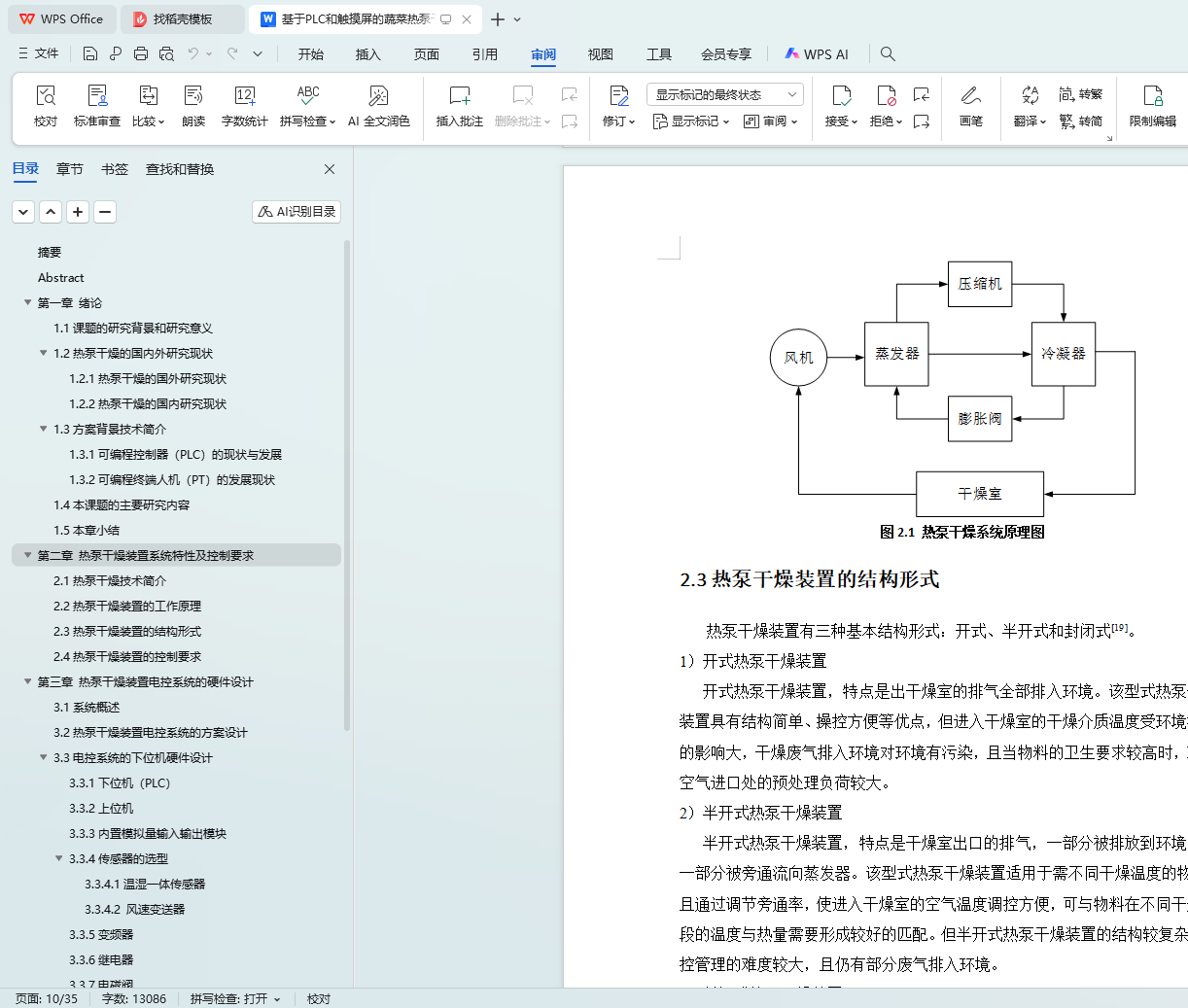
2.2热泵干燥装置的工作原理
2.3热泵干燥装置的结构形式
2.4热泵干燥装置的控制要求
第三章 热泵干燥装置电控系统的硬件设计
3.1系统概述
3.2热泵干燥装置电控系统的方案设计
3.3电控系统的下位机硬件设计
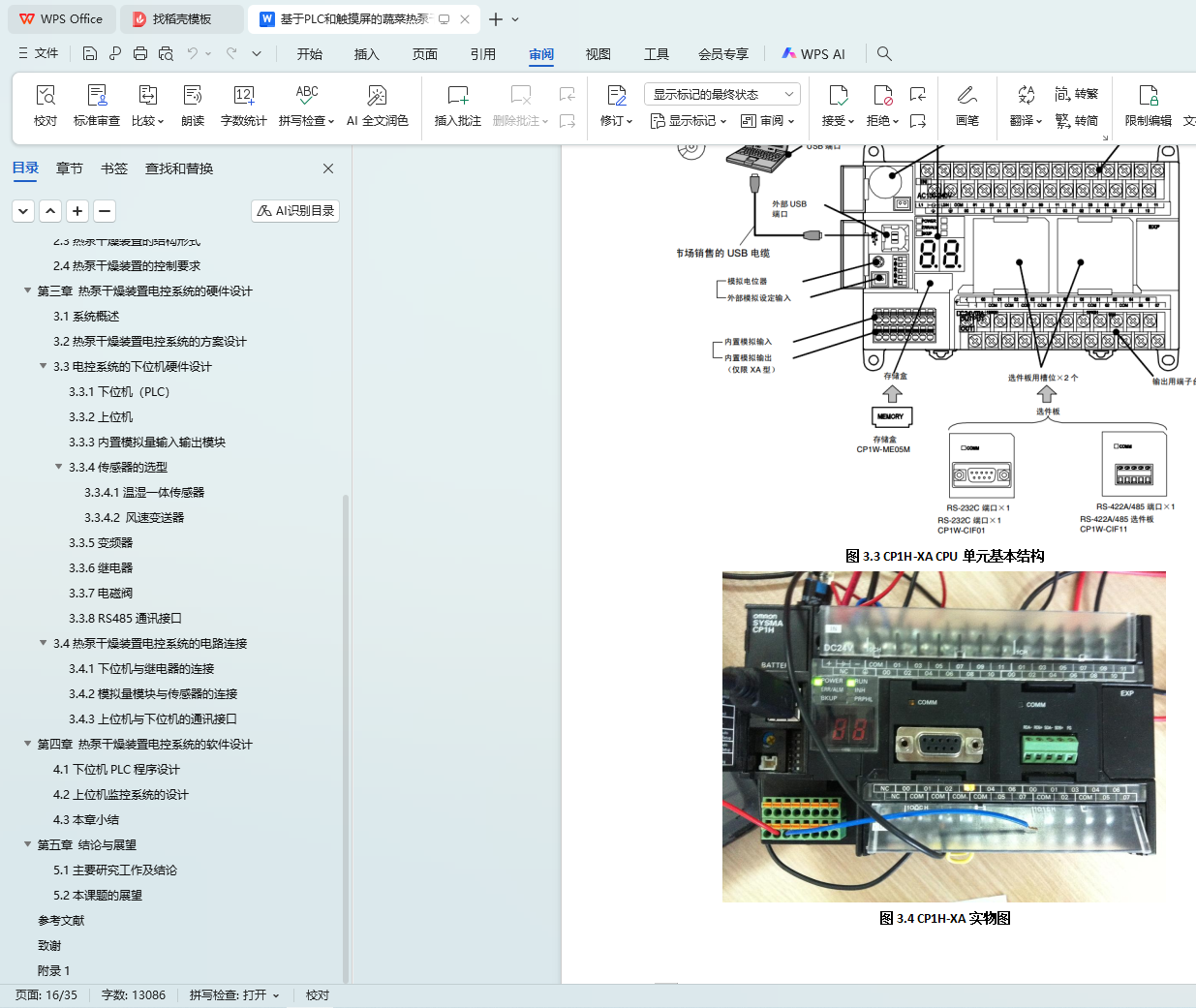
3.3.1下位机(PLC)
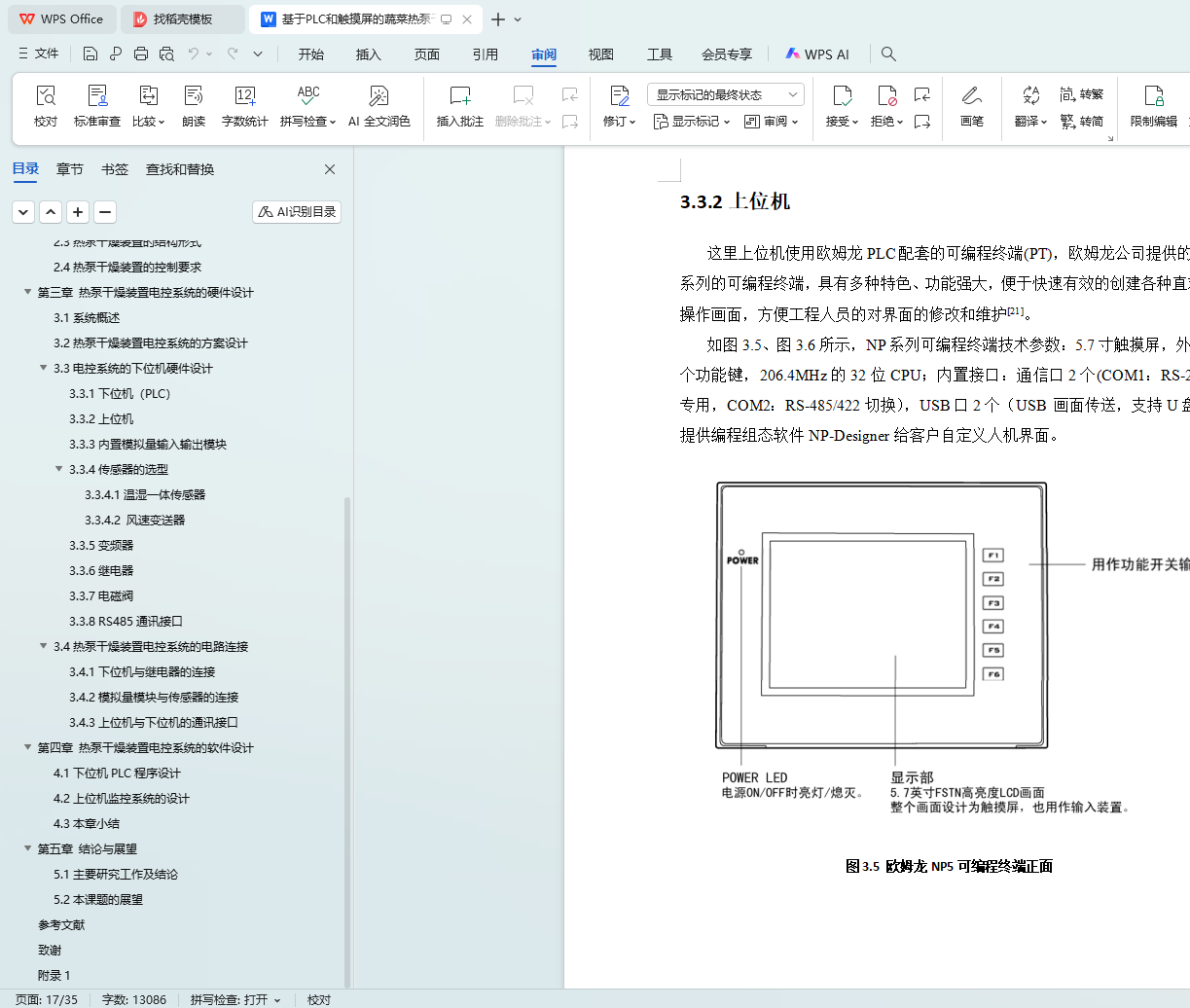
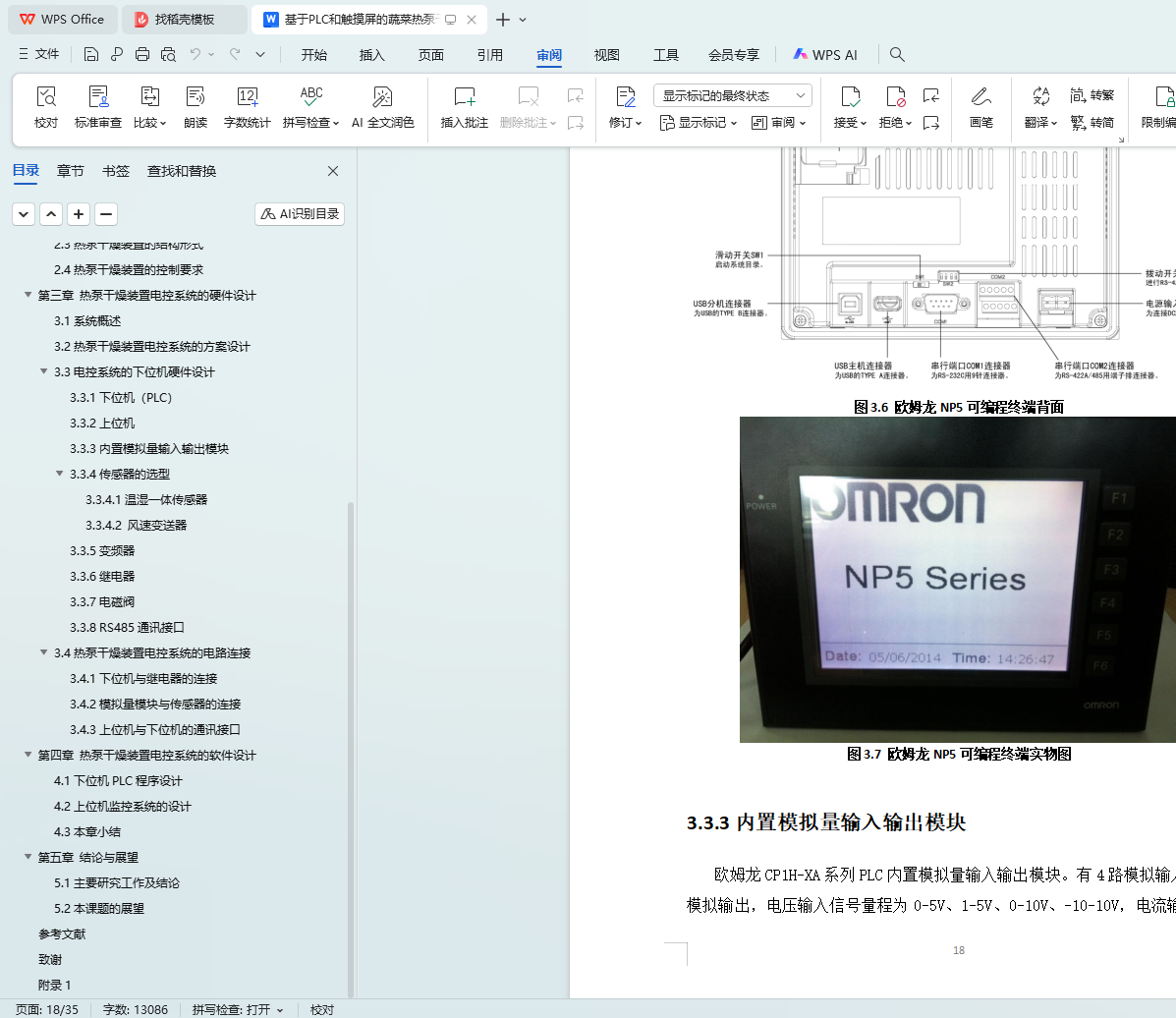
3.3.2上位机
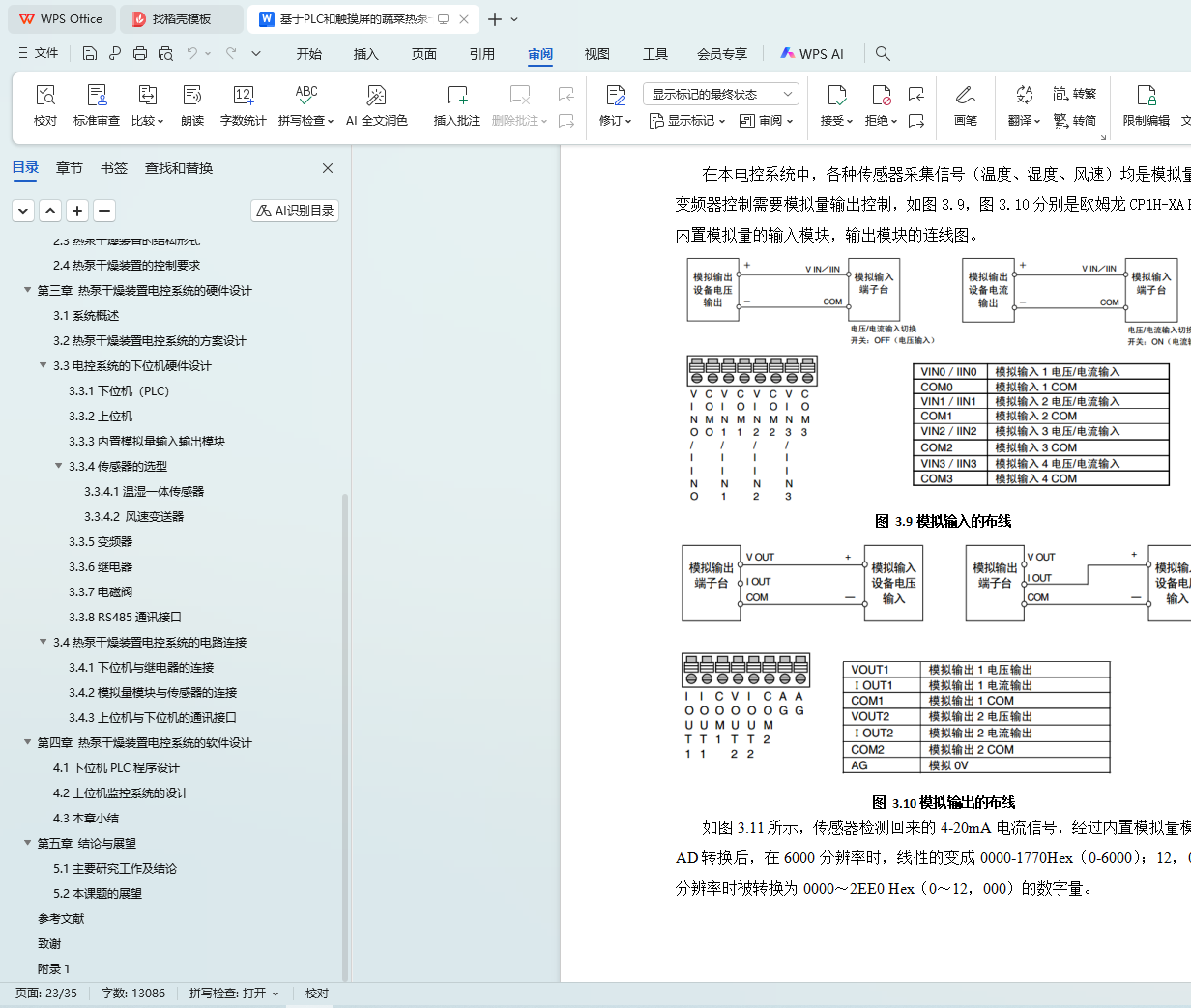
3.3.3内置模拟量输入输出模块
3.3.4传感器的选型
3.3.5变频器
3.3.6继电器
3.3.7电磁阀
3.3.8 RS485通讯接口
3.4热泵干燥装置电控系统的电路连接
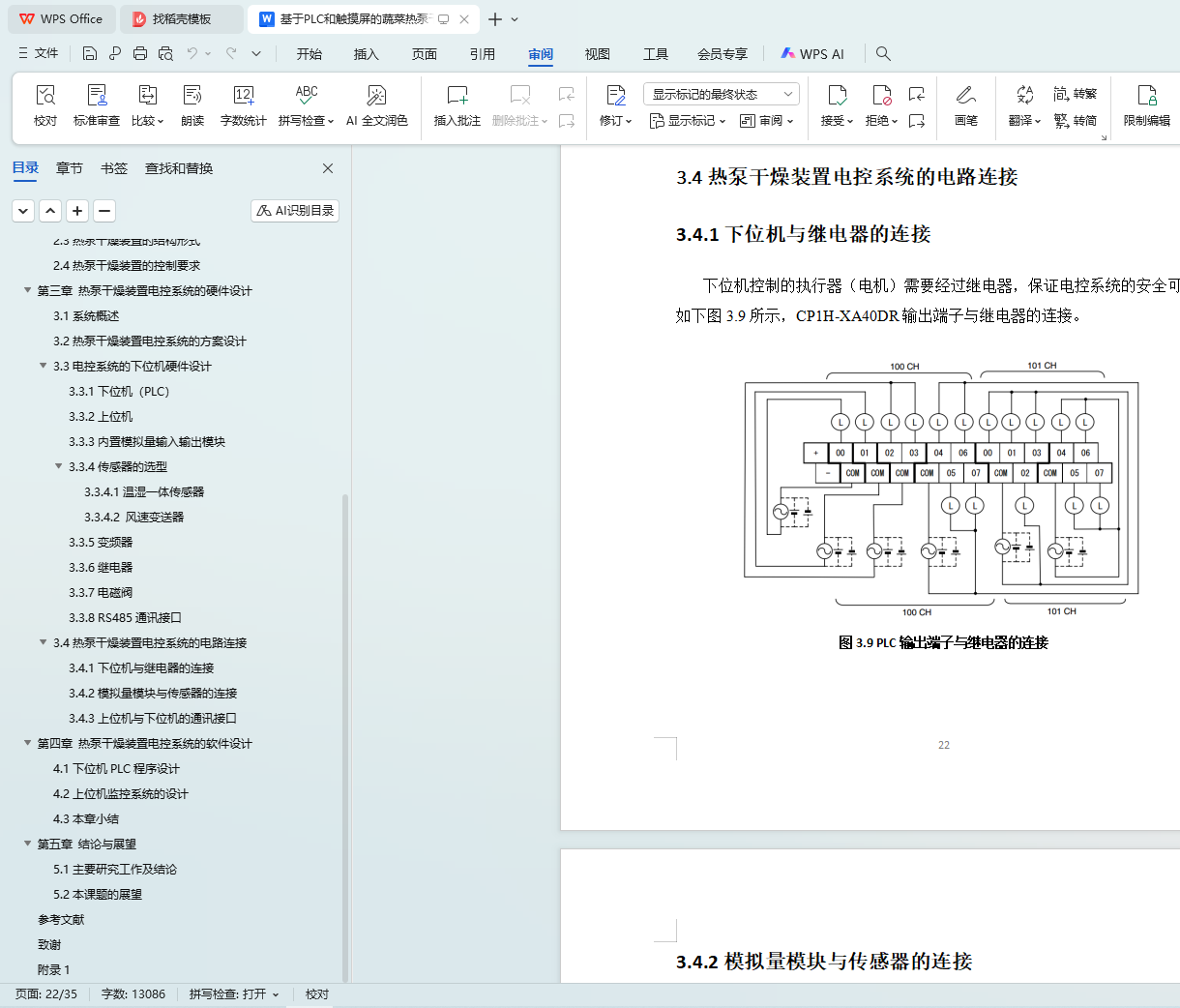
3.4.1下位机与继电器的连接
3.4.2模拟量模块与传感器的连接
3.4.3上位机与下位机的通讯接口
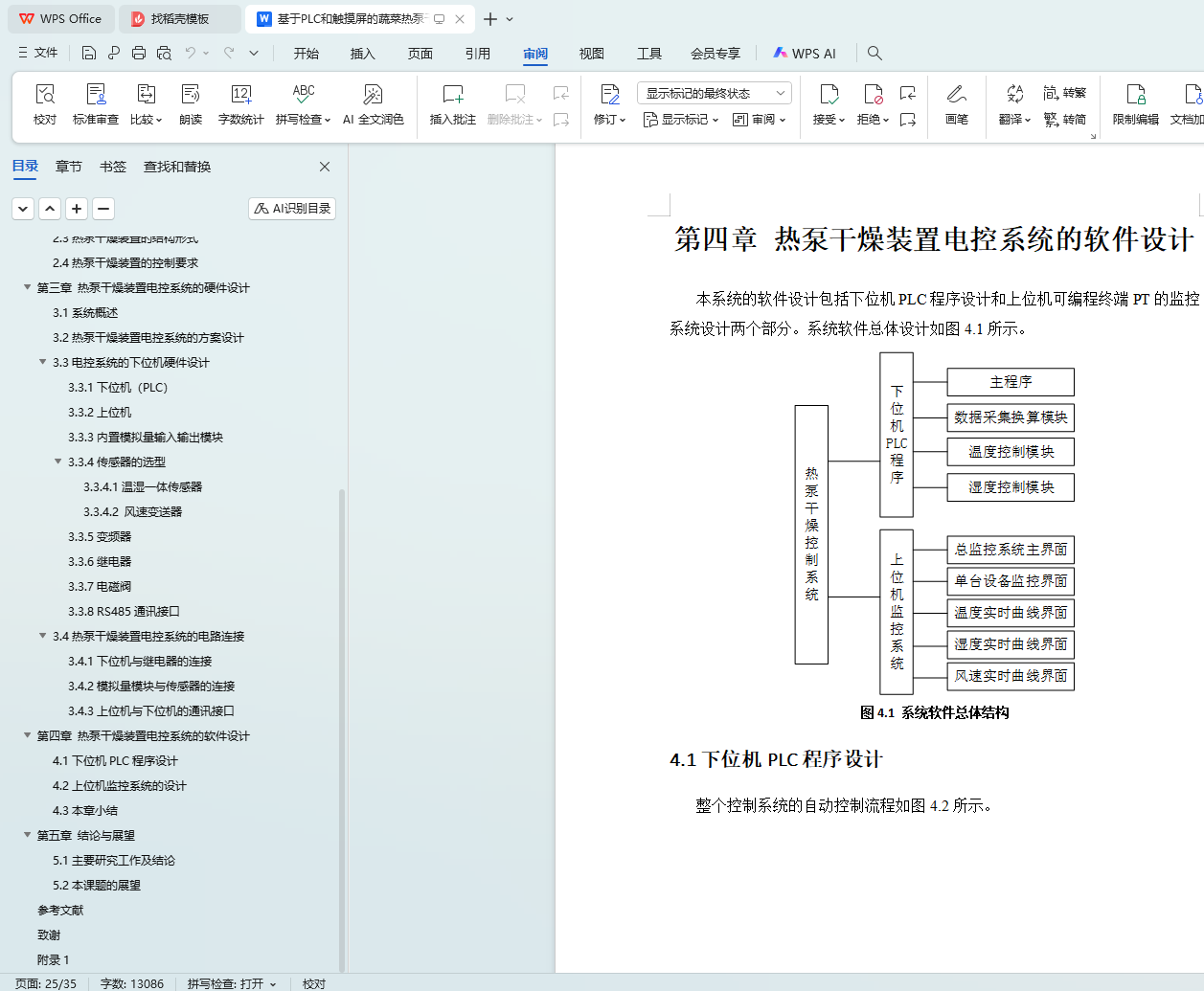
第四章 热泵干燥装置电控系统的软件设计
4.1下位机PLC程序设计
4.2上位机监控系统的设计
4.3本章小结
第五章 结论与展望
5.1主要研究工作及结论
5.2本课题的展望
参考文献
致谢
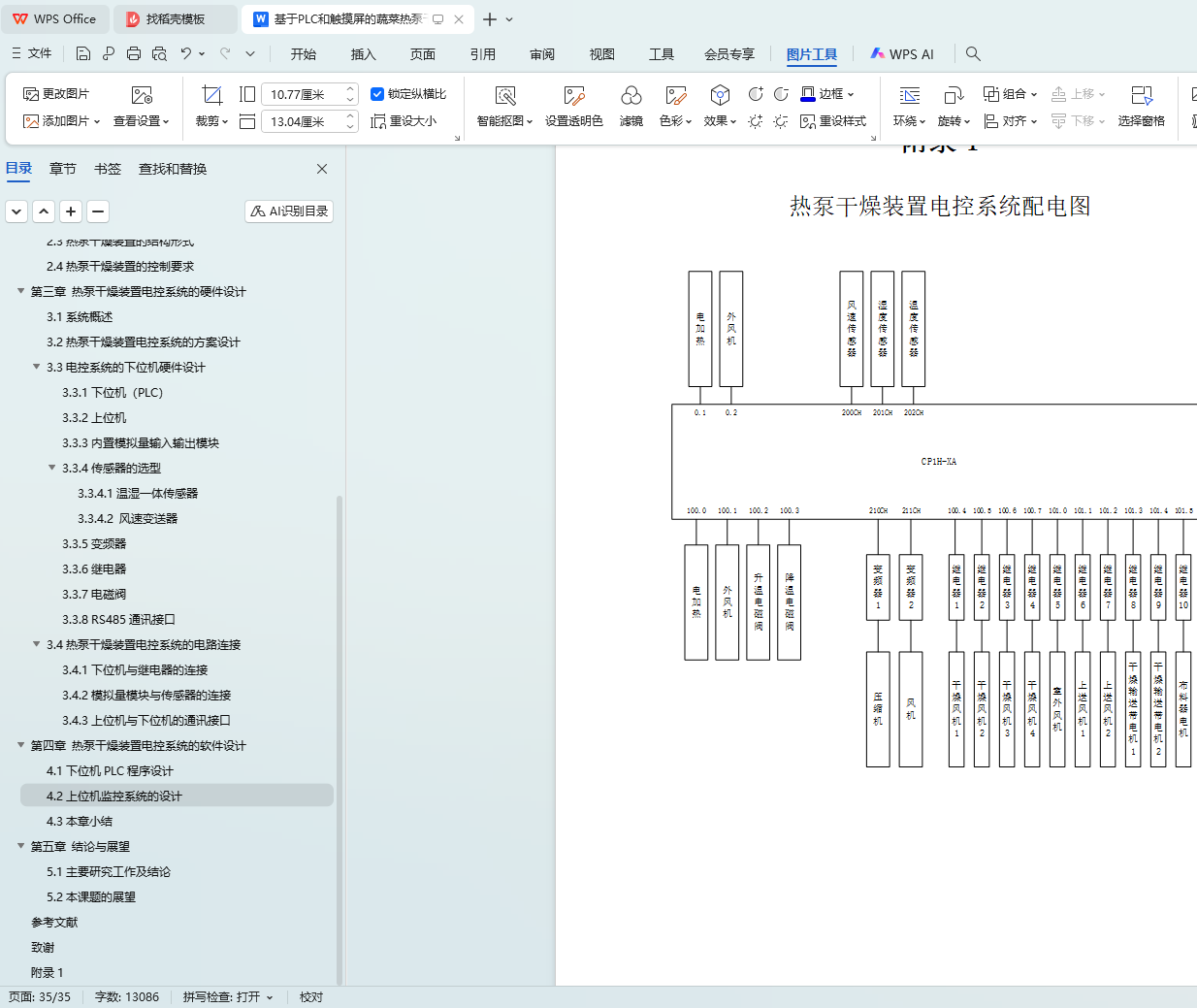
附录1