摘要
目前中国正在从经济旧常态走向经济新常态,供给侧改革和去产能成为时代主题。我国传统行业如钢铁、水泥等出现严重的产能过剩问题,依靠市场这只看不见的手已经难以进行有效调节。为了响应供给侧改革,政府多次强调要加大宏观调控和金融支持力度,推动企业兼并重组,优化资源配置效率、提高企业效益。2016 年新一轮国企改革启动,政府指导意见要“做强做优做大”国有企业,其中一条就是“鼓励非国有资本投资主体通过出资入股、收购股权、认购可转债、股权置换等多种方式,参与国有企业改制重组或国有控股上市公司增资扩股以及企业经营管理”。在此宏观背景下, 企业并购和银行业竞争引起了市场高度重视,成为当下经济金融热议话题。
企业并购不仅具有时代意义,一直以来也是企业的一项重要投资活动,近十几年间发展尤其迅速。并购能够实现企业之间的控制权转移,改善企业的经营和治理环境。此外,并购还能为企业进入或退出某一行业、某一个市场提供便利。但是企业并购受到诸多因素的影响,如融资约束会影响企业并购决策、支付方式,公司治理会影响企业并购绩效。要研究企业并购,就离不开对企业融资和治理环境的研究。
银行业竞争是加大金融支持力度的有效途径。我国的金融体系以银行业为主导,银行在引导金融资源流向实体经济的过程中发挥着不可替代的作用。而受制于我国传统银行业以四大国有行为主导的格局,银行资源对实体经济的支持并不公平,许多企业面临融资难、融资贵的现实问题。但在过去十几年间,我国银行业结构正在经历巨变。国有四大行的市场地位动摇,股份制商业银行迅猛发展,城市商业银行和农村商业银行异军突起,银行业正面临前所未有的竞争态势。银行业竞争的不断加剧优化了金融资源配置,更多资金流向了有需求、成长能力好的企业,企业融资环境有所改善。

 在此背景下,本文从理论和实证两个角度探究了银行业竞争对企业并购的影响。以2008-2015 年沪深 A 股的并购数据为基础,本文通过构建计量模型对二者关系进行了实证研究。本文研究结果发现,银行业竞争的加剧通过缓解企业融资约束提高了企业参与并购的可能性和现金支付比例,但是降低了并购中的累计超额收益率。本文从融资约束和公司治理两个角度对影响机制进行了理论和实证探讨。银行作为最大的金融中介,对企业最直接的影响就是融资。银行业竞争的加剧降低了借贷成本,提高了信贷供给,通过缓解企业融资约束,提高了企业参与并购的可能性和现金支付比例。除了融资影响外,银行作为企业债权人,也是企业行为的重要监督者。但银行在企业监管中存在鉴定效应和利益冲突两种影响,即银行既可能监督企业活动又可能产生寻租行为。银行业竞争的加剧弱化了银行的监督作用,强化了利益冲突问题,最终导致银行
在此背景下,本文从理论和实证两个角度探究了银行业竞争对企业并购的影响。以2008-2015 年沪深 A 股的并购数据为基础,本文通过构建计量模型对二者关系进行了实证研究。本文研究结果发现,银行业竞争的加剧通过缓解企业融资约束提高了企业参与并购的可能性和现金支付比例,但是降低了并购中的累计超额收益率。本文从融资约束和公司治理两个角度对影响机制进行了理论和实证探讨。银行作为最大的金融中介,对企业最直接的影响就是融资。银行业竞争的加剧降低了借贷成本,提高了信贷供给,通过缓解企业融资约束,提高了企业参与并购的可能性和现金支付比例。除了融资影响外,银行作为企业债权人,也是企业行为的重要监督者。但银行在企业监管中存在鉴定效应和利益冲突两种影响,即银行既可能监督企业活动又可能产生寻租行为。银行业竞争的加剧弱化了银行的监督作用,强化了利益冲突问题,最终导致银行
对企业监管放松,降低了并购中的累计超额收益率。融资约束机制和公司治理机制既有理论背景,又符合经济常识,是可靠的解释渠道。
本文的主要贡献有四点。第一,本文通过理论和实证研究,首次证明了银行业竞争对企业并购的影响。第二,本文找到了融资约束和公司治理两条可能的渠道来解释研究结论,既有文献支撑,又有实证依据。第三,本文完善了已有文献。从并购角度补充了银行业竞争对企业行为影响的文献,从银行竞争角度补充了融资约束和银行监管对企业并购影响的文献。第四,本文具有深刻的现实意义,能够为企业管理者和政策制定者提供参考意见。
基于本文的实证结论,本文提出两点建议。首先,政府应该合理引导银行业结构调整,有序推动行业内竞争的展开,但要注意防范银行的不规范行为和系统性风险。第二,企业可以在经营活动中更多利用银行资源,优化自身融资结构和成本,但在与银行接触中要审慎对待银行意见,做出最有利于企业自身经营的决策。
关键词:银行业竞争,企业并购,融资约束,公司治理
ABSTRACT

The Effect of Bank Competition on Mergers and Acquisitions
ABSTRACT
China is experiencing a change from old normal to new normal economy, where supply-side reform and address overcapacity become the major theme of the times. The biggest problem of traditional industry is overcapacity, especially in industries like iron, steel and cement. Since it is hard to solve this problem by the invisible hand of market, government macro-control has increased a lot. Government policies give support to financial development and appeal to prompt mergers and reorganizations within industry, which could increase firm efficiency. In 2016, the new round of SOE reform was carried out, whose topic is “stronger, better and bigger SOEs”. One tip of the government guidance is “encourage non-state capital to join in the reform and recombination of SOEs, capital increase and share expansion of listing firms holding by SOEs and operating management of SOEs, through buying shares, undertaking acquisitions, purchasing convertible bonds and equity replacement.” Under these macro environments, mergers, acquisition, and bank competition get great attention from the market. They are the hottest topic in China now.
Mergers and acquisitions are one of the most important corporate investment activities all the time. It experienced great development over last decades. Firms could realize control rights transfer through mergers and acquisitions, as well as improvements in operating management and corporate governance. Besides, firms may undertake acquisitions to enter or exit some special industries or markets. Many factors could affect mergers and acquisitions. Financial constraints have effect on mergers and acquisitions decision and payment choice, while corporate governance matters to its performance. We cannot ignore corporate finance and governance if we want to look into mergers and acquisitions.
Bank competition is a good way to give greater support to financial development. In China, financial system is dominated by banks, who play a vital role in transferring financial resource to real economy. However, state-owned commercial banks hold a dominant positions in domestic banking industry, which result in unfair support of bank resource to real economy. Many enterprises, especially those middle and small-sized enterprises, find it hard to finance from banks. However, over the last decades, banking industry witness great structure transform. The status of state-owned banks are threatened by the rapid expansion of joint-stock commercial banks, city commercial banks and rural commercial banks. The banking industry has never been this competitive before. The increase in bank competition improves the efficiency of resource allocation, transferring more capital to firms with great
financing demand and growth opportunity. Firms’ financial constraints are alleviated.
Based on this macro environment, we analyze the effect of bank competition on mergers and acquisitions theoretically and empirically. We test their relationship using M&A data of A-share companies during 2008 to 2015. Our empirical results find that on the one hand, more bank competition increases the likelihood of undertaking an acquisition and its cash payment ratio. While on the other hand, it decreases the cumulative abnormal return during mergers and acquisitions. Then we discuss these results from two aspects, the financial constraint mechanism and corporate governance mechanism. As the biggest financial intermediary, the direct effect of bank is financing. More bank competition leads to lower borrowing cost and more credit supply. By alleviating financial constraints, bank competition then increase the likelihood of undertaking acquisitions and cash payment ratio. Besides this, as a debt holder, bank also act as a credit supervisor in corporate governance. There are two effects working, the certification effect and interest conflict. The certification effect means banks will screen information and monitor firm activities. The interest conflict is between bank and firm shareholder, since bank works as debt holder. This may result in rent-seeking behavior of bank, which will harm shareholder wealth. The two mechanisms are reliable, because both of them have theoretical foundations and meet the economic common sense.
We have four contributions. At first, we prove the relationship between bank competition and mergers and acquisitions empirically. Secondly, we find two reliable mechanisms to explain the effects. Both of the mechanisms have theoretical foundations and empirical results support. Thirdly, we fill the research gab between bank competition and M&As. Finally, the results are meaningful for managers and policy makers.
Based on our empirical results, we give two suggestions. First, government should prompt banking industry restructuring to increase industry competition. But at the same time, more attention should be paid to avoid disorderly conduct and systematic risk. Second, corporate may take more advantage of bank resources to reduce it financing cost and improve capital structure. Considering rent-seeking behavior of bank, corporate should be more cautious to their suggestions.
KEY WORDS: Bank Competition, Mergers and Acquisitions, Financial Constraints, Corporate Governance
ABSTRACT

摘要 I
ABSTRACT III
目录 VI
— 绪论 1
(一) 研究背景 1
(二) 研究目的与意义 2
1. 理论价值 2
2. 现实意义 3
(三) 具体研究问题 3
(四) 研究贡献与创新 4
(五) 研究框架 6
二 文献综述 7
(一) 银行业竞争研究 7
1. 银行业竞争与企业融资约束 7
2. 银行业竞争与银企关系 8
3. 银行业竞争的其他影响 9
(二) 企业并购研究 10
1. 并购与融资约束 10
2. 并购与公司治理 12
3. 其他企业并购相关行为 13
三 背景 15
(一) 银行业现状 15
1. 银行业历史沿革 15
2. 银行业发展现状 16
(二) 企业并购现状 16
四 理论分析与研究假设 18
(一) 研究假设 18
1. 银行业竞争与企业是否参与并购 18
2. 银行业竞争与现金支付比例 20
 <目录
<目录
3. 银行业竞争与超额收益 21
五 研究设计 23
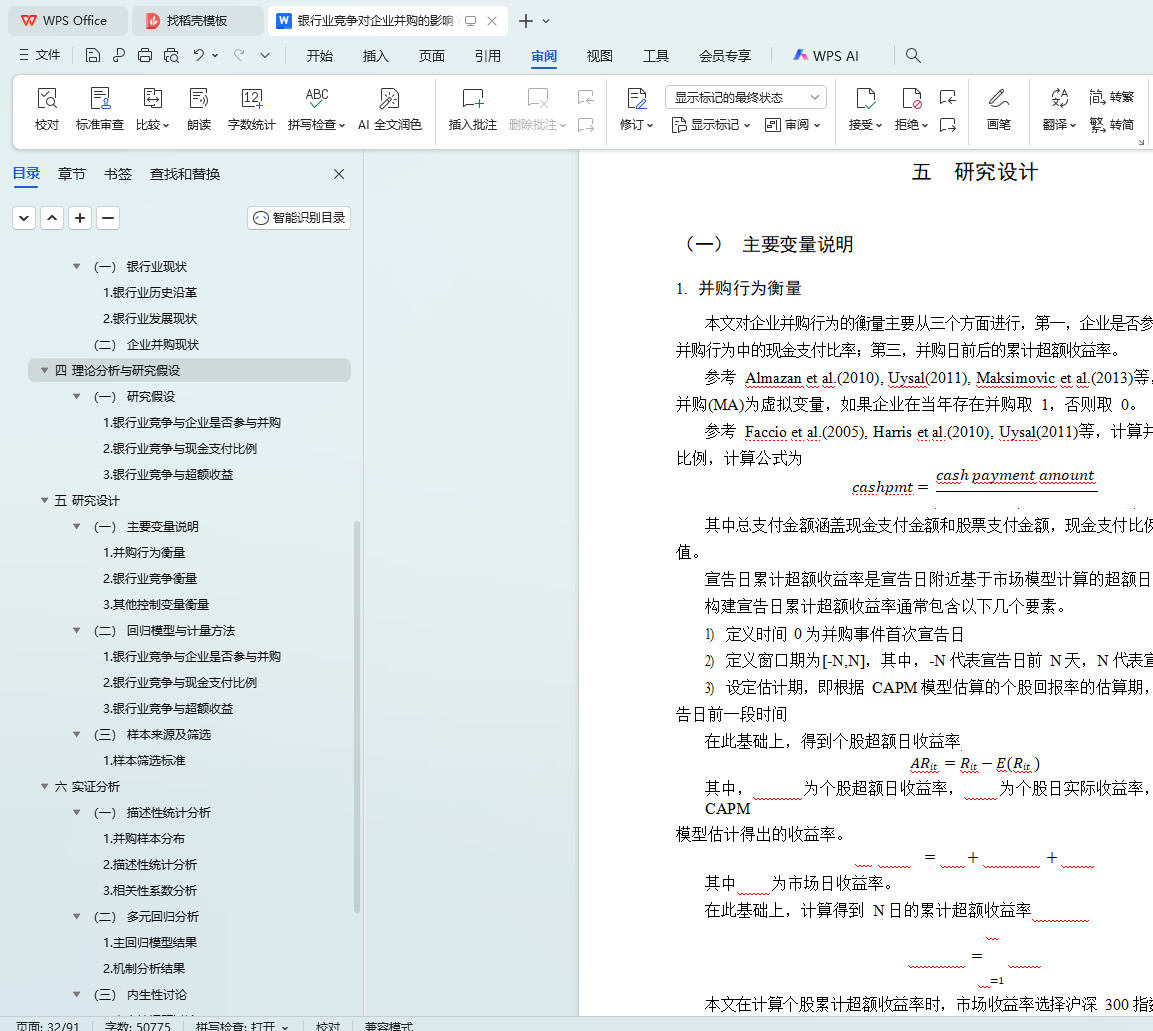
(一) 主要变量说明 23
1. 并购行为衡量 23
2. 银行业竞争衡量 24
3. 其他控制变量衡量 25
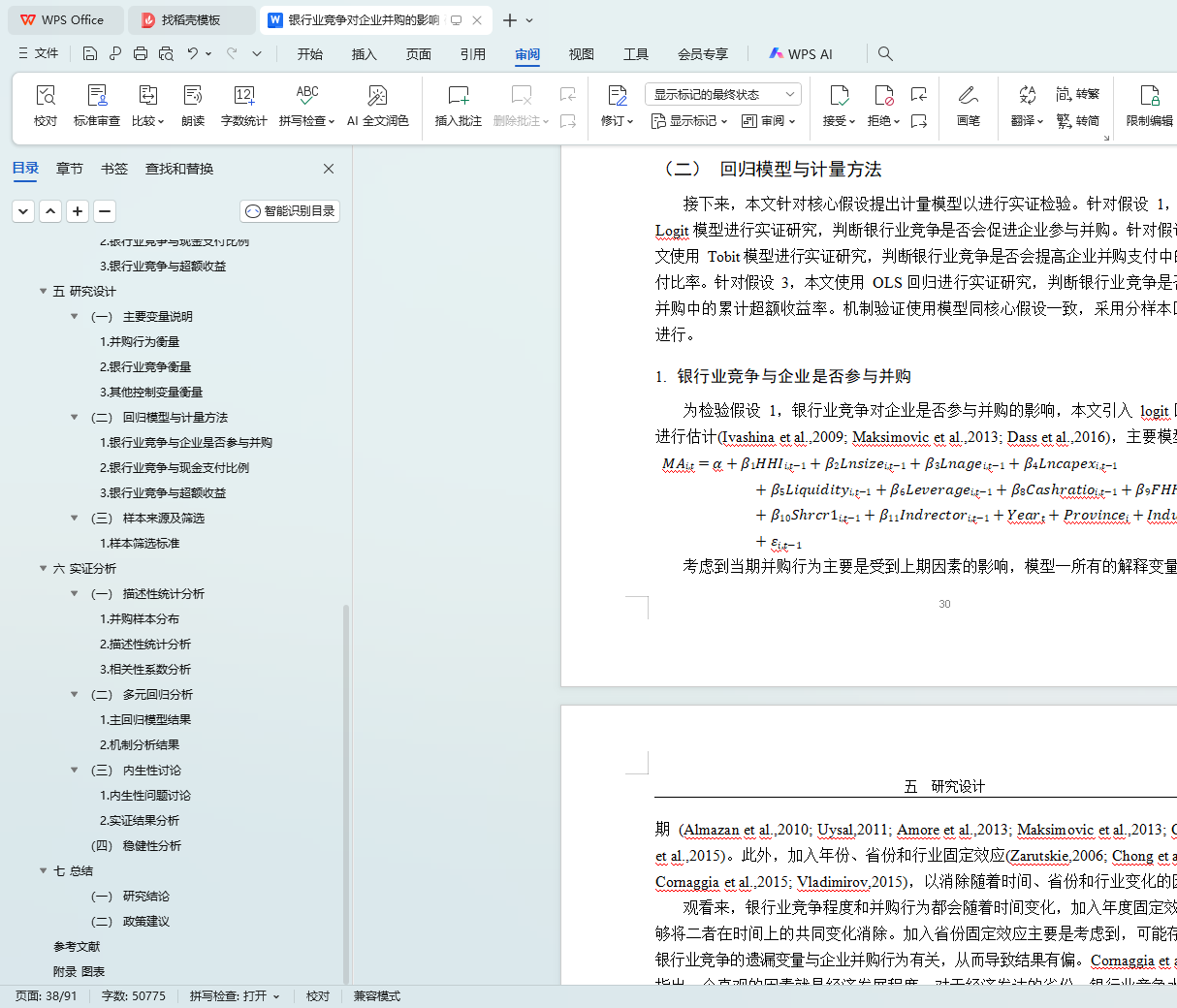
(二) 回归模型与计量方法 26
1. 银行业竞争与企业是否参与并购 26
2. 银行业竞争与现金支付比例 27
3. 银行业竞争与超额收益 27
(三) 样本来源及筛选 28
1. 样本筛选标准 28
六 实证分析 30
(一) 描述性统计分析 30
1. 并购样本分布 30
2. 描述性统计分析 30
3. 相关性系数分析 32
(二) 多元回归分析 32
1. 主回归模型结果 32
2. 机制分析结果 37
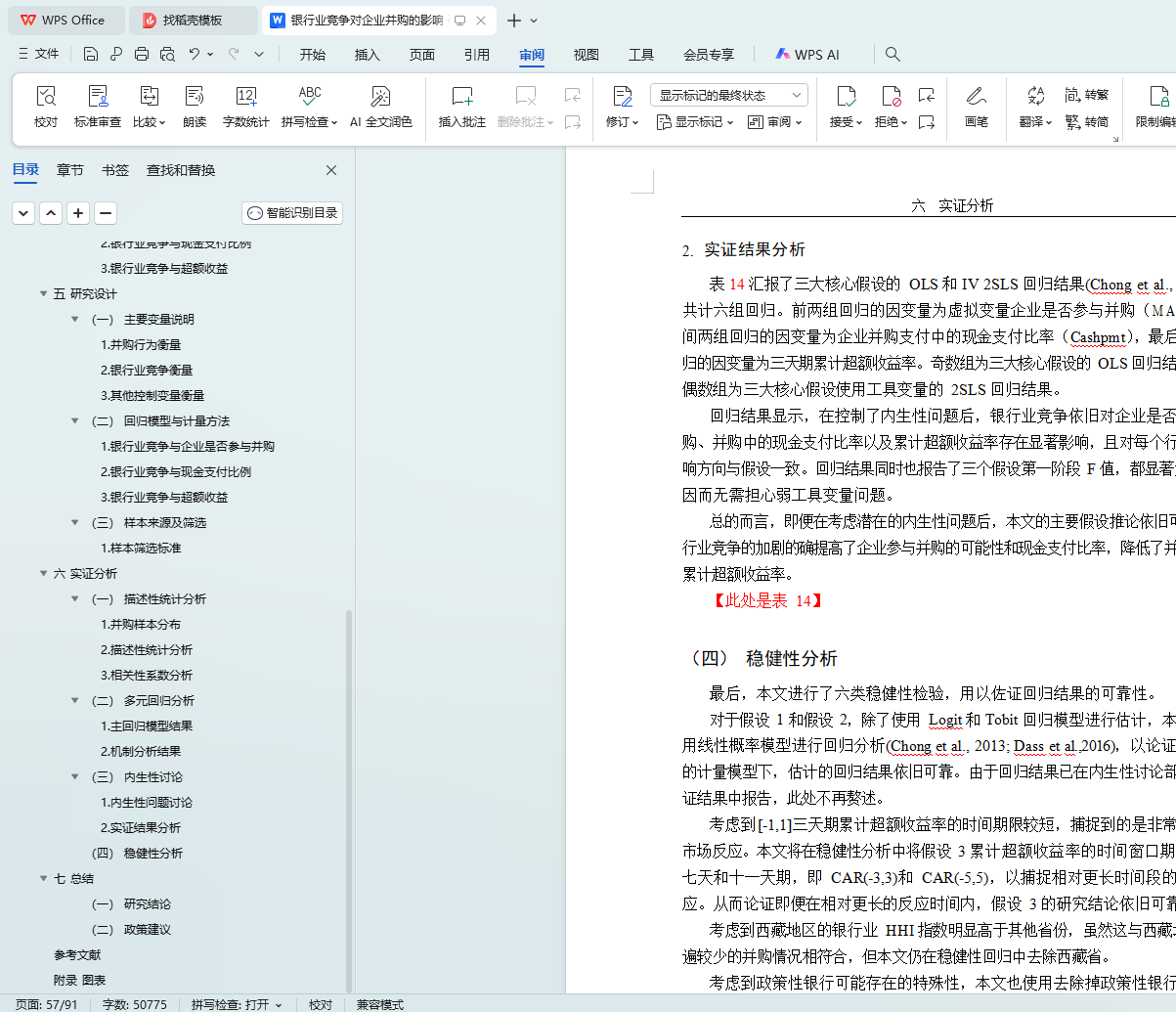
(三) 内生性讨论 38
1. 内生性问题讨论 38
2. 实证结果分析 41
(四) 稳健性分析 41
七 总结 43
(一) 研究结论 43
(二) 政策建议 44
参考文献 45
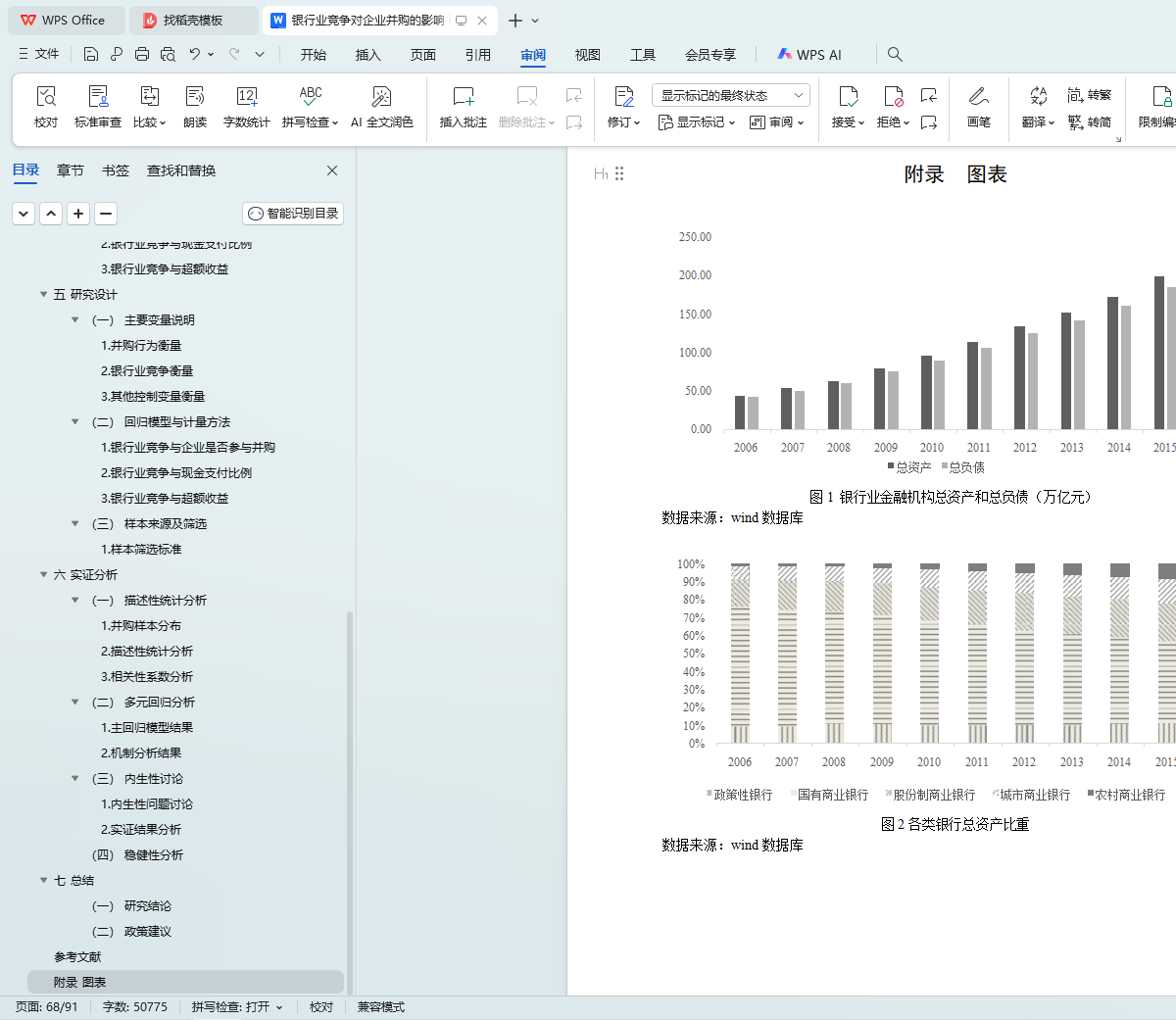
附录 图表 51
致谢.............................................................. 错误!未定义书签。