基于行为设计的自主式小型机器鼠系统研究
摘要
移动机器人是近年来发展起来的一门综合学科,集中了机械、电子、计算机、自动控制以及人工智能等多学科最新研究成果,代表了机电一体化的最高成就。移动机器人在工业生产中常用来完成运输和上下料等任务,同时也被广泛用于农业、医疗等不同行业。
在移动机器人相关技术研究中,路径规划技术是一个重要研究领域[17]。本文首先初步讨论总结了目前主要的路径规划技术。从基于事例、基于环境模型和基于行为三个方面全面而系统地综述了移动机器人路径规划技术的研究现状,对于目前普遍采用的路径规划方法及其实际应用情况进行了较为详细介绍和分析。
基于行为的方法是由MIT的Brooks在他著名的包容式结构[42]中建立,它是一门从生物系统得到启发,而产生的用来设计自主机器人的技术,也是本文所重点研究的目标。它采用类似动物进化的自底向上的原理体系,尝试从简单的智能体来建立一个复杂的系统。将其用于解决移动机器人路径规划问题是一种新的发展趋势,它把导航问题分解为许多相对独立的行为单元,比如跟踪、避碰、目标制导等。这些行为单元是一些由传感器和执行器组成的完整的运动控制单元,具有相应的导航功能,各行为单元所采用的行为方式各不相同,这些单元通过相互协调工作来完成导航任务。
基于行为的机器人学反对抽象的定义, 因此采用具体化的解释更适合该领域的哲学思想。基于行为的机器人学的重要研究内容是系统结构而不是算法, 基于行为设计的机器人在非结构化动态环境中的性能非常优越,用基于符号的机器人学设计的类似机器人无法达到如下性能:
a. 高速度,高灵活性。在动态复杂环境中的移动速度很快;
b. 高鲁棒性。 可以承受局部损坏;
c. 高效性。 软件代码可以是传统的几百分之一,硬件可以是传统的几十分之一;
d. 经济性。价格是传统的十几分之一;
e. 可扩展性。很少改变原有系统便可增加性能;
f. 可靠性。分布式自组织并行工作,可靠性强。
为进一步研究基于行为的规划方法,而引入一个真实环境及任务模型,即IEEE每年举办的微型机器鼠比赛,通过设计基于行为的机器鼠模型论证该算法的可行性。此项比赛要求机器人能够自主在未知环境中完成迷宫穿越的任务。针对机器鼠比赛项目的环境模型未知或不确定,以及该机器人本身的某些限制, 采用基于行为的研究方法, 实现了自行设计的自主式小型移动机器人在未知、动态环境中的自动避障。通过对机器鼠所运行的环境建模,根据基于行为的方法对机器鼠的执行任务、沿墙行走、判断障碍旋转进行分解构建,以及对机器鼠传感器布置及机械平台设计进行理论分析。
本文所研究的模型是自行搭建的机器鼠实物平台, 它由两步进电机驱动, 其外形如图1所示。在机器鼠正向和侧向共有3个漫反射式红外线光电传感器, 距离为10cm~20cm ,两个碰撞开关,传感器位置布置如图2所示,当传感器前方有障碍物时, 传感器的输出为1, 否则为0。


图1 机器鼠外形照片
采用了ATMEL公司的AT89S52单片机控制,小型四相步进电机及专用的PMM8713步进电机驱动方案,红外接近开关作为主要传感器,差动式底盘结构,初步实现针对微型机器鼠竞赛的机器鼠的设计。
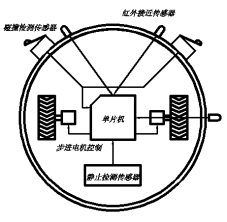
图2 机器鼠传感器布置
行为的设计与机器人的能力密切相关,机器人的硬件限制了机器人的某些行为的能力,根据机器鼠的比赛任务,对机器鼠的行为中作如图3分解。
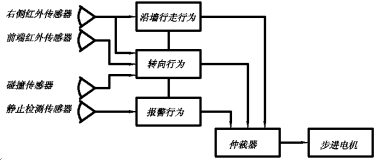
图3 机器鼠的基本行为组件
机器鼠的设计是对基于行为的规划方法的一种验证设计,这种算法正广泛应用于家庭服务类机器人,最典型的实例是自主吸尘机器人。在机器鼠传感和控制系统的基础上,本文进一步针对自主吸尘机器人提出一种机械底盘设计方案,使机器鼠的实用意义得以提升。
关键词:移动机器人;路径规划;单片机控制步进电机驱动;红外接近开关传感器;自主吸尘机器人
Research on the System of Behavior Based Autonomous Navigation of Mobile Robert
Abstract
The mobile robot is a recently developing synthetic discipline, which combines the latest researching results of mechanics, electronics, computer, auto-control, artificial intelligence, etc., and also represents the supreme achievements of mechanical-electrical integration. In the field of industry, the mobile robot is used to accomplish the task of loading and blanking, etc., also it is widely used in other fields, like agriculture, medical science and so on.
Among the relevant technical researches of mobile robot, path planning is an important researching field. This dissertation first briefly discusses and generalizes the current major techniques of path planning. Then from case-based, environment-model-based, behavior-based aspects, it introduces and analyzes in detail the path planning methods commonly used now and their practical applications.
Behavior-based method was constructed by Brooks from MIT in his famous containment type structure. This method, which is inspired by biological system, and generated to design the technique of autonomous robots, is the key researching object in the dissertation. With the principle system similar to animal evolution’s bottom-up system, this method tries to build a complex system out of a simple intelligent agent. To put this in resolving path planning problems of mobile robot is a new developing trend. In terms of navigation, this method separates it into many relatively independent behavior units, such as tracing, collision avoidance, goal directing, etc. and these behavior units are completed motion-control units composed of some sensors and executers, with corresponding navigational functions. Also every unit adopts different behavior patterns, and coordinates with each other to accomplish the task of navigation.
The behavior-based robotics is against the abstract definition, so embodiment explanation is more suitable to this field’s philosophical ideology. The most important researching content of this study is not algorithm, but system construction. Furthermore, this kind of robot has an excellent performance in non-structurized dynamic environment, and with the similar robot designed by symbol-based robotics, there are certain function performance can’t be achieved. They are as follows:
a. High speed and high flexibility. Moving fast in a dynamic complex environment;
b. High robustness. Endure local damages;
c. High efficiency. Software code being one several percent of traditional one and hardware being one several dozens of;
d. High economy. Price being one dozens of traditional one;
e. Expandability. Adding function performances without changing inhering system;
f. Reliability. Distributed self-organized parallel working.
For the further research of behavior-based planning method, a real environment and a task model will be introduced, that is the robotic mice contest hold by IEEE every year, which aims at demonstrating the feasibility of the algorithm, through designing a behavior-based robotic mice model. This contest demands the robot to accomplish tasks of maze crossing autonomously in an unknown circumstance. Because the environmental models of the contest are uncertain and the robot’s intrinsic defeats, therefore, by adopting behavior-based researching method, it can be achieved that the mobile robot can avoid obstacle automatically in an unknown and dynamic environment. Through modeling the robotic mice’s running environment, this dissertation decomposes and constructs the its task performing, along wall walking and obstacle-rotating judging according to the behavior-based method, also analyzes its censors arrangement and mechanical platform designing from an ideological point of view.
The model researched in this dissertation is a self-constructed physical object platform, driven by two drive circuit of step motors (As shown in fig.1). There are 3 infrared opto electronics of diffuse reflection in the front and side of the robotic mice, with a distance being 10cm~20cm, two impact switches and censors (The position arrangement is shown in fig.2). When obstacles are in front of the censors, its’ output is 1, or on the contrary case, 0.


Fig.1 pictures of robotic mice’s appearance
To preliminarily realize the robotic mice for the contest, it uses AT89S52 singlechip from ATMEL Company as controlling; the PMM8713 step motor specialized for mini four phase step motor as the driving plan; infrared remote control switch controller as major censor and differential chassis structure.
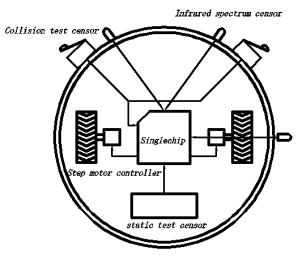
Fig.2 arrangement of robotic mice’s censors
The behavior’s designing is closely correlated to the robot’s abilities, and its hardware restricted abilities of certain behaviors. According to the tasks of the robotic mice’s contest, there is the decomposition of the robotic mice. (As shown in fig.3)
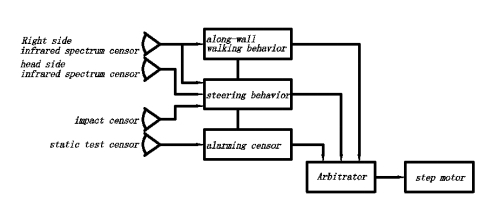
Fig.3 robotic mice’s basic behavior modules
The robotic mice’s design is a verifying design to behavior-based planning method. This algorithm is widely applied in home service robot, with the auto dust collecting robot being a typical example. On the basis of robotic mice censor and control system, this dissertation further come forward a design plan of mechanical chassis to the auto dust collecting robot for improving robotic mice’s practical meaning.
key words:Mobile robot;Path planning;Singlechip-controlling drive circuit of step motor;Infrared remote control switch controller;Autonomous cleaning robots



