The oil suction and delivery actions of a piston pump depend upon the size change of the chamber produced by the reciprocating movement of the pistons within their cylinder bores. For piston pumps,the circular piston ang their corresponding cylinder bores can make high precise match-up and ensure good preformance of seal.High volumetric ang overall efficiencies can be acquires even in operation under high pressure.The piston pumps can be divided into radial and axial types according to their pistons'arrangements and their diffent moving directions with respect to the transmission shafts.The signal piston pump shown in Fig.1-1 is a radical type. The piston is located arectly due to its failure to provide oil continuously(a signal piston pump scuks oil in the first halfcircle and delivers oil in the second).A radial piston pump usually consists of three or more pistons for continuous suction and discharge.
1.1.1Valve shaft radial piston pumps
1.Operating principle
Fig.3-5 shows a radial piston pump operation .The piston bores are arranged radially on rotor (cylinder)2 with an equal apart.Five piston are set in the piston bores and can move freely within them.Bush 3 is mounted in the rotor bores and rotates with the rotor.Valve shaft 5 is stationary and there exists an eccentricity e between its center and that of the stator.The stator moves in the horizontal direction .As the rotor rotates in the clockwise direction,the piston are pressed against the inner wall of stator 4 under centrifugal force or low pressure oil in the reservior into chamber b through orifice a of the valve shaft; while the pistons in the next semicircle are pushed inward by the inner wall of the stator,which reduces the working volume of the oil tight chamber and forces a quantity of liquid in chamber c out of the cylinder through orifice d on the valve shaft. In each radial bore,the piston suck deliver oil once per revolution of the rotor.
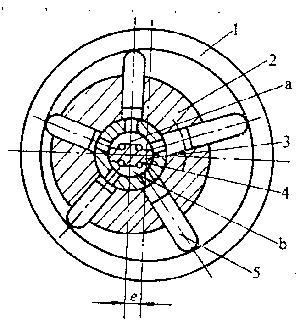
Fig.1-1 配流轴式径向柱塞泵
The pump's delivery is expressed by:
V=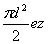 (1-1)
(1-1)
Where d is the piston diameter;e is the offset between the stator and cylinder case(rotor);z is the number of the pistons.
2.Structure features
1)The inlet and outlet ports of the valve shaft are separated by a center land and balancing grooves are set in their opposite directions.The hydraulic radial forces acting on the valve shaft are balanced out by the balancing grooves.Not only the wear of its sliding surface but also leakage viaclearance are reduced,thus increasing the volumetric efficiency..
2)The delivery of the pump can be changed simply by changing the eccentricity e of the stator with respect to the rotor; while the inlet and outlet directions can be changed by changing the direction of e (i.e.,e becomes negative from positive).In this concept,radial piston pumps can be changed into singal-acting or double-acting variable displacement pumps.
3.Radial piston pumps with load-sensitive variable displacement capacity
This type of pump gets its name from the fact that the output pressure of the pump depends upon the load.The components of this pump are identified in Fig.3-6.The output oil with a pressure of p (working pressure)enters the actuator through control valve V
(working pressure)enters the actuator through control valve V ,whose output pressure p
,whose output pressure p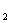 depends upon the `load on the actuator.Two paths of oil(with the pressures of p
depends upon the `load on the actuator.Two paths of oil(with the pressures of p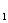 and p
and p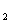 )connect with the two ends of three-proted valve V
)connect with the two ends of three-proted valve V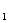 repectively.When valve V
repectively.When valve V and F
and F is the spring force in the right end of its valve core.
is the spring force in the right end of its valve core.
If F is considered constant,then(p
is considered constant,then(p -p
-p )is also constant(0.2-0.3MPa). I.e.,a certain flow is put out for a certain size of orifice in valve V
)is also constant(0.2-0.3MPa). I.e.,a certain flow is put out for a certain size of orifice in valve V .Three exists an eccentricity of the stator with repect to the rotor.The moving direction and displacement of the stator depend upon the pressure differential of the left and right variable displacement pistons.To meet the requirements for flow rate and pressure changes of actuators,the output flow rate and pressure of the pump must be adjusted.This can be accompoloshed by the stator's displacement,which will change the eccentricity e of the stator.
.Three exists an eccentricity of the stator with repect to the rotor.The moving direction and displacement of the stator depend upon the pressure differential of the left and right variable displacement pistons.To meet the requirements for flow rate and pressure changes of actuators,the output flow rate and pressure of the pump must be adjusted.This can be accompoloshed by the stator's displacement,which will change the eccentricity e of the stator.
For this type of pumps,if the output flow rate q is constant,the pressure difference of valve V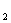 (Δp=p
(Δp=p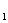 -p
-p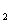 )will increase by reducing the orifice of valve V
)will increase by reducing the orifice of valve V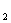 .Then the valve core of three-prorted valve V
.Then the valve core of three-prorted valve V moves in the right due to uneven forces,opening valve orifices a and c.Immediately this happens the pressurized oil in the left variable piston cylinder opens to the reservoior and the pressure p
moves in the right due to uneven forces,opening valve orifices a and c.Immediately this happens the pressurized oil in the left variable piston cylinder opens to the reservoior and the pressure p falls down. The stator moves in the left due to uneven forces,reducing the eccentricity e and thus the output flow rate q and the pressure differential of valve V
falls down. The stator moves in the left due to uneven forces,reducing the eccentricity e and thus the output flow rate q and the pressure differential of valve V .The three-proted valve V
.The three-proted valve V will again balance out when the pressure differential returns to its original value. At this moment,the valve core of valve V
will again balance out when the pressure differential returns to its original value. At this moment,the valve core of valve V returns to its home position and valve orifices a and c are cut off again. No further oil flows into the left variable piston cylinder and the stator stays at a new position.A certain amount of flow rate on request is put out with respect to the orifice of valve V
returns to its home position and valve orifices a and c are cut off again. No further oil flows into the left variable piston cylinder and the stator stays at a new position.A certain amount of flow rate on request is put out with respect to the orifice of valve V .Similarly,when the orifice of valve V
.Similarly,when the orifice of valve V increases,the eccentricity will increase and thus the output flow rate.
increases,the eccentricity will increase and thus the output flow rate.
Recent improvements in the design of radial piston pumps have resulted in the widespread use of these pumps at a rated pressure high up to 35MPa.
1.1.2 Swashplate axial piston pumps
1.Operating principle
The swashplate axial piston pump is also called straight shaft axial piston pump.The center lines of the piston,are arranged axially on the cylinder with an equal distance apart.The pistons can move freely within their corresponding piston bores.The swashplate is positioned at an angle β relative to the piston axis to create a reciprocating motion.The swashplate and the valve plate themselves keep stationary and the pistons are pressed on the swashplate under low pressure oil or spring force.There are two waist shaped ports on the valve plate and are separated from each other by the transition region.The width of this traindition is equal to or slight longer than the waist shaped ports(the inlet and outlet ports).
As the cylinder roates with the transmission shaft in a direction shown in the Figure,the pistons in the upper semicircle are forced outward gradually under low pressure oil.The oil tight working volume in the cylinder bores is on the increase and a vacuum is formed,drawing the oil into port a of the valve plate.While the pistons in the next semicircle are pushed inward by the swashplate gradually,reducing the oil tight working volume and forcing the oil out through port b of the same valve plate.Each pistion moves reciprocatingly once with one suction and delivery action per revolution of the cylinder.
Note the diameter of the piston as d,the diameter of the cylinder bore distribution cricle as D,the piston number as z,the angle of the swashplate with respect to the piston axis as β,then the delivery of the swashplate axial piston pump is:
V=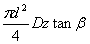 (1-2)
(1-2)
Obviouely,the delivery V can be changed by varying the angle of the angle of the swashplate.Several means are available to achive this from various manufacturers.Fig.3-7 shows a manual variable-displacement piston pump With the help of drive key,adjusting piston 7 moves up and down when screw 9 rotates synchronously with handwheel 10. Then the swashplate swings about its center through pin 6, thus changing the swashplate angle with respect to the pistoni axis.With the largest swashplate angle shown in Fig.3-7, the pistons have the longest stroke within the cylinder barrel, i.e. , β=β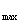 , s=s
, s=s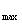 .
.
Note the vertical distance between the pin (force applying point) and the swashplate gyration centerline as L, then
tanβ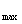 =s
=s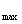 /L
/L
Because the displacement of the pin equals that of the adjusting piston, then tanβ=s/L,substituing it into formula (1-2),we have:

Fig.1-2 斜盘式轴向柱塞泵
From formula (1-3), we can see that the pump delivery is proportional to the pump's displacement.To limit the hydraulic side forces on the pistons, we swashplate largest angle β should be less than 18°~20°.
should be less than 18°~20°.
2.Structure features
1)For piston pumps, the machining accuracy between the pistons and the cylinder bores is easy to acquire; and they can reach high volumetric effciency; high rated pressure (high up to 32MPa) .
2)To avoid pressure pulsation at the ends of pistons (tight volumes ) where oil pressures are changed from suction to delivery, damping grooves (or holes) are set in the front ends of the suction and delivery prots of valve plate, or the valve plate is placed an angle along the cylinder rotating direction.
3)Leaking past the clearance among the pistons, piston shoes and cylinder block face are carried through the pump body and out a case drain connection to the reservoir, which carries away the heat generated and prevents any heat buildup and overheating within the pump.
4)The instantaneous theoretical flow rate of the swashplate axial piston pumps , radial piston pumps described above and bent axis axial pumps which will be described later are changing periodcally with cylinder rotation, and the changing frequency is function of pump rotation speed and piston number. The flow pulsation in a pump with odd number pistons is lower than one with even number by theory, thus piston pumps always have an odd number of pistons,usually 5, 7 or 9.
1.1.3 Bent-axis axial piston pumps
1.Operating principle
Fig.1-3 shows the operation of a bent-axis axial piston pump.As transmission shaft 5 rotates with the electric motor, pistons 2 are driven back and forth in their cylinder bores by connecting rod 4. The side face of the connecting rod also brings the pistons and the cylinder together to revolve. Suction and delivery actions in the inlet and outlet ports respectively are accomplished through stationary valve plate 1. Similar to swashplate axial piston pumps, the delivery of a bent-axial piston pump can be changed by the change of cylinder slanted angle γ and changing the slanted direction makes a double-action piston pump. The delivery formula of bent-axial piston pumps is the same as that of swashplate axial piston pumps.
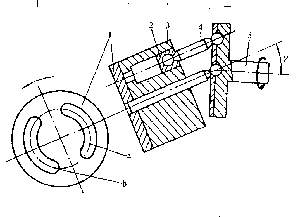
Fig.1-3 斜轴式轴向柱塞泵
2.Constant power variable displacement bent-axis axial piston pump
Here is a bent-axis axial piston pump with the function of constant power variable displacement. Fig.1-3 shows its operation.
1)Variable displacement process (composed by components 1-4):the upper chamber of adjusting piston 13 connects with the pump's outlet port.The oil enters into the oil chamber of control piston 7 through stationary damping orifice 6. Variable springs 9 and 10 form a dual-spring with the distance s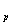 between the installation height of inner spring 10 and the spring plate. Spring 12 is Iocated at the down end of servo-valve 11. When the hydaulic pressure acting on the control piston 7 exceeds the resultant set force of springs 9 and 12, control piston 7 will push servo-valve core 11 to move downwards.Then oil prots a and b connect with each other and the pressurized oil enters into the down charmber of the variable piston 13.The variable piston will move upwards due to its larger area of the down chamber than of the upper chamber,causing valve plate 4 and cylinder block 1 to swing about the point "o"through pin 5,which in turn reduces the swing anfle γof the cylinder.
between the installation height of inner spring 10 and the spring plate. Spring 12 is Iocated at the down end of servo-valve 11. When the hydaulic pressure acting on the control piston 7 exceeds the resultant set force of springs 9 and 12, control piston 7 will push servo-valve core 11 to move downwards.Then oil prots a and b connect with each other and the pressurized oil enters into the down charmber of the variable piston 13.The variable piston will move upwards due to its larger area of the down chamber than of the upper chamber,causing valve plate 4 and cylinder block 1 to swing about the point "o"through pin 5,which in turn reduces the swing anfle γof the cylinder.
2)Variable displacement with servo constant power process(composed by components 5-13):With the reduction of swing angle γ, variable displacement piston 13 moves up and provides a feedback for compression spring 9 through pin 5. Then control piston 7 and servo-valve core 11 move up to their home postion, closing the oil ports a and b.They hydraulic pressure acting on the control piston and the spring pressure are balanced out.The pump puts out a certain amount of flow because the adjusting piston and the cylinder are kept at a certain position.When the stroke of the adjusting piston reaches s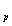 ,inner spring 10 works, i.e. , the hydraulic pressure acting on the control piston and the resultant force of the springs 5,6 and 8 are balanced out.
,inner spring 10 works, i.e. , the hydraulic pressure acting on the control piston and the resultant force of the springs 5,6 and 8 are balanced out.
3)Characteristic curves: The constant power variable characteristic curve is illustrated in Fig. The slope of line 1 is regulated by the stiffness of spring 9, while the slope of line 12 is used to control the horizontal postion of curves BCD.As can be seen from this curve, the hydraulic pressure acting on the control piston becomes larger with the increase of the pump's output pressure,while the servo variable displacement process makes its output flow increase inversely with the output pressure.The product of output pressure p and flow rate q is almost cinstant,pump with such way of delivery also named constant power pump.
Compared with the swashplate piston pump, in a bent-axis piston pump,the radial force on the pistons and the cylinder is smaller.A larger slanted angle and a larger scope of variable displacement are avaiable.But both the size and the inertia of the variable mechanism are larger,causing a longer response time for the variable mechanism.



