摘 要
能源危机是我们面对的最大挑战之一,风力发电是具有大规模发展潜力的可再生能源,在远期有可能成为世界重要的替代能源。尽管水平轴风力机是目前应用最广的一种风力发电机,但垂直轴风力机有着优越的性能,并越来越被人们所重视。垂直轴风力机具有比水平轴风力发电机更好的商业开发价值,应用领域十分宽广。
阐述了垂直轴风力机的发展历史及基本现状,从各方面比较了水平轴风力机以及垂直轴风力机,得出垂直轴风力机在各方面的优势,并介绍了达里厄风力机的改进型式。论证了垂直轴风力机的整体方案,确定了风力机固定攻角及可变攻角两种方案的运行方式。由于风力发电装置所需的发电机未形成标准和系列,无法选型,因此自主设计了50kW发电机。最后详细设计了垂直轴风力机的机械本体,确定了风力机各部分结构的最终数据,经校核验证垂直轴风力发电机的性能满足设计要求。
关键词:风能;垂直轴;风力发电机
ABSTRACT
The energy crisis is one of the biggest challenge that we have ever faced. Wind electric power generating, which is a reproducible resource that have large-scale development potential, will be an important alternative energy in the future. Although the horizontal axis wind turbine is used widely, the vertical axis wind turbine has attracted the notice of us because of the extraordinary performance of it. Having much more commercial value than the horizontal axis wind turbine, the vertical axis wind turbine can be used in many areas.
This issue introduces the basic situation and phylogeny of the vertical axis wind turbine, shows us the advantages in many aspects by comparing with the horizontal axis wind turbine, and introduces the improved version of the Darrieus. The design program of the vertical axis wind turbine has been demonstrated, and the running modes of fixed angle and variable angle are designed either. Since the power generator of the wind turbine can not be available because of no standards or series are formed, so one 50kW power generator is designed in special. All the mechanisms of the vertical axis wind turbine have been designed in detail, and all the dimensions of the components are chosen either. It can be proved that the vertical axis wind turbine can meet the demands perfectly after being checked.
Key words: wind energy; vertical axis; wind turbines
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 前言 1
1.2 世界及我国风力发电发展现状 1
1.3 国内外风力机研究现状 3
1.3.1 风力机的造型 3
1.3.2 水平轴风力机 3
1.3.3 垂直轴风力机 3
1.4 垂直轴达里厄型风力机 4
1.4.1 达里厄风力机的发展历史 5
1.4.2 达里厄风力机与水平轴螺旋桨风力机的比较 6
1.4.3 达里厄风力机的改进 7
1.5 设计选题目的及意义 8
1.6 设计的主要内容及具体要求 8
第2章 总体方案的论证设计 9
2.1 总体结构布局的初步确定 9
2.2 风力机运行方式的设计 9
2.2.1 固定攻角风力机的设计 10
2.2.2 可变攻角风力机的设计 11
2.3 本章小结 15
第3章 电机的设计 16
3.1 电磁设计的依据和任务 16
3.2 主要尺寸和极数的选择 16
3.2.1 主要尺寸的确定 16
3.2.2 极弧系数 与电磁负载
与电磁负载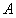 及
及 的选择 18
的选择 18
3.2.3 极数的选择 20
3.3 电枢设计 20
3.3.1 电枢绕组、槽数和槽型 20
3.3.2 换向器的主要尺寸与电刷的选择 22
3.4 磁路计算 23
3.4.1 直流电机的磁路与主极漏磁系数 23
3.4.2 气隙 24
3.4.3 电枢齿部 24
3.4.4 主极 24
3.4.5 定子轭部 25
3.5 电机轴的设计 26
3.6 本章小结 26
第4章 机械本体设计及校核 27
4.1 联轴器的选取 27
4.2 制动器的选取 27
4.3 支承轴及其附件的设计校核 28
4.3.1 支承轴最小直径的确定 28
4.3.2 支承轴的校核 29
4.3.3 支承轴上键的校核 32
4.3.4 深沟球轴承的校核 33
4.3.5 推力球轴承的的校核 34
4.4 旋转支撑筒的设计及校核 34
4.5 等速同向传递机构的设计及校核 35
4.5.1 轴的设计 35
4.5.2 齿轮的设计校核 40
4.5.3 轴承的选择 42
4.6 横杆的设计及校核 43
4.6.1 横杆部分数据的确定 43
4.6.2 下横杆的受力分析 44
4.7 横杆与法兰连接处螺栓的选取及校核 46
4.8 叶片与横杆连接处的设计校核 47
4.8.1 连接轴的设计校核 47
4.8.2 校核连接板的拉伸强度 48
4.8.3 轴承的选择及校核 48
4.9 本章小结 49
结论 50
参考文献 51
致谢 53

小型风力发电机部分零部件三维图
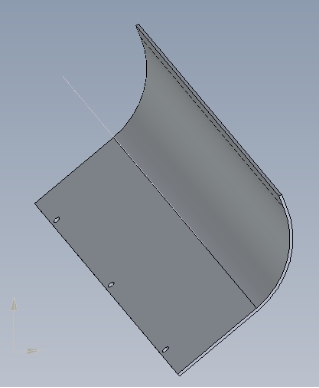
图1 小型风力发电机叶片三维图
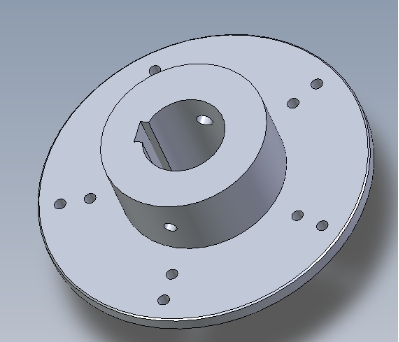
图2 小型风力发电机轴毂三维图
图3 小型风力发电机风力机三维图1
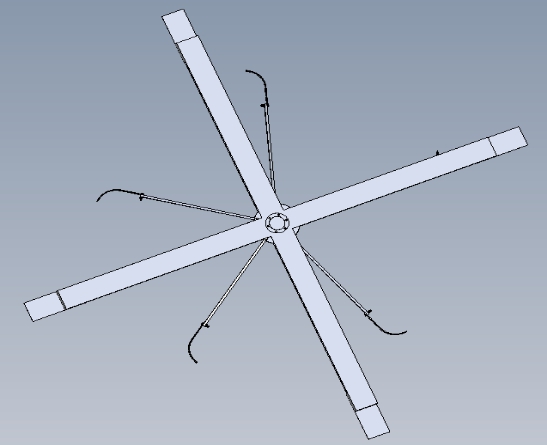
图4 小型风力发电机风力机三维图



