摘 要
水面无人船(unmanned surface vessel, USV)近年来受到国内外专家学者越来越多的关注。为了总结分析USV现有路径规划方法及其优缺点,通过对USV路径规划研究进行分类综述和分析,从获取环境空间障碍物的方式,将USV路径规划分为基于海洋环境信息的全局路径规划和基于传感器信息的局部路径规划。总结基于各类研究方法的主要研究成果及其主要特点,剖析其存在的主要问题,阐明USV路径规划的研究思想和意义,提出USV路径规划今后可能的发展方向。
本文提出一种新的方法去解决海上应急搜救的无人船路径规划问题。通过连接空间和持续时间,用飞机的最长的续航时间T,研究一种简单的空中搜索资产模型。打算通过这个模型去最大化的检测合作目标(应急搜救)。提出的模型是基于假设现存的先验信息(比如信息融合过程的结果),在可能的地理位置上去建立一个遏制空间分布可能位置的模型。这个可能性区域是基于一个定向模型获得,这个模型不但运用了切割阈值去定义和牵制搜索路径的概率而且还努力的按照不同的等级的经行搜索力度的分配。最后我们验证模型在实例中的应用。
关键词:海上搜救;应急搜救;定向运动模型;无人船;路径规划
Abstract
Surface unmanned surface vessel (USV) has attracted more and more attention from experts and scholars at home and abroad in recent years. In order to summarize and analyze the existing path planning methods of USV and their advantages and disadvantages, this paper summarizes and analyzes the research of USV path planning by classification and analysis. USV path planning is divided into global path planning based on marine environmental information and local path planning based on sensor information. This paper summarizes the main research results and their main characteristics based on various research methods, analyzes the main problems existing in them, and clarifies the main problems of USV path planning. Research ideas and significance, and propose the possible future development direction of USV path planning.
In this paper, a new method is proposed to solve the problem of route planning for unmanned ships in maritime emergency search and rescue. By connecting space and duration, a simple model of air search assets is studied using the aircraft's longest life span (T). This model is intended to maximize the detection of cooperative targets (emergency search and rescue). The proposed model is based on the assumption of the existing prior information (such as the result of the information fusion process) and establishes a model to contain the possible location of the spatial distribution on the possible geographical location. This possibility region is obtained on the basis of a directional model that not only uses the cutting threshold to define and constrain the generality of search paths Rate and also try to according to different levels of meridian search strength distribution. Finally, we verify the application of the model in an example.
Keywords: maritime search and rescue; emergency search and rescue; directional movement model; unmanned ship; path planning
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
1绪论 1
1.1选题背景及意义 1
1.2路径规划研究现状 2
1.2.1基于海洋环境信息的全局路径规划 2
1.2.2基于传感器信息的局部路径规划 3
1.2.3无人船路径规划的发展方向 4
1.3研究方向 5
2 MATLAB可视化界面快速海上应急搜救规划路径 6
3面向海上应急搜救模型的建立 7
4面向海上应急搜救的无人船路径规划问题描述 9
5无人船可能的搜索路径规划 11
6面向海上应急搜救的无人船路径定向模型 14
6.1变量 14
6.2约束条件 15
6.3目标函数 17
6.4非线性混合整数规划模型 18
7验证结果 19
结 论 22
参考文献 23
搜索的第一步在于识别可能包含搜索目标的边界区域(PC)。主观的信息如(规则,庄家评判)和客观的信息(如历史数据,传感器融合的数据一般都用来去定义和约束这个区域。比如,国际海陆空搜索搜救手册就给出了建立这样的可能区域的指导方针。其他的一些方法比如概率分布函数或者模糊函数也可能被应用在建立搜索区域模型上。然后,将这个可能存在搜救目标的区域划分为J个小单元。
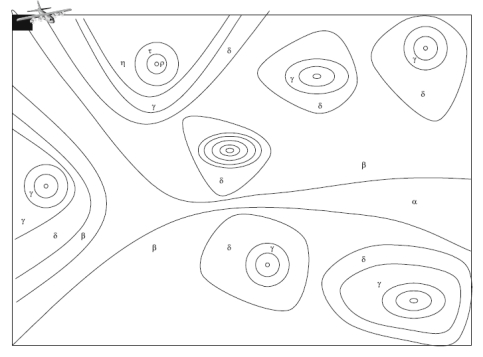
图2 用2维视图来展示目标可能分布的位置
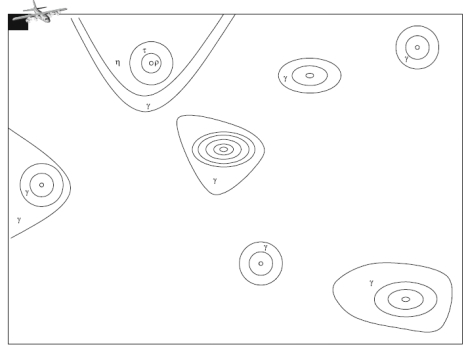
图3  切割图
切割图



