摘要
合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar,SAR)与其他类型遥感成像技术相比具有独特的优势,现已广泛应用在国民生活和国防安全等各个领域。SAR图像的特性决定了其应用的广泛性,但也因其特性增加了SAR图像翻译和分析工作的困难程度。尽管现有大量的研究已经提出了SAR图像目标自动检测方法,但检测性能仅可在特定的条件下得以保证,当面对复杂背景以及目标存在变体、伪装和欺骗等等复杂的开放环境时,现有计算机自动分析方法的检测性能远不能满足实际需求。现如今依赖专家识别的方式仍是最为可靠的SAR图像目标检测方法,但是传统的人工判读检测方法存在着耗时费力等明显缺点。脑机接口技术(Brain-computer Interface,BCI)为解决以上两种问题提供了一种新的思路,通过脑机接口技术解码判读人员脑响应反映判读人员是否观测到目标。
脑机接口技术以检测脑电波(Electroencephalography,EEG)的方式获取人类脑活动,然后通过计算机解码脑电波信号获得人类脑响应并在计算机上展示和交互。已有研究表明,以快速序列视觉呈现(Rapid Serial Visual Presentation,RSVP)方式的“odd-ball”实验范式可以有效地诱发脑电波的P300事件相关电位(event-related potential,ERP)。由于脑电波的事件相关电位是基于单试次脑电信号平均而产生的,所以基于识别ERP信号的BCI系统不能保证其实时性。基于上述研究,本文设计一种基于脑机接口的实时SAR图像目标检测系统,该系统采用RSVP方式的“odd-ball”实验范式诱发判读人员的P300成分,并设计一种单试次脑电分类算法识别判读人员脑电波中是否含有P300成分,进而反映对应刺激切片中是否包含目标影像。为确保系统的实时性和稳定性,本研究包含以下三个设计:第一,设计一种适用于单试次脑电信号分类的算法——ERP Attention Net,用于单试次脑电信号的分类。第二,设计一种适用于稳定诱发P300成分的刺激切片生成及呈现方案,用于判读人员检测目标影像。第三,设计一种多进程同步解码的BCI系统,满足任务实时高效的要求。
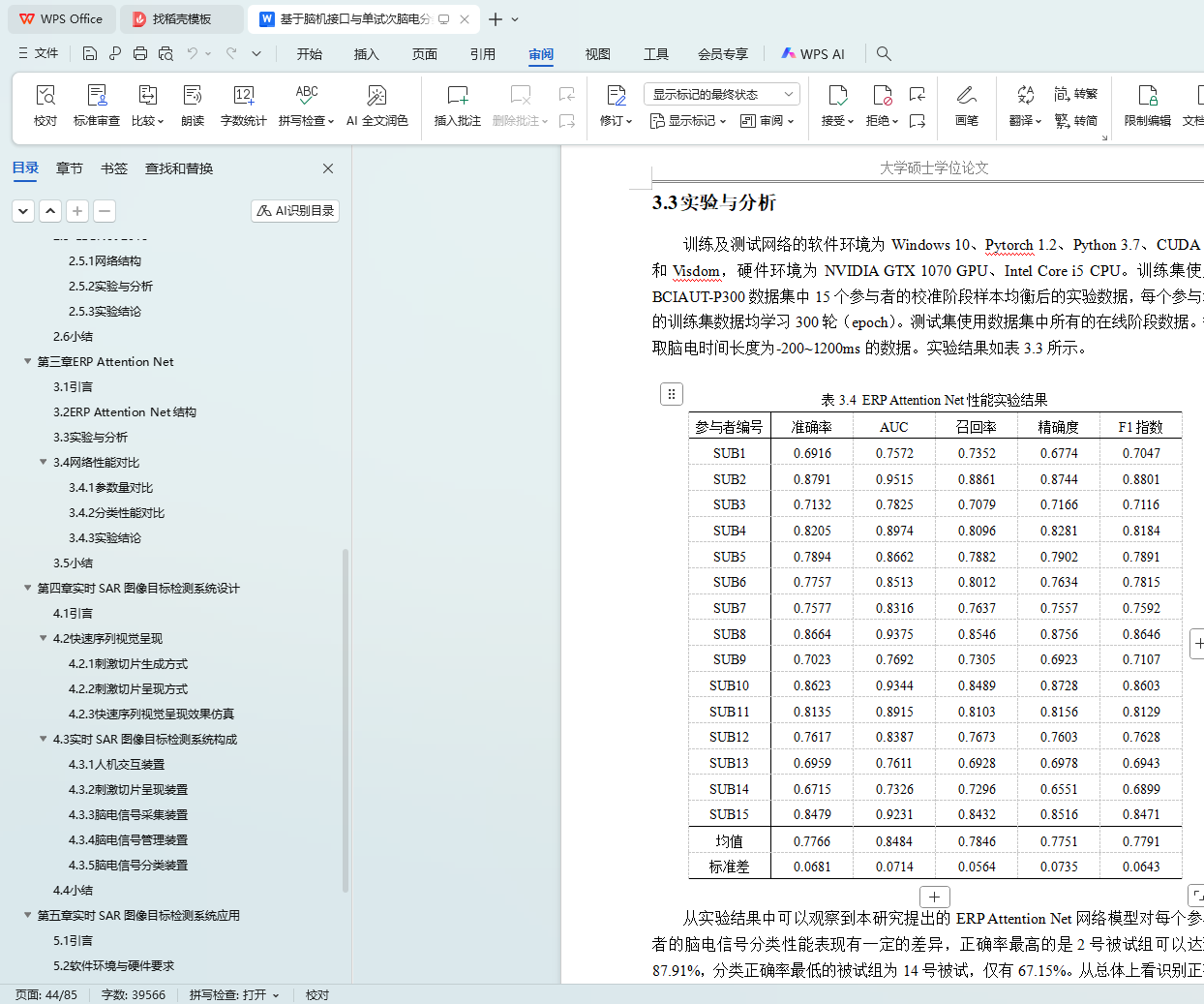
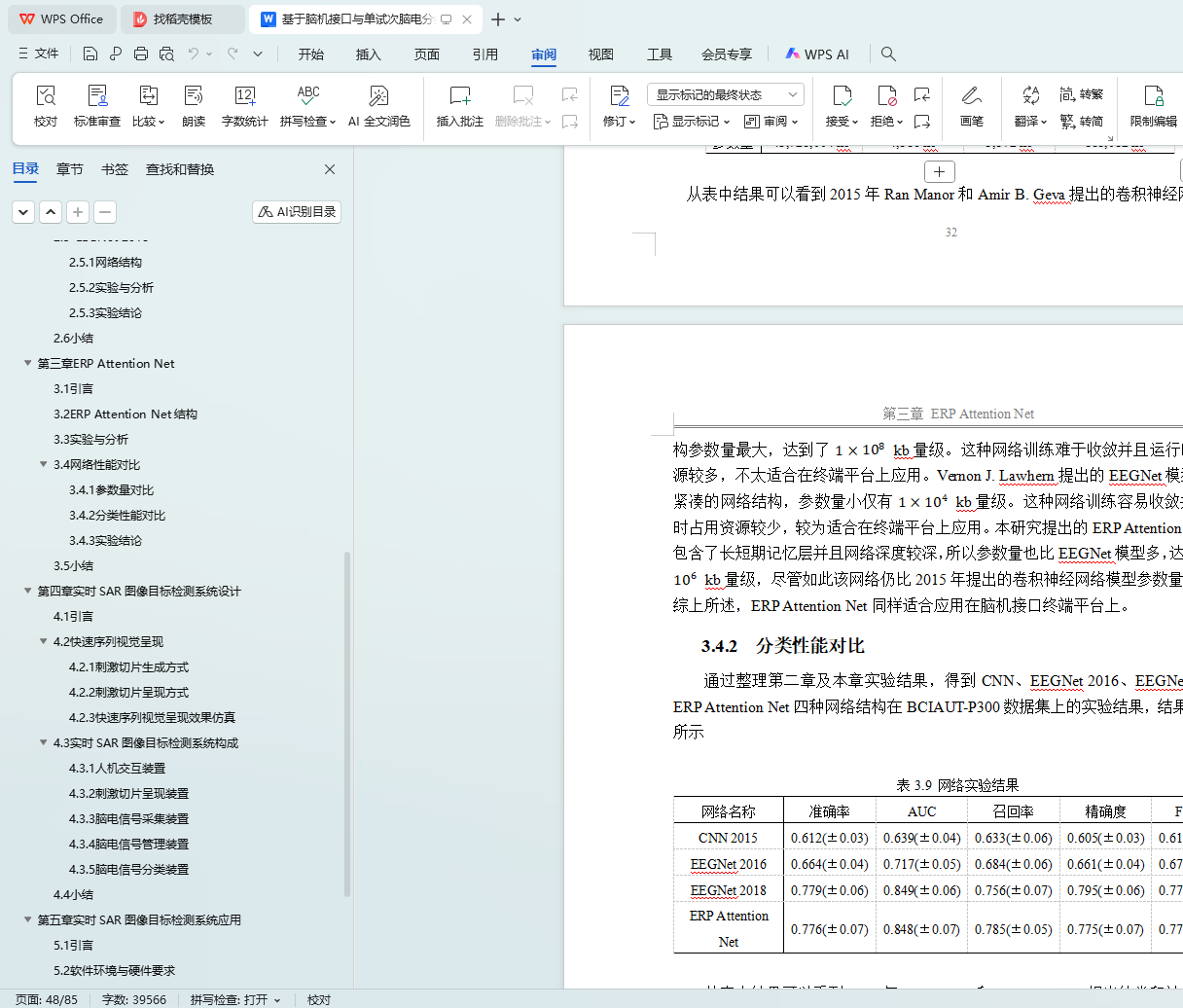
在单试次脑电分类算法的研究中,本文使用BCIAUT-P300数据集作为算法研究的训练集及测试集,该数据集以其参与者人数训练周期长多为特点,为那些依赖大量训练数据的分类算法提供了有效的数据支撑。分别对比了Ran Manor提出的卷积神经网络模型、Vernon J. Lawhern提出的EEGNet模型以及本研究设计的ERP Attention Net模型在BCIAUT-P300数据集上的表现。从实验结果上看,EEGNet的分类性能表现最好,单试次脑电信号的平均分类正确率可以达到77.94%,相比之下Ran Manor提出的卷积神经网络模型表现较差,平均分类正确率仅有66.47%。本研究所设计的ERP Attention Net模型平均分类正确率为77.6%,和EEGNet差距极小,但在召回率指数上ERP Attention Net表现的更好,达到了78.5%,高出EEGNet约3.1%。通过实验验证了本研究设计的ERP Attention Net模型在单试次脑电分类性能的有效性。另外,本研究还通过多组对比试验及消融实验讨论所设计的ERP Attention Net模型中各个模块的性能。
在实时SAR图像检测系统的设计中,首先考虑的是设计刺激切片的生成及呈现方案。本研究发明了一种适用于快速视觉呈现的刺激切片生成及呈现方案,该方案可以有效的避免目标密集区域目标刺激切片连续出现的问题,通过仿真实验证明了该方案地有效性。然后考虑设计实时SAR图像检测系统的系统架构,因为存在P300信号潜伏期长和刺激切片呈现时长短的冲突、脑电信号实时采集获取及分类的问题,本研究设计了人机交互装置、脑电信号采集装置、脑电信号管理装置、脑电信号分类装置及刺激切片呈现装置五个装置,通过脑电管理装置解决P300潜伏期与刺激时长的冲突问题。以及通过设计的脑电采集进程、脑电管理进程及人机交互进程三个进程间的同步配合解决了脑电信号实时采集获取及分类的问题。
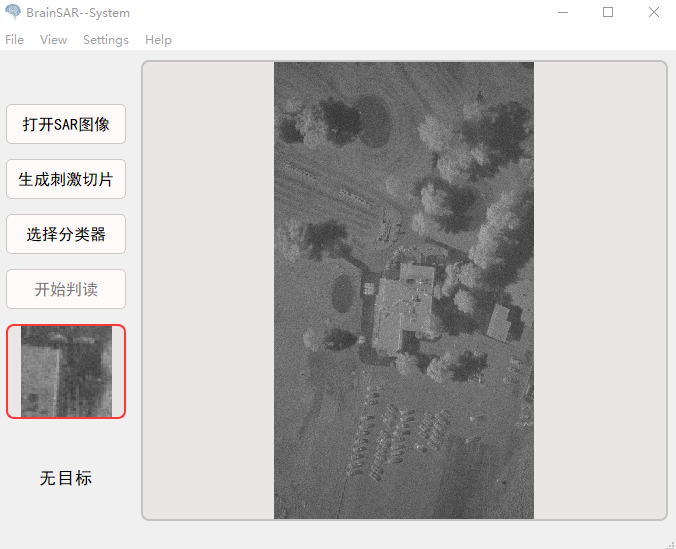
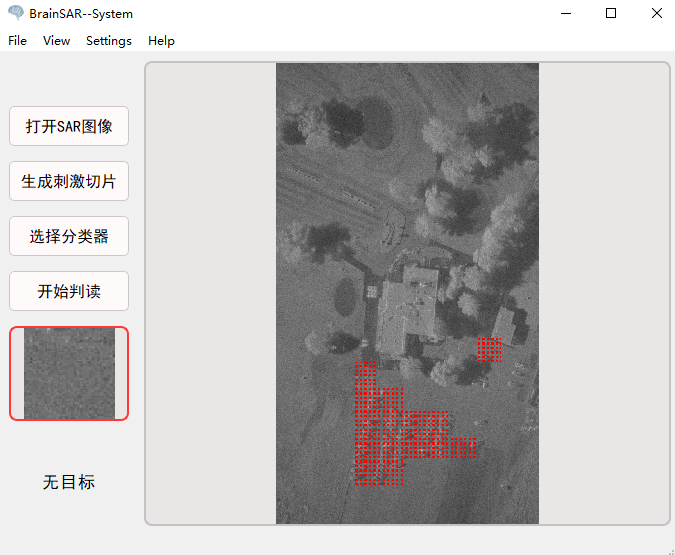
最后,将本研究设计的单试次脑电分类算法装载入基于脑机接口的实时SAR图像目标检测系统中,招集一名健康被试使用该系统并进行判读实验。该系统所设计的各个功能实现了预期要求,能够标注大幅面SAR图像中的目标影像,用户反馈意见少,操作中未出现异常情况。综上,本文研究设计的,包含单试次脑电分类算法、适用于快速视觉呈现的刺激切片生成及呈现方案及基于脑机接口的实时SAR图像目标检测系统,整套系统或许为解决现今SAR图像目标检测存在的问题提供了一套新的解决方案。
关 键 词:SAR图像目标检测, P300信号, 单试次脑电分类, 脑机接口技术
ABSTRACT
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) compared with other types of remote sensing imaging technology, it has been widely used in various fields such as people's life and national defense security. The characteristics of SAR images determine the wide range of applications, but they also increase the complexity of SAR image translation and analysis due to their characteristics. Although a large number of existing researches have proposed automatic detection methods for SAR images, the performance can only be guaranteed under specific conditions. When faced with complex backgrounds and complex open environments such as target variants, camouflage and deception, the performance of existing computer automatic analysis methods is far from meeting actual needs. Nowadays, expert recognition is still the most reliable method of SAR image target detection, but the traditional manual interpretation detection method has obvious shortcomings such as time-consuming and labor-intensive. Brain computer interface (BCI) technology provides a new way to solve the above two problems, relying on BCI technology to decode the interpreter's brain response and reflect whether the interpreter has observed the target.
The brain-computer interface technology obtains human brain activity by detecting Electroencephalography(EEG), and then decodes the brain wave signals through the computer to obtain the human brain response and display and interact on the computer. Existing studies have shown that the "odd-ball" experimental paradigm with rapid serial visual presentation (RSVP) can effectively induce the P300 event-related potential (ERP) of brain waves. Because the event-related potentials of brain waves are generated based on the average of single-trial EEG signals, the BCI system based on recognizing ERP signals cannot guarantee its real-time performance. Based on the above research, this paper designs a real-time SAR image target detection system based on a brain-computer interface. The system uses the RSVP "odd-ball" experimental paradigm to induce the P300 component of the interpreter, and designs a single-trial EEG classification. The algorithm recognizes and interprets whether the person’s brain waves contain the P300 component, and then reflects whether the corresponding stimulus image contains the target image. In order to ensure the real-time and stability of the system, this research invention designed the following three schemes: First, design an algorithm suitable for single-trial EEG signal classification-ERP Attention Net, which is used for single-trial EEG signals. Then, design a stimulus slice generation and presentation scheme that is suitable for stable induction of P300 components, which is used for interpreters to detect target images. Finally, a BCI system using multi-process synchronous decoding is designed to meet the requirements of real-time and efficient tasks.
In the research of single-trial EEG classification algorithm, this paper uses the BCIAUT-P300 data set as the training set and test set of the algorithm research. This data set is characterized by its long training period and large number of participants. It is suitable for those classification algorithms which rely on a large amount of training data. The performance of the convolutional neural network model proposed by Ran Manor, the EEGNet model proposed by Vernon J. Lawhern, and the ERP Attention Net model designed in this study on the BCIAUT-P300 data set are compared respectively. From the experimental results, EEGNet has the best classification performance. The average classification accuracy of the single-trial EEG signals can reach 77.94%. In contrast, the convolutional neural network model proposed by Ran Manor performs poorly and the average classification is correct. The rate is only 66.47%. The average classification accuracy rate of the ERP Attention Net model designed by this research is 77.6%, which is very close to EEGNet, but ERP Attention Net performs better on the recall index, reaching 78.5%, which is about 3.1% higher than EEGNet. Through experiments verifies the effectiveness of the ERP Attention Net model designed in this study in the single-trial EEG classification performance. In addition, this study also discussed the performance of each module in the designed ERP Attention Net model through multiple sets of comparative experiments and ablation analysis.
In the design of SAR image real-time detection system, the first consideration is to design the generation and presentation scheme of stimulus slices. This research has invented a stimulus slice generation and presentation scheme suitable for RSVP, which can effectively avoid the problem of continuous occurrence of target stimulus slices in target dense areas. Simulation experiments have also proved the effectiveness of the scheme. Then consider the design of the system structure of the real-time SAR image detection system. Because of the conflict between the long latency of the P300 signal and the presentation time of the stimulation slices, the real-time acquisition and classification of EEG signals, this research designed a human-computer interaction device, EEG signal acquisition device, EEG signal management device, EEG signal classification device and stimulation slice presentation device. Through the EEG management device, the conflict between the P300 latency and the stimulation duration is solved. And through the synchronization of the designed three processes of brain electricity acquisition process, brain electricity classification process and human-computer interaction process, the problem of real-time acquisition and classification of brain electricity signals is solved.
Finally, the single-trial EEG classification algorithm designed in this research is loaded into the real-time SAR image target detection system based on brain-computer interface, and a healthy subject is recruited to use the system and conduct experiments. The various functions designed by the system have fulfilled the expected requirements, and can mark targets in the large-format SAR image. There are few user feedbacks and no abnormalities occurred in the operation. In summary, the research and design of this article include a single-trial EEG classification algorithm, a stimulus slice generation and presentation scheme suitable for fast visual presentation, and a SAR image target real-time detection system based on a brain-computer interface. The whole system may provide a new solution to the problem of SAR image target detection.
Keywords: SAR image target detection, P300 signal, single-trial EEG classification, brain-computer interface technology
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT III
插图索引 VII
表格索引 IX
符号对照表 XI
缩略语对照表 XIII
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景及研究意义 1
1.2 SAR图像目标检测 2
1.3 脑机接口系统 3
1.4 P300脑电成分 5
1.5 本文的研究内容和组织结构 7
第二章 基于深度学习的RSVP脑电分类研究 9
2.1 引言 9
2.2 BCIAUT-P300数据集 9
2.2.1 视觉呈现实验 10
2.2.2 脑电信号采集及处理 11
2.2.3 分析与结论 13
2.3 Convolutional Neural Network 13
2.3.1 网络结构 13
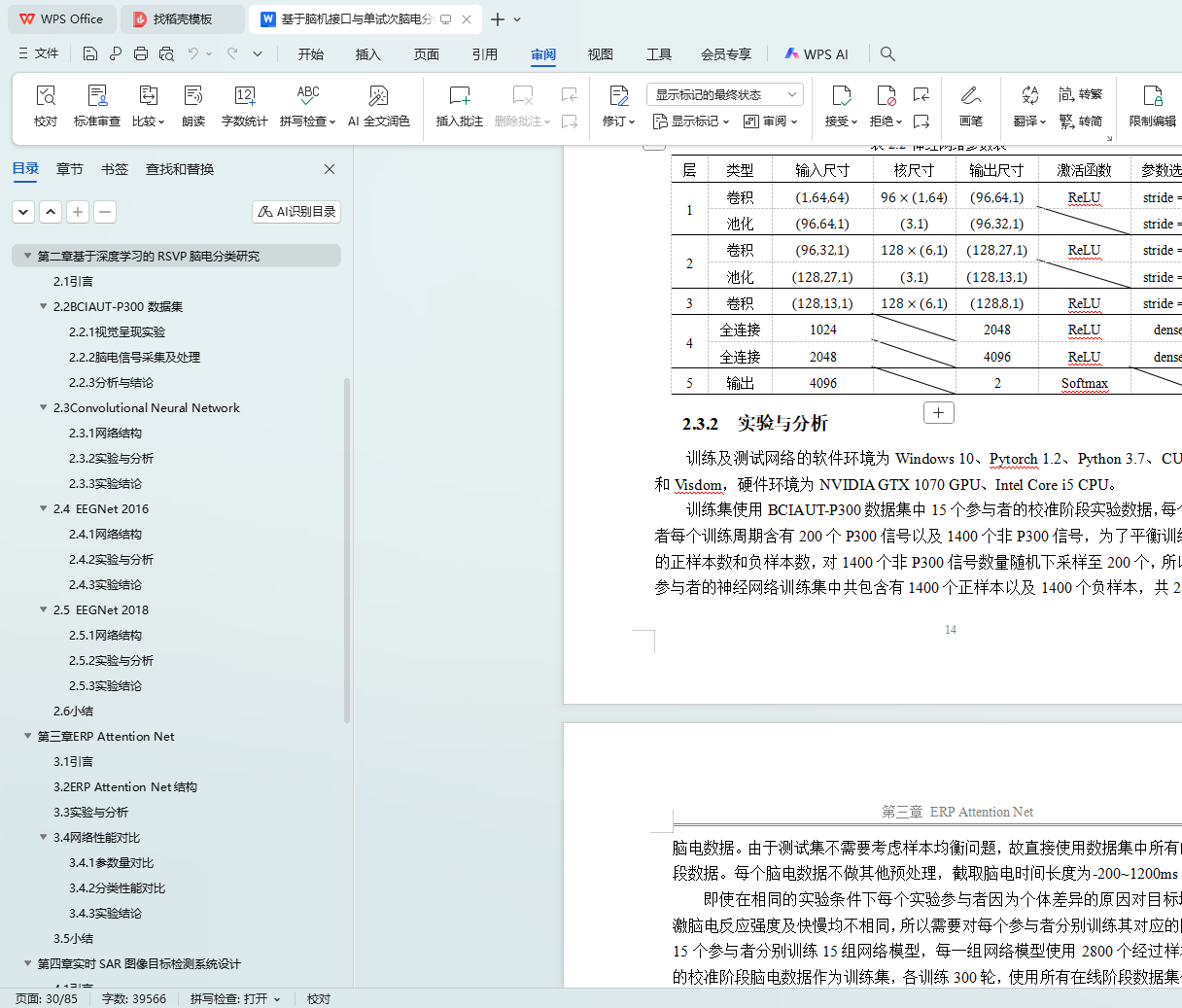
2.3.2 实验与分析 14
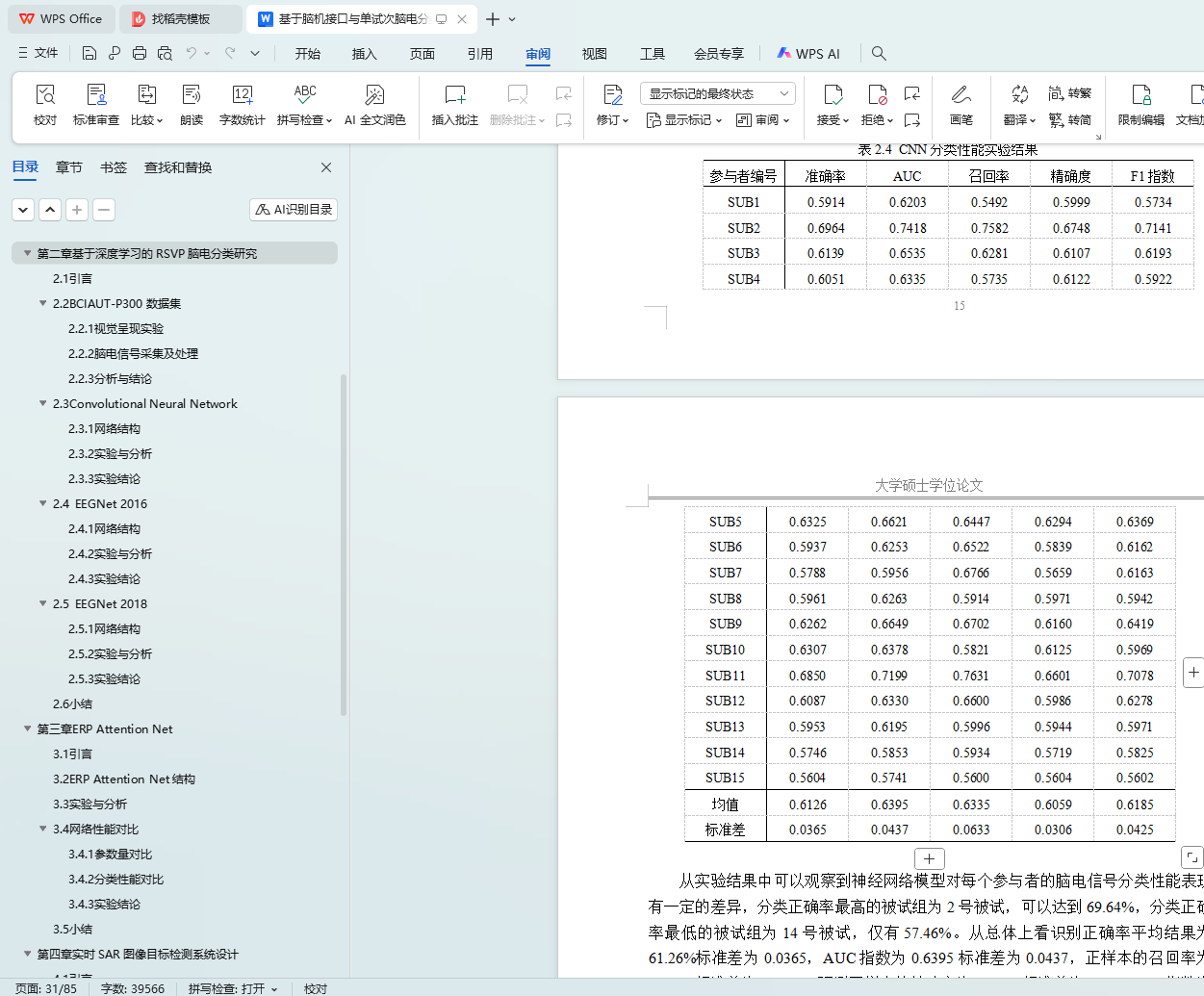
2.3.3 实验结论 16
2.4 EEGNet 2016 16
2.4.1 网络结构 17
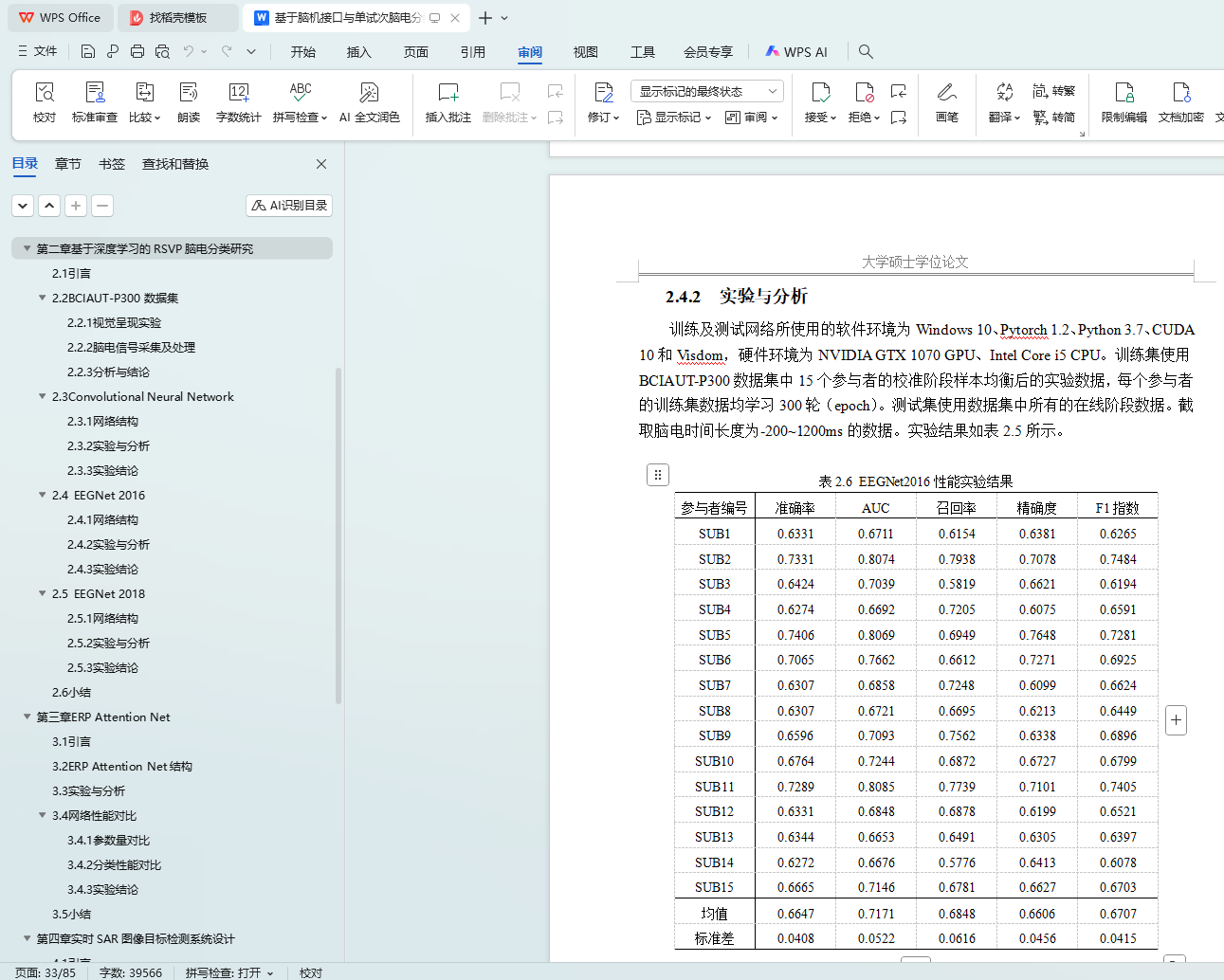
2.4.2 实验与分析 18
2.4.3 实验结论 19
2.5 EEGNet 2018 19
2.5.1 网络结构 19
2.5.2 实验与分析 20
2.5.3 实验结论 21
2.6 小结 21
第三章 ERP Attention Net 23
3.1 引言 23
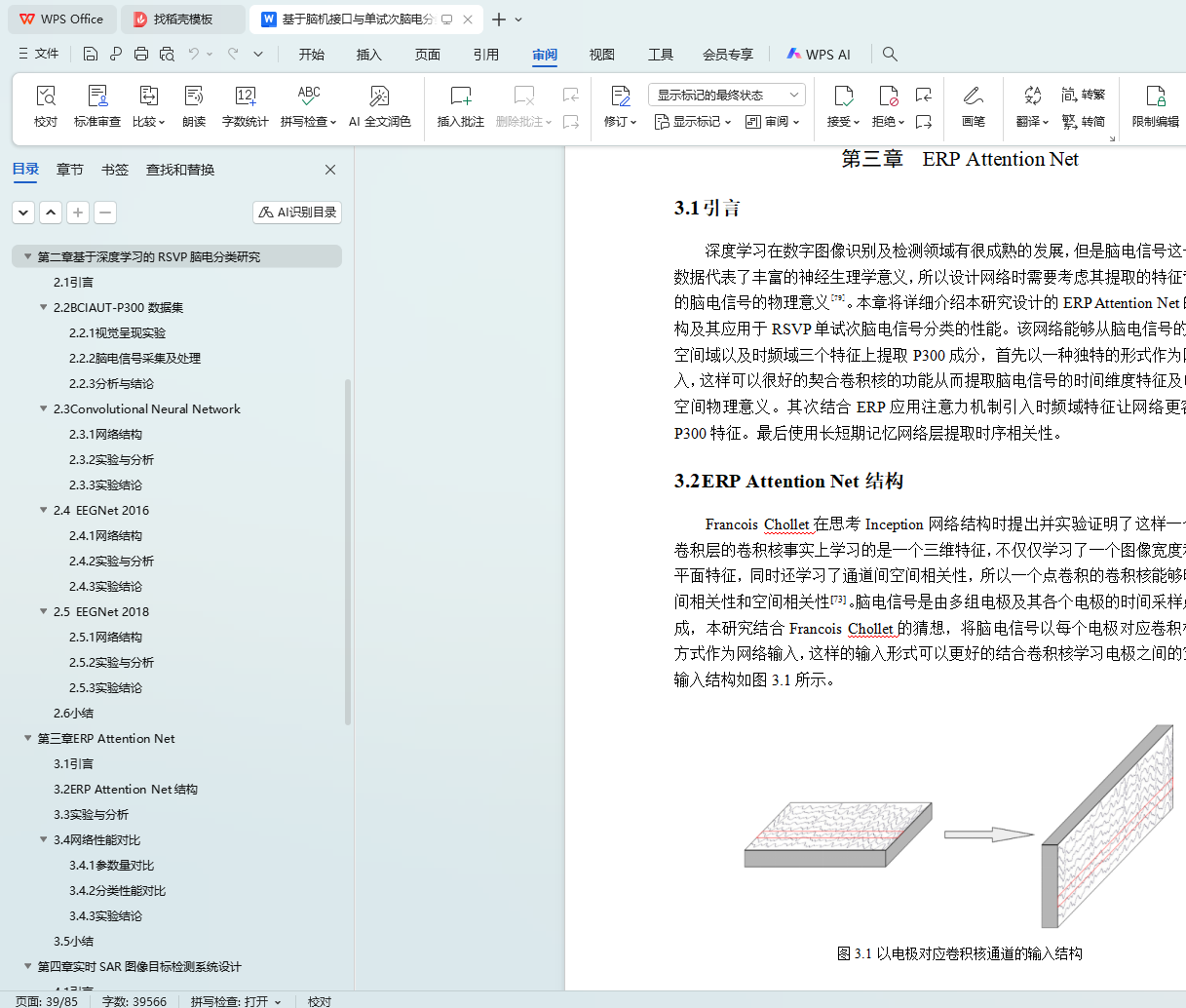
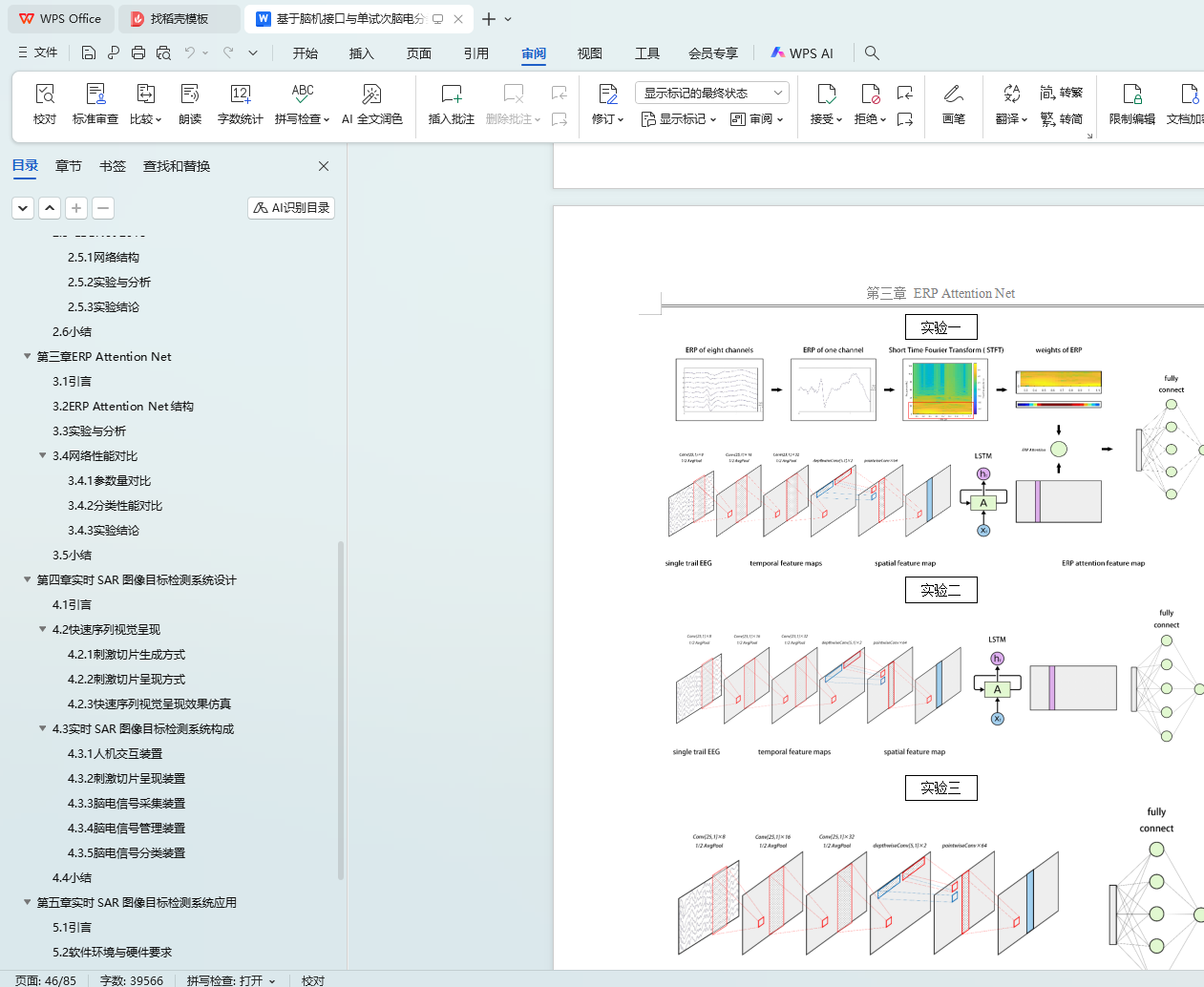
3.2 ERP Attention Net结构 23
3.3 实验与分析 28
3.4 网络性能对比 32
3.4.1 参数量对比 32
3.4.2 分类性能对比 33
3.4.3 实验结论 33
3.5 小结 34
第四章 实时SAR图像目标检测系统设计 35
4.1 引言 35
4.2 快速序列视觉呈现 35
4.2.1 刺激切片生成方式 35
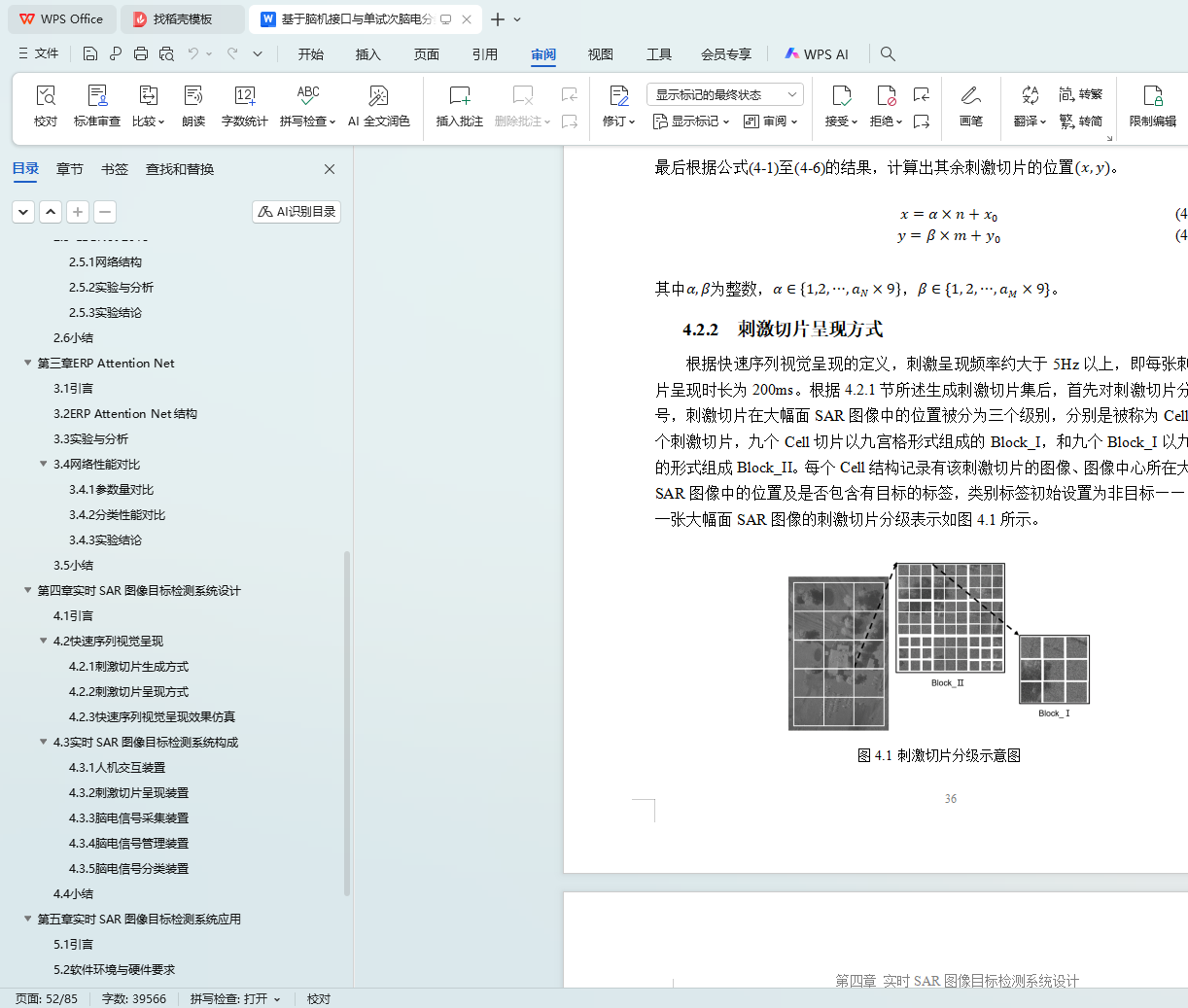
4.2.2 刺激切片呈现方式 36
4.2.3 快速序列视觉呈现效果仿真 38
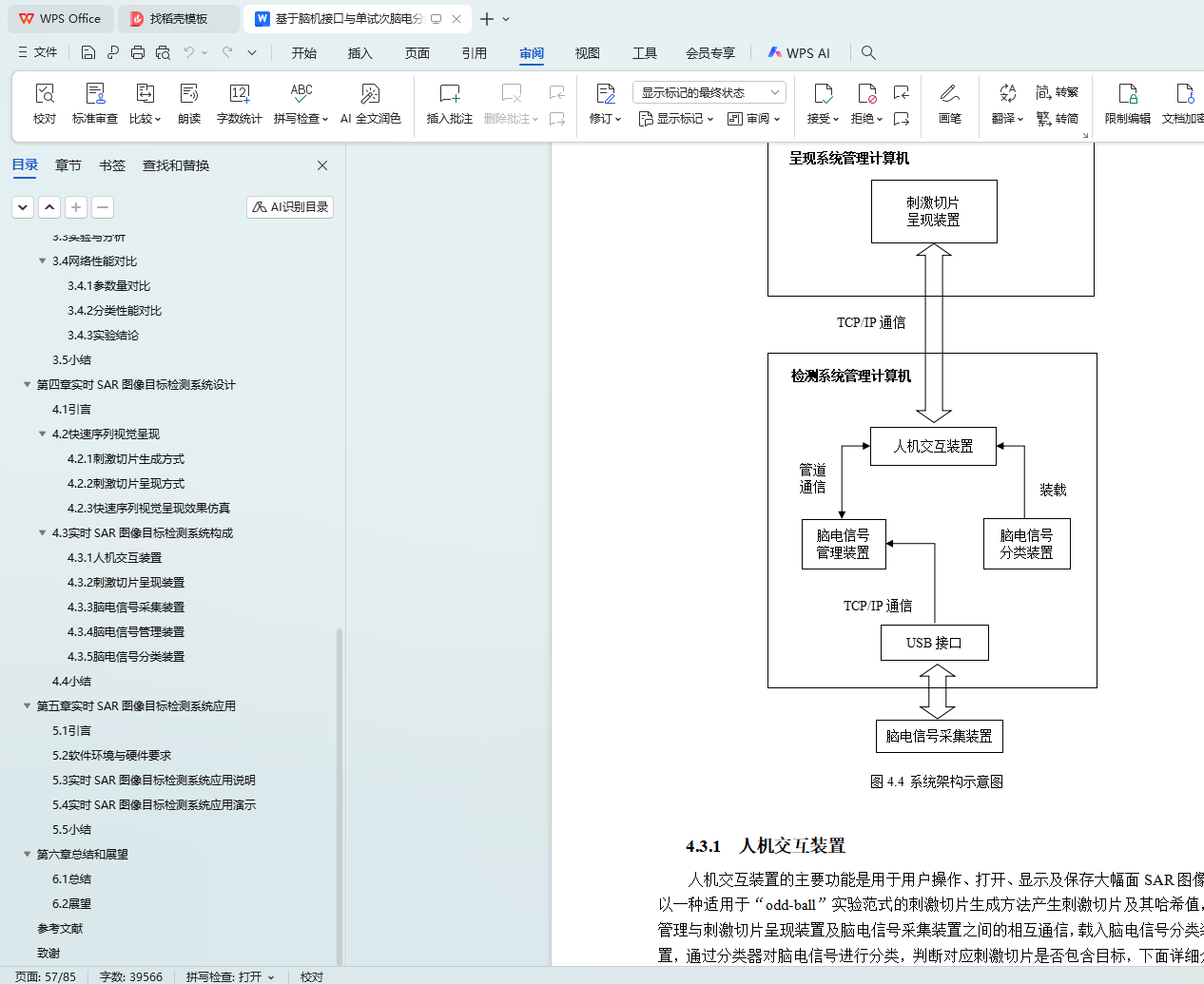
4.3 实时SAR图像目标检测系统构成 40
4.3.1 人机交互装置 41
4.3.2 刺激切片呈现装置 43
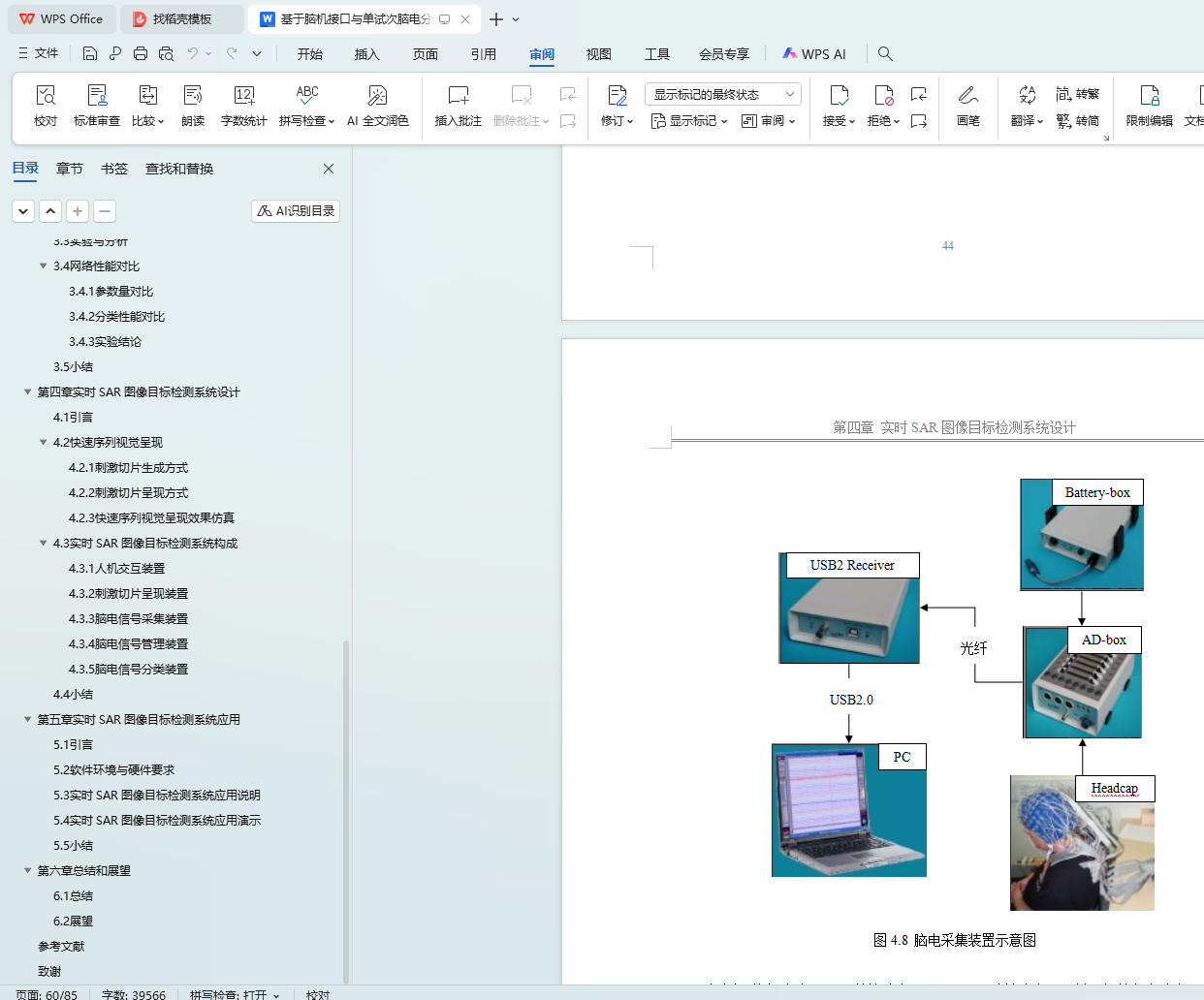
4.3.3 脑电信号采集装置 44
4.3.4 脑电信号管理装置 45
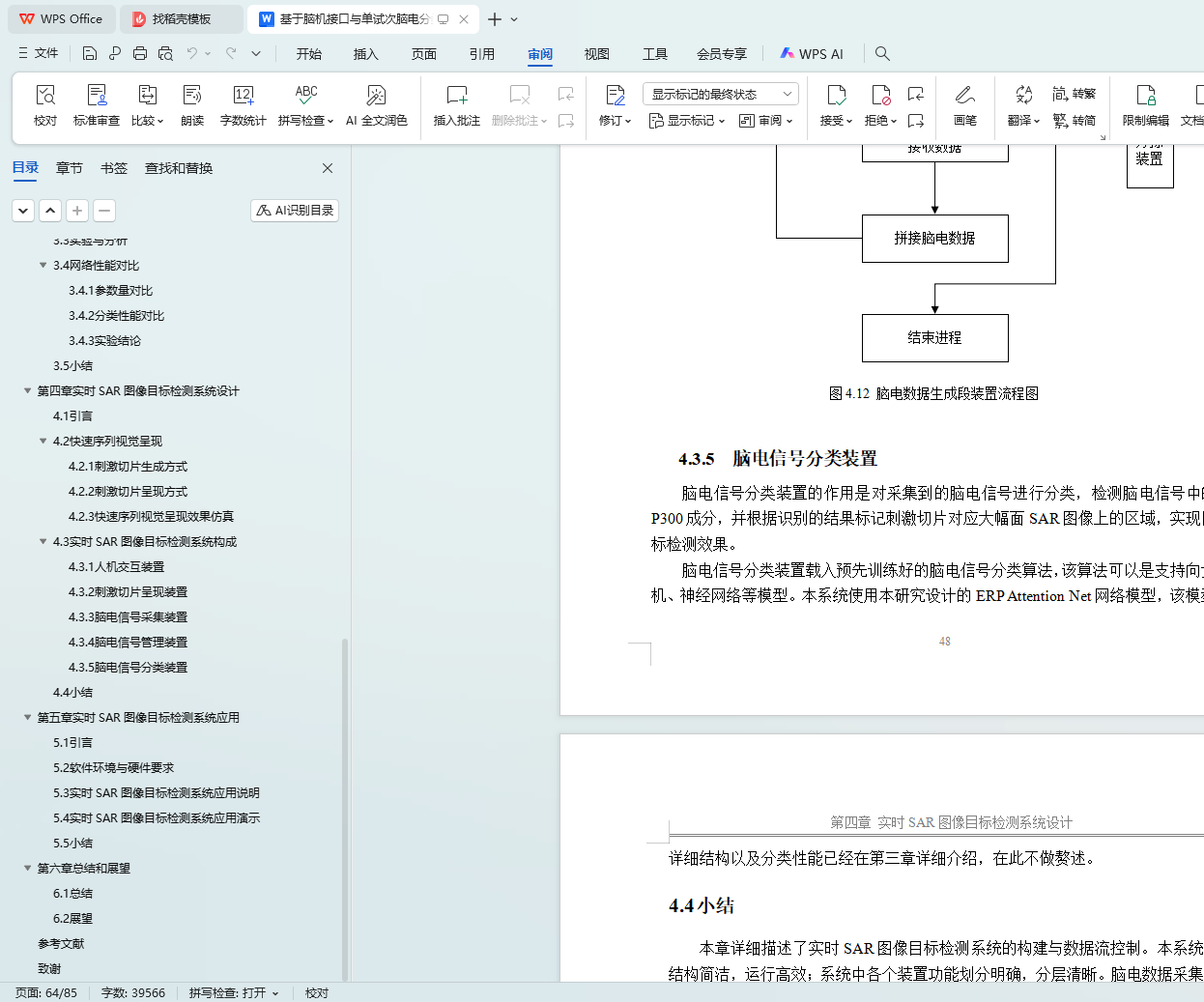
4.3.5 脑电信号分类装置 48
4.4 小结 49
第五章 实时SAR图像目标检测系统应用 51
5.1 引言 51
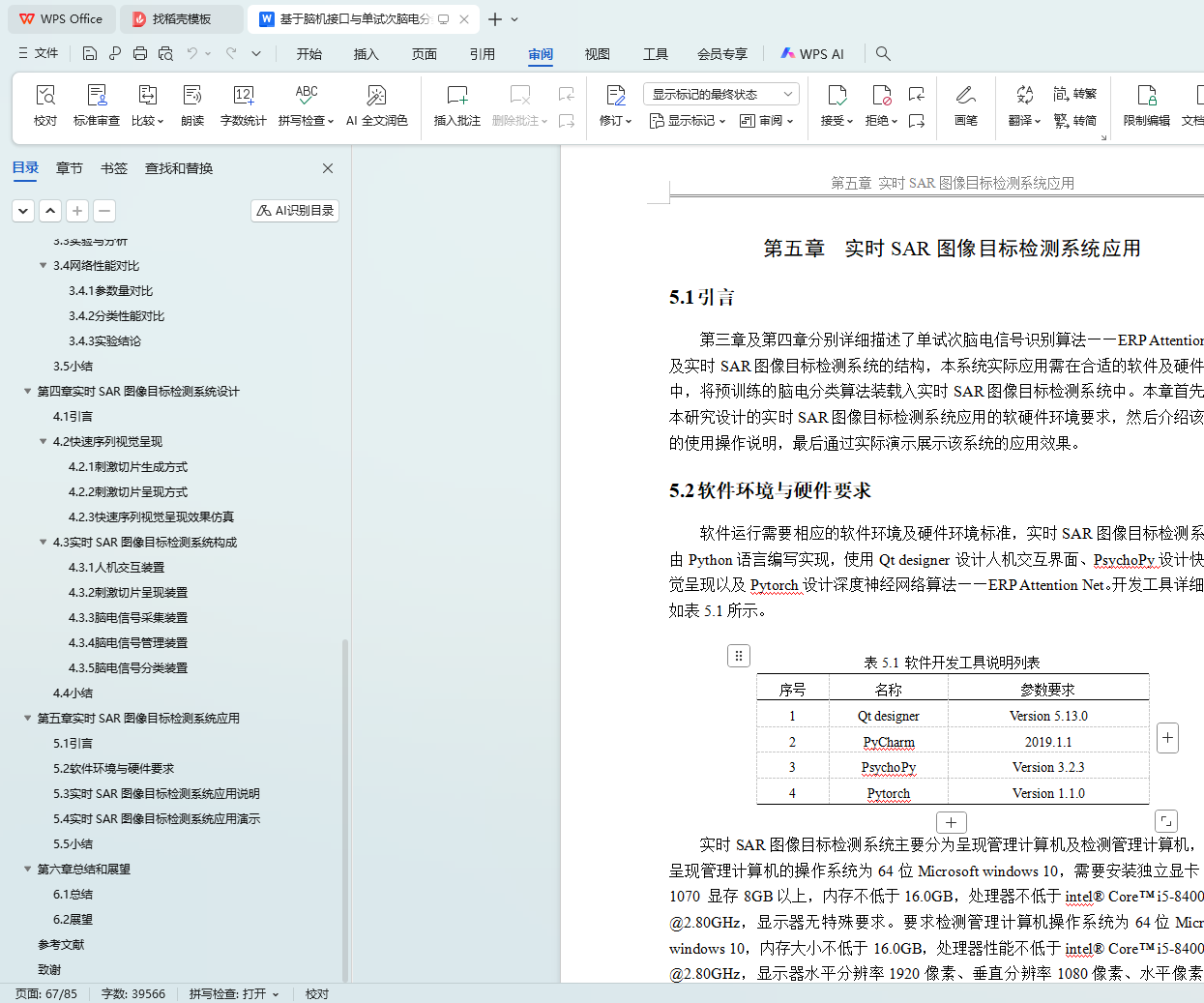
5.2 软件环境与硬件要求 51
5.3 实时SAR图像目标检测系统应用说明 52
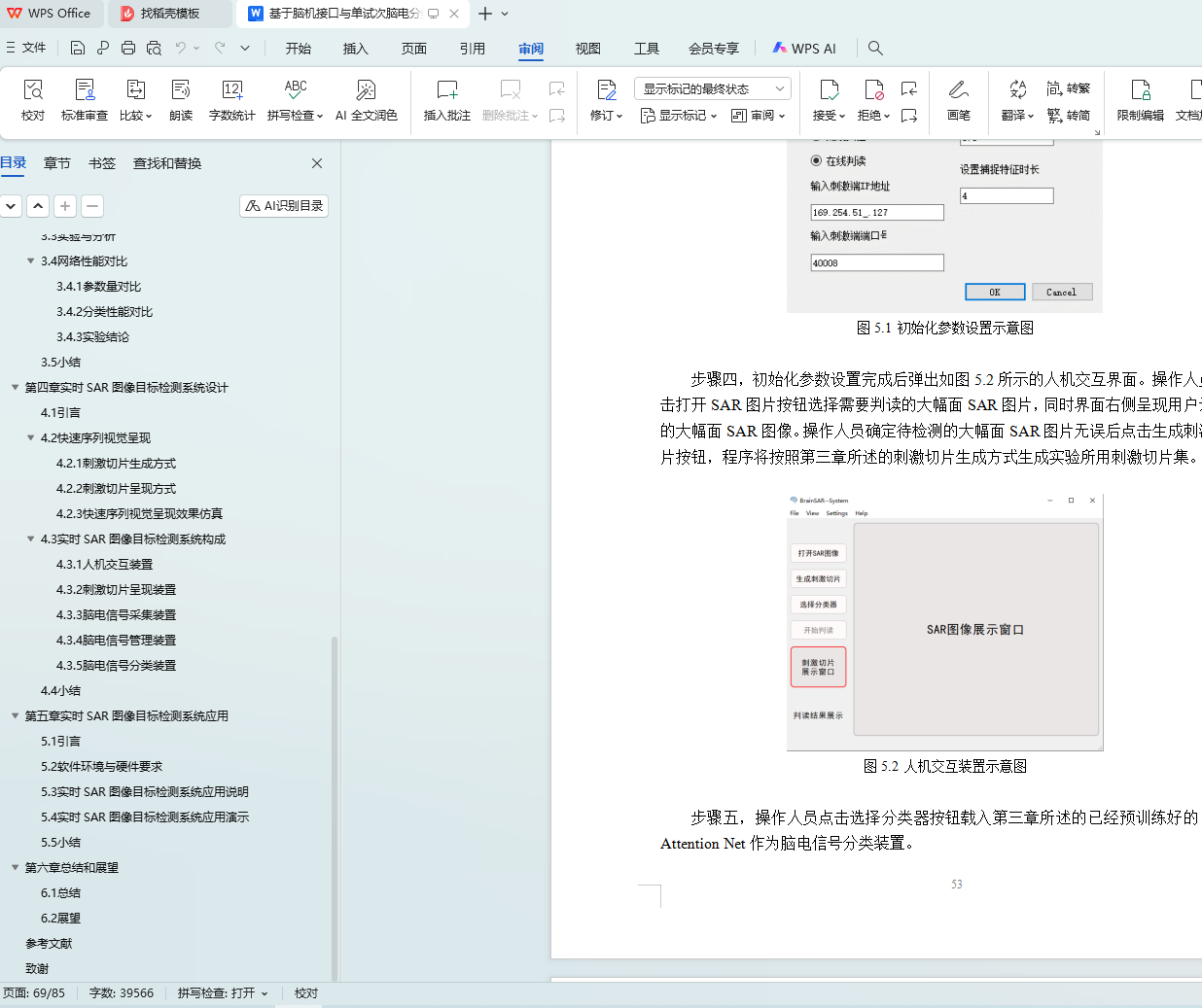
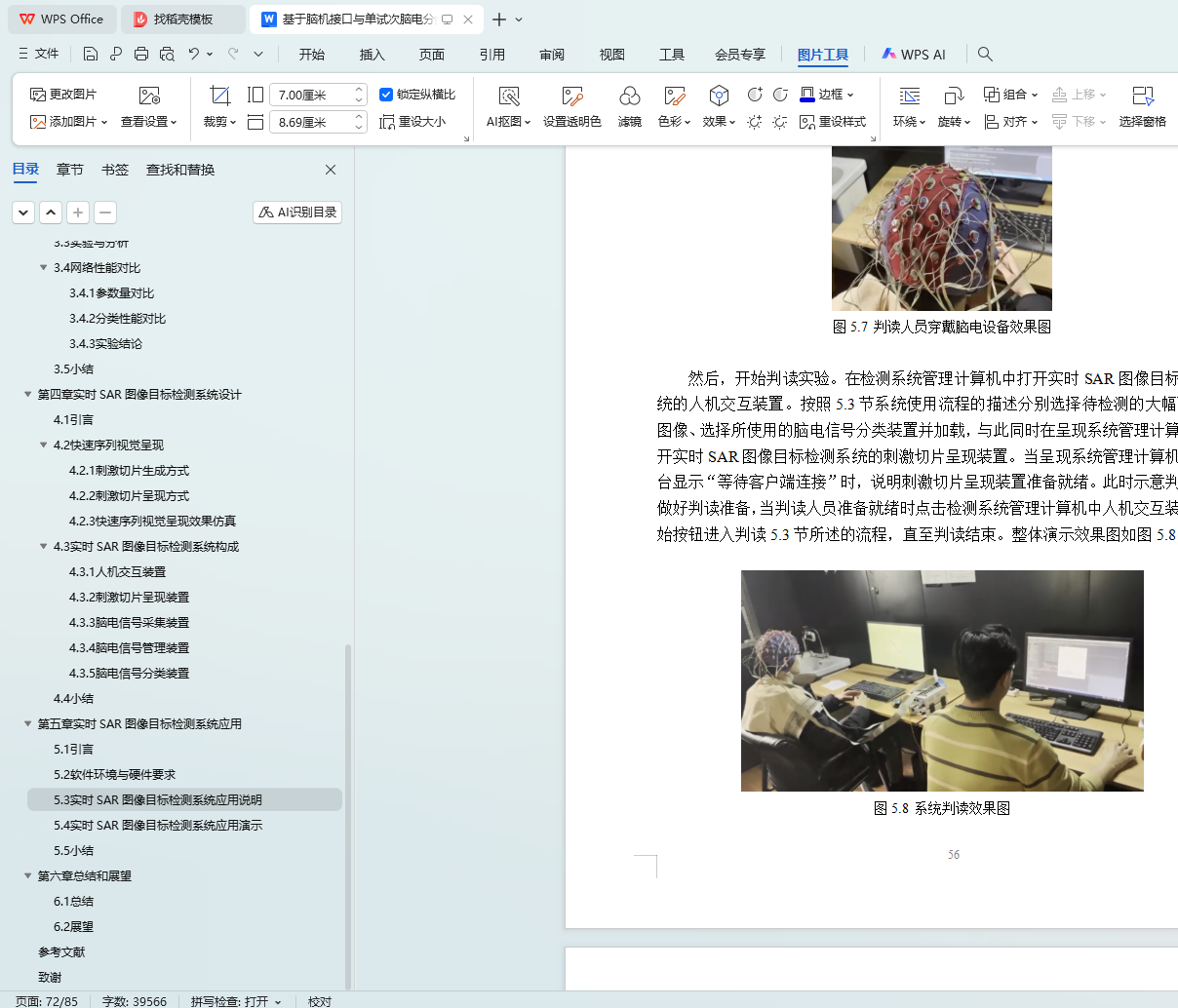
5.4 实时SAR图像目标检测系统应用演示 55
5.5 小结 58
第六章 总结和展望 59
6.1 总结 59
6.2 展望 60
参考文献 63
致谢 69