摘要
性活动在生物体中尤其重要,对物种的生存和繁衍具有重要意义。同时,性活动具有动物属性和社会属性,其背后的神经机制十分复杂,涉及认知、情绪、动机、抑制控制等多个成分,同时,受到自主神经系统的调节和控制。
男性性功能障碍是一种常见的男性功能性疾病。在我国,勃起功能障碍(erectile dysfunction, ED)是一种流行性较高的男性性功能障碍,其主要的行为表现为男性在性交过程中无法获得或维持足够的勃起。ED对患者的身心健康和正常生活有着严重的危害,对患者的家庭关系和工作状态等有着严重的负面影响。临床上,根据是否存在器质性病变将ED分为器质性勃起功能障碍和心因性勃起功能障碍(psychogenic erectile dysfunction, pED)。流行病学统计表明,超过90%的青年患者的ED是由心理因素导致,同时,pED患者在中年ED人群中的占比也超过了50%。目前,pED的研究仍处于探索阶段,它的致病机理仍未被阐明且仅被笼统地认为和中枢性因素有关。在临床治疗方面,pED属于难治型ED,药物治疗的方式并未显现出良好效果。
前人针对pED中枢机制的神经影像学研究采取了视觉任务刺激的方式,通过对比正常人和病患在视觉性刺激下大脑响应模式的差异来揭示可能的致病机理。然而,通过较为全面的pED文献综述,本研究组并未发现关于pED患者存在对性刺激的低级加工缺陷的报导。基于上述事实,本文认为,pED患者对性信息的高级认知加工可能出现了问题。鉴于大脑对性信息的高级认知加工并不局限于任何一种特定的感觉信息输入模式,本文借助静息态功能磁共振成像(functional magnetic resonance imaging, fMRI),通过对比pED患者和健康被试(normal control, NC)静息态大脑活动的差异,从多个角度对pED的神经机制进行了研究。
经过一系列严格的被试筛选,本文入组了27名pED患者和27名健康对照被试。首先,前人的研究表明,基线活动在fMRI研究中十分重要,大脑基线活动的变更可能会改变大脑在任务态下的空间激活并使最终的研究结果发生改变。因此,本文将大脑基线活动模式的研究作为pED系列研究的切入点。本文首先使用低频振荡幅度(amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, ALFF)对病患和健康人大脑基线活动的差异进行了检测,发现pED患者右侧前脑岛(anterior insula, aINS)的基线活动出现显著减弱。其次,由于性响应是通过多个大脑区域之间的交互而非单个脑区的作用进行调节的,因此,在进一步的研究中,本文将基线活动发生显著改变的脑区作为种子区域,使用功能连接(functional connectivity, FC)方法,对pED患者以脑岛为中心的大脑功能连接模式进行了研究,在pED患者的另一部分右侧aINS,右侧背外侧前额叶皮层(dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, dlPFC)和右侧颞顶联合区(temporoparietal junction, TPJ)发现了显著变更的以脑岛为中心的功能连接模式。随后,从上一研究中pED患者右侧aINS内部的功能连接模式的变更出发,本文推测,pED可能伴随着部分脑区功能同质性的改变。因此,本文通过局部同质性(Regional Homogeneity, ReHo)方法,在全脑范围内对pED组和NC组被试的脑区功能局部同质性进行了差异检测,在右侧aINS和右侧岛盖观察到显著的组间差异。最后,由于本文的前三项研究的发现均出现在大脑的右侧半球,但前人的研究中并未呈现与pED有关的大脑偏侧性趋势,因此,本文使用体素镜像同伦性(Voxel-Mirrored Homotopic Connectivity, VMHC)方法,对pED患者两侧大脑半球同源脑区间的交互模式进行了研究,在尾状核发现了与勃起功能显著相关的功能同伦性变更。
本文的研究结果表明,pED患者的大脑基线活动、以脑岛为中心的功能连接模式、功能局部同质性和大脑左右半球间的交互模式均存在异常。上述的发现可能主要与pED患者对自身状态和需求的异常表征以及对性响应的异常抑制控制有关。本文的研究发现为pED的相关神经机制的揭示带来了新的证据。
关 键 词:心因性勃起功能障碍, 静息态, 功能磁共振成像, 前脑岛
ABSTRACT
Sexual activity is of great significance to the survival and reproduction of both human being and other species. Meanwhile, sexual activity has animal and social attributes, whose underpinning neural mechanisms are extremely complex, involving components of cognition, emotion, motivation, inhibition and mediated by the autonomic nervous system.
The male sexual dysfunction is a common male functional disorder. Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a highly prevalent male sexual dysfunction in China. It is characterized in the disability to gain or maintain adequate penile erection during sexual intercourses. ED does serious harm to suffers' physical and mental health. It also has serious negative impact on their family relationships and social life. Clinically, ED can be divided into organic erectile dysfunction and psychogenic erectile dysfunction (pED) according to the existence of organic lesions. Epidemiological survey showed that pED patients consist of 90% of ED population in youth, and compose of more than half of the population in middle-aged ED group. Nowadays, the studies on pED are still in its infancy and its pathogenesis has not been explicitly elucidated. Accordingly, no satisfactory treatment has been identified for pED and drug therapy did not show good effects in its clinical efficacy.
Previous studies exploring the neural mechanism of pED focused on brain activity under visual tasks. By comparing the differences in brain response patterns between normal controls (NC) and pED patients under visual sexual stimulation, these studies initiated to investigate the possible neural mechanism in pED. However, our group hold a different view. After a thorough literature review on pED, no empirical data and previous studies on pED report impairment in the low order processing of sexual stimulus. Therefore, we suggest that pED patients may have defects in the high-level cognitive processing of sexual information. However, the high-level cognitive processing of sexual information is not limited to any specific sensory input modality, in this paper, we adopted the resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which is free of sensory input and investigated the neural mechanism of pED from multiple perspectives based on the resting-state brain activity in pED patients and matched NC.
In our study, after rigorous participant inclusion procedure, 27 pED patients and 27 NC were enrolled in this study. Previous studies show that the baseline issue is rudimentary in fMRI studies, particularly for studies adopting tasks, in that the changes in baseline brain activity may smear the spatial activation under task and bring biased results. Therefore, in this study, we started from the investigation of the baseline brain activity. Firstly, amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) was used to investigate the baseline brain activity in pED patients, and significantly reduced baseline activity was observed in the right anterior insula (aINS). Secondly, in view that sexual response is mediated by spread brain regions rather than a single region, the region whose baseline changed, i.e. the right aINS, was used as the seed for further examination of the alterations in functional connectivity (FC), results elucidated the disrupted homogeneity within the right aINS and aberrant connection patterns between the right aINS and the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC), as well as the right aINS and the right temporoparietal junction (TPJ) respectively in pED group, as compared with the NC group. Subsequently, in accordance with the changed functional connectivity pattern within the right aINS in pED group, we speculated that pED may be accompanied by changes in functional homogeneity in some brain regions. Therefore, we used the regional homogeneity (ReHo) method and investigated the difference of functional regional homogeneity between pED and NC groups through the whole brain. Significant group-wise difference was observed in right aINS and right operculum. Finally, for all the aforementioned finding were happen to located in the right hemisphere of brain but previous studies show that laterality was not an issue in pED, we adopted the voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity (VMHC) method and investigated the interaction pattern of homologous brain regions between hemispheres and significant erectile function related VMHC alteration was observed in caudate.
In conclusion, our results demonstrated the aberrant baseline brain activity, disrupted insula-centered functional connectivity, changed functional homogeneity and interaction pattern of homologous brain regions between bilateral cerebral hemispheres in pED patients. We suggest that pED is likely to be related to the abnormal representation of internal bodily state or needs in the sexual context, which may lead to excessive inhibitory control of sexual responses. Last but not least, we propose that findings in this study may shed new light on the central mechanism of pED.
Keywords: psychogenic erectile dysfunction, resting state, functional magnetic resonance imaging, anterior insula
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT III
插图索引 V
表格索引 VII
符号对照表 IX
缩略语对照表 XI
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题研究背景和研究意义 1
1.2 性响应模型 1
1.2.1 人类性响应环路模型 2
1.2.2 包含五个成分的性唤起模型 3
1.2.3 性刺激加工模型 4
1.3 心因性勃起功能障碍的影像学研究现状 5
1.4 本文的研究内容及组织结构 6
第二章 静息态功能磁共振成像及数据分析 9
2.1 功能磁共振成像 9
2.1.1 功能磁共振成像简介 9
2.1.2 基于血氧合水平依赖的功能磁共振成像 9
2.2 静息态功能磁共振成像 10
2.2.1 静息态功能磁共振成像简介 10
2.2.2 静息态功能磁共振成像的发展和应用 11
2.3 功能磁共振成像数据分析方法 11
2.3.1 功能磁共振成像数据预处理 11
2.3.2 功能磁共振成像数据分析方法及应用 12
2.4 小结 13
第三章 心因性勃起功能障碍患者静息态脑功能的基线活动研究 15
3.1 引言 15
3.2 材料与方法 15
3.2.1 伦理学声明 15
3.2.2 被试信息 15
3.2.3 数据获取 16
3.2.4 数据预处理 16
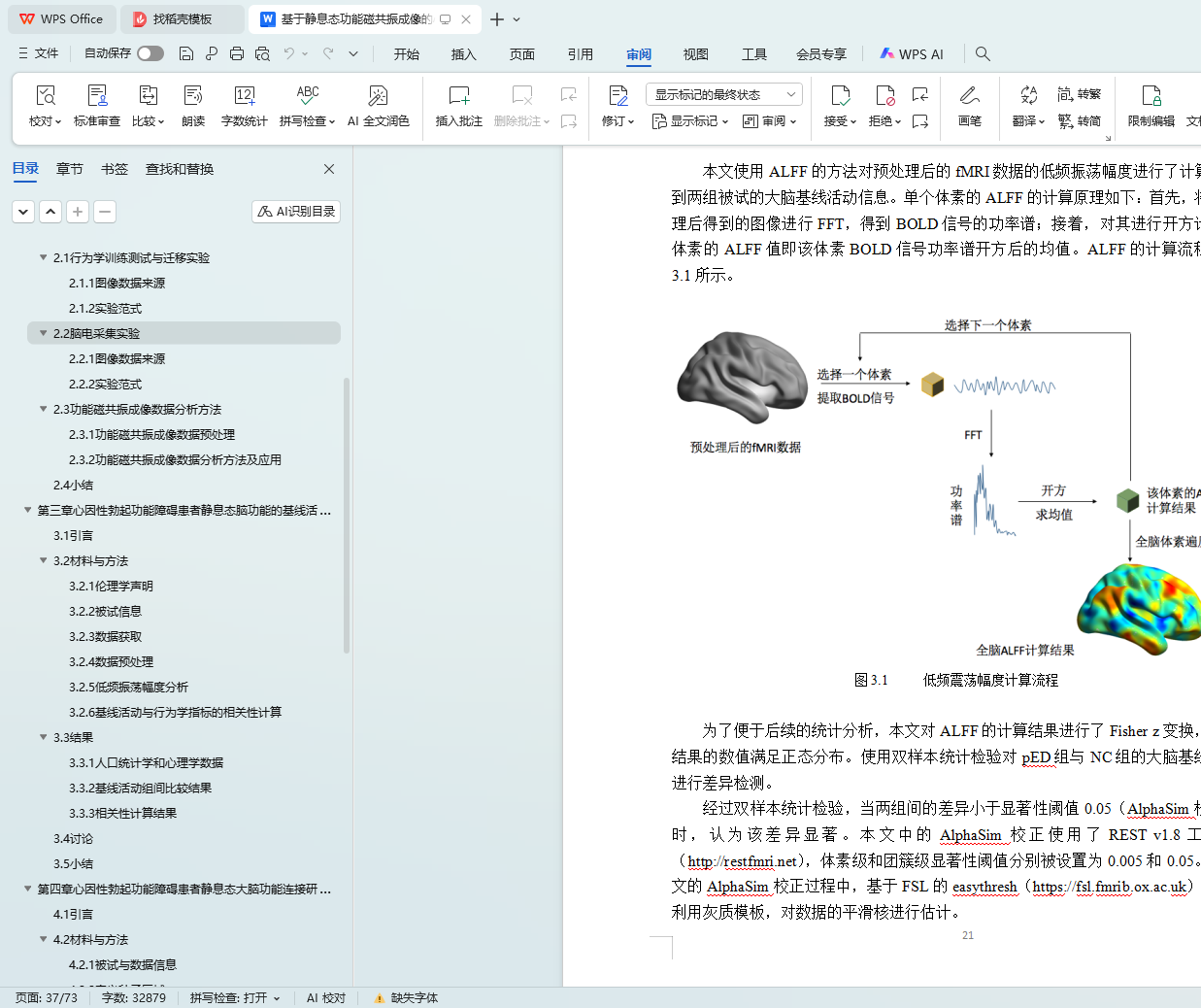
3.2.5 低频振荡幅度分析 17
3.2.6 基线活动与行为学指标的相关性计算 18
3.3 结果 18
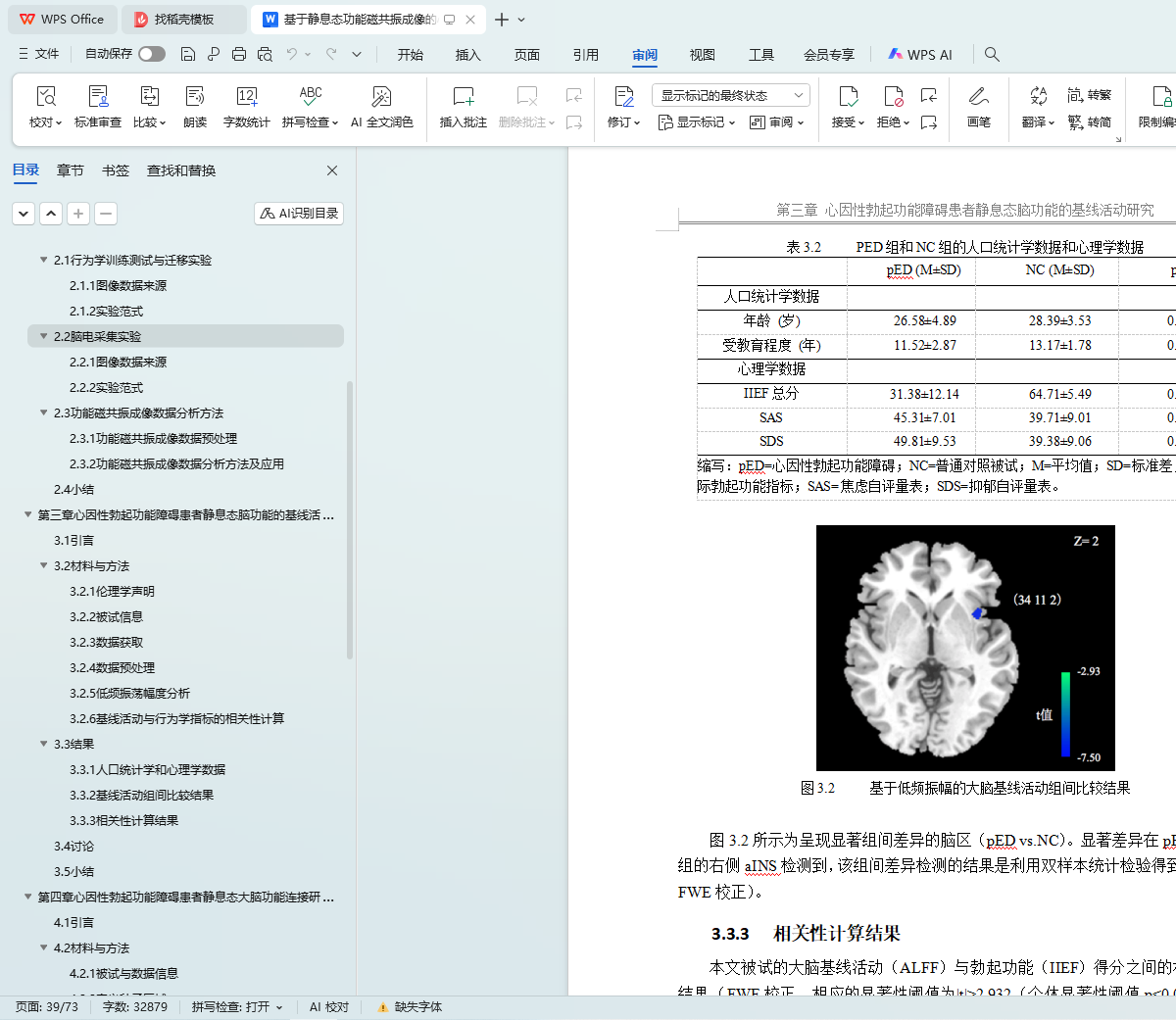
3.3.1 人口统计学和心理学数据 18
3.3.2 基线活动组间比较结果 18
3.3.3 相关性计算结果 19
3.4 讨论 20
3.5 小结 21
第四章 心因性勃起功能障碍患者静息态大脑功能连接研究 23
4.1 引言 23
4.2 材料与方法 23
4.2.1 被试与数据信息 23
4.2.2 定义种子区域 24
4.2.3 以脑岛为中心的功能连接度分析 24
4.2.4 功能连接度与行为学指标的相关性计算 25
4.3 结果 25
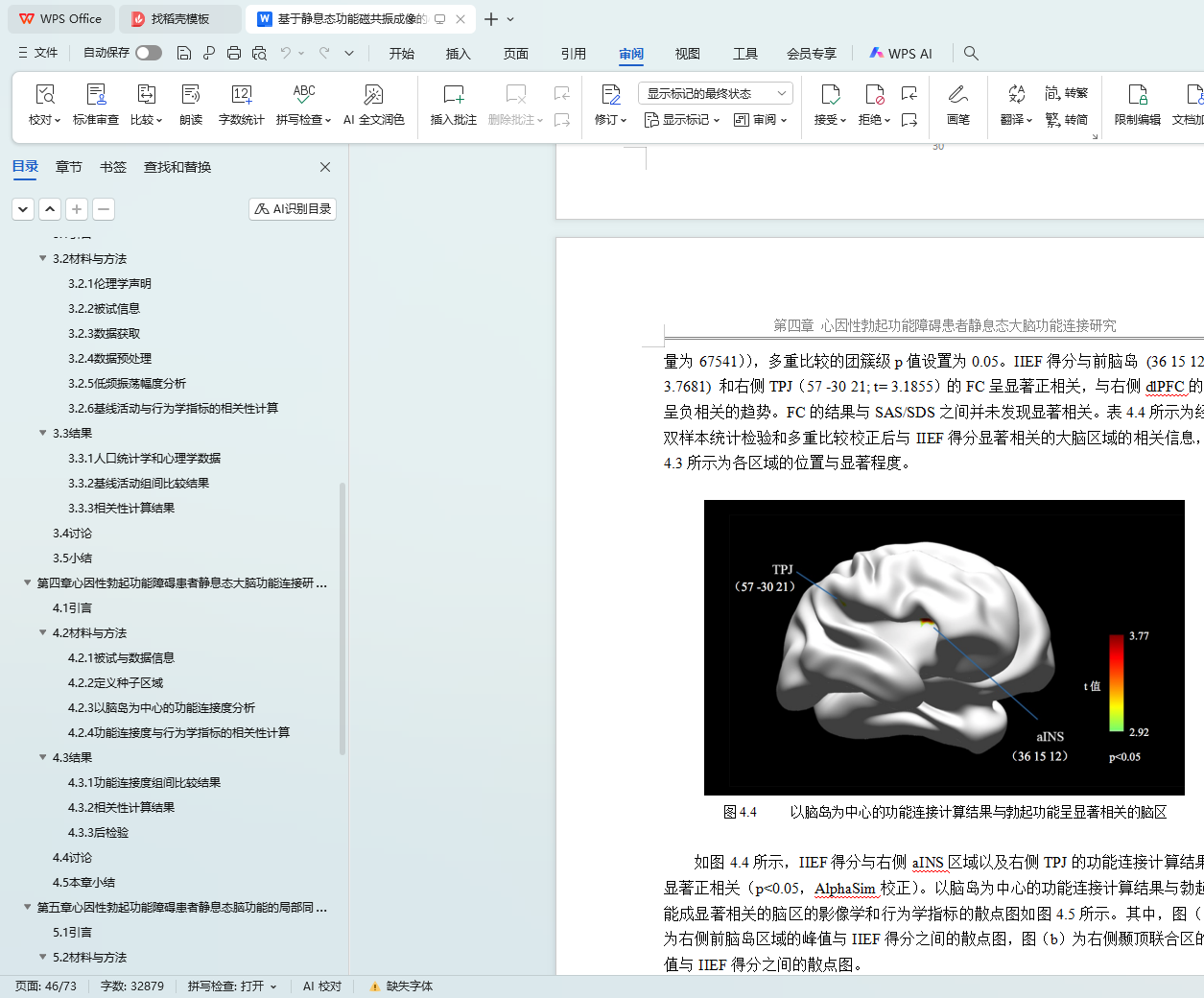
4.3.1 功能连接度组间比较结果 25
4.3.2 相关性计算结果 26
4.3.3 后检验 28
4.4 讨论 29
4.5 本章小结 30
第五章 心因性勃起功能障碍患者静息态脑功能的局部同质性研究 31
5.1 引言 31
5.2 材料与方法 31
5.2.1 被试与数据信息 31
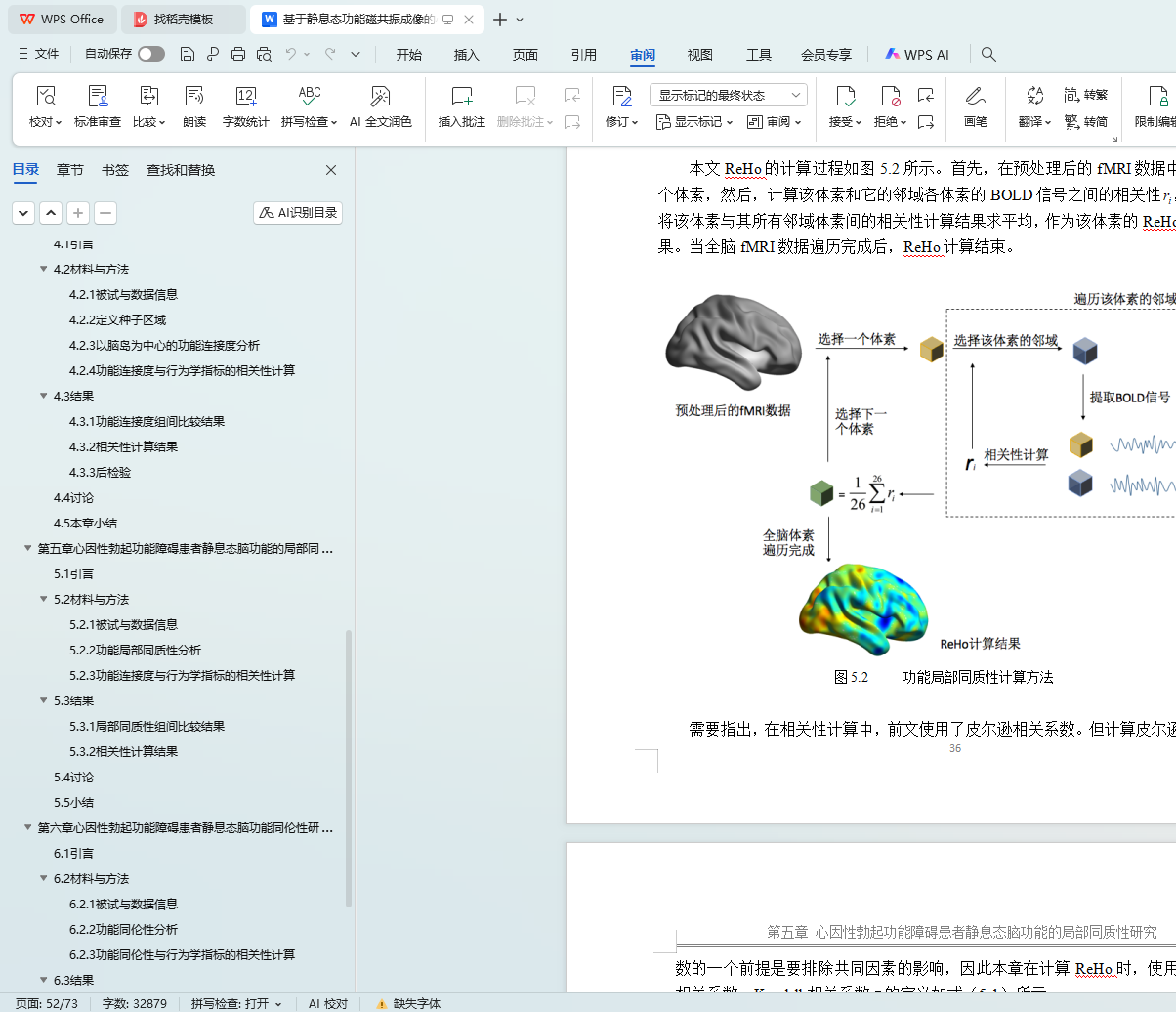
5.2.2 功能局部同质性分析 31
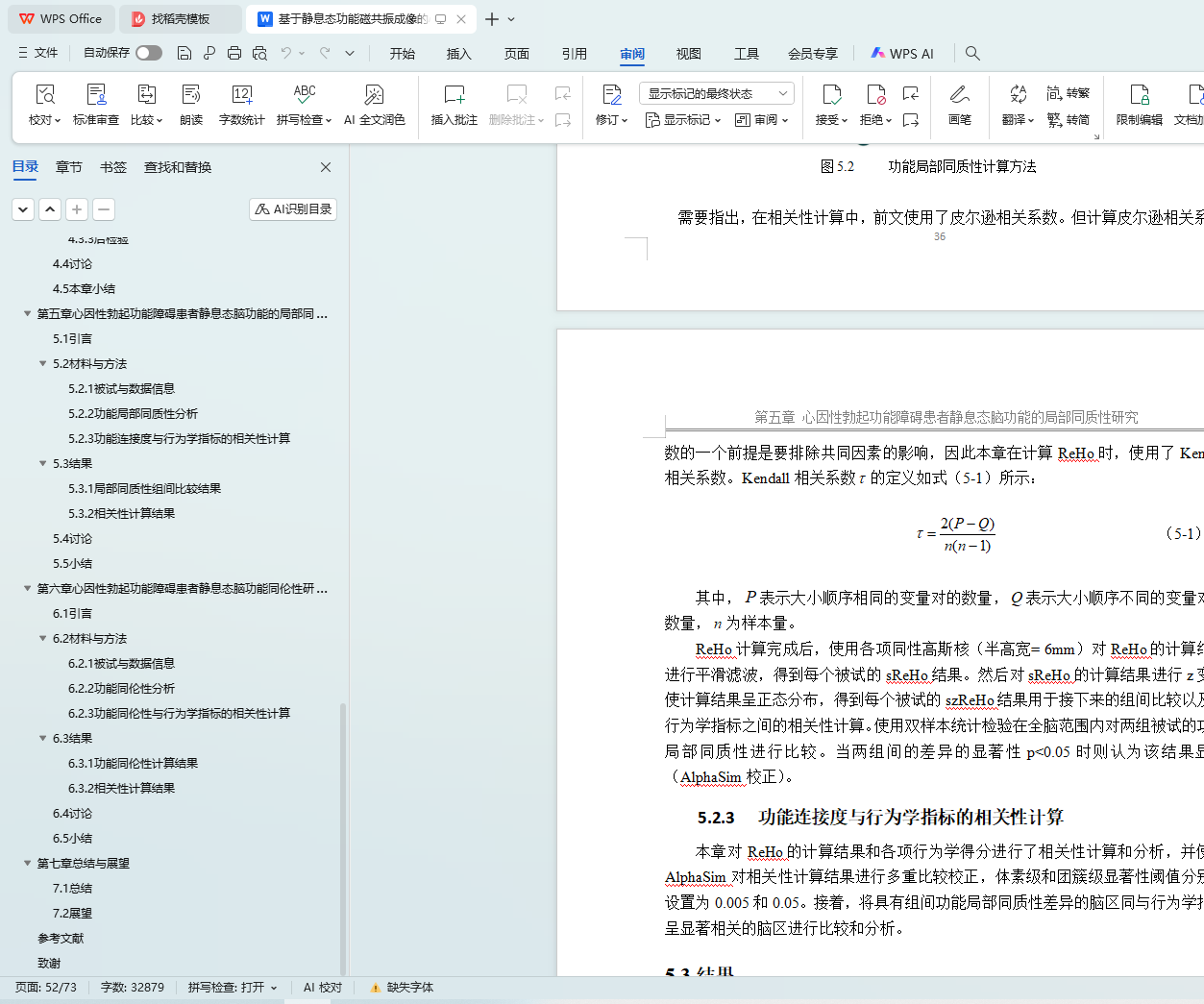
5.2.3 功能连接度与行为学指标的相关性计算 33
5.3 结果 33
5.3.1 局部同质性组间比较结果 33
5.3.2 相关性计算结果 34
5.4 讨论 35
5.5 小结 35
第六章 心因性勃起功能障碍患者静息态脑功能同伦性研究 37
6.1 引言 37
6.2 材料与方法 37
6.2.1 被试与数据信息 37
6.2.2 功能同伦性分析 37
6.2.3 功能同伦性与行为学指标的相关性计算 39
6.3 结果 39
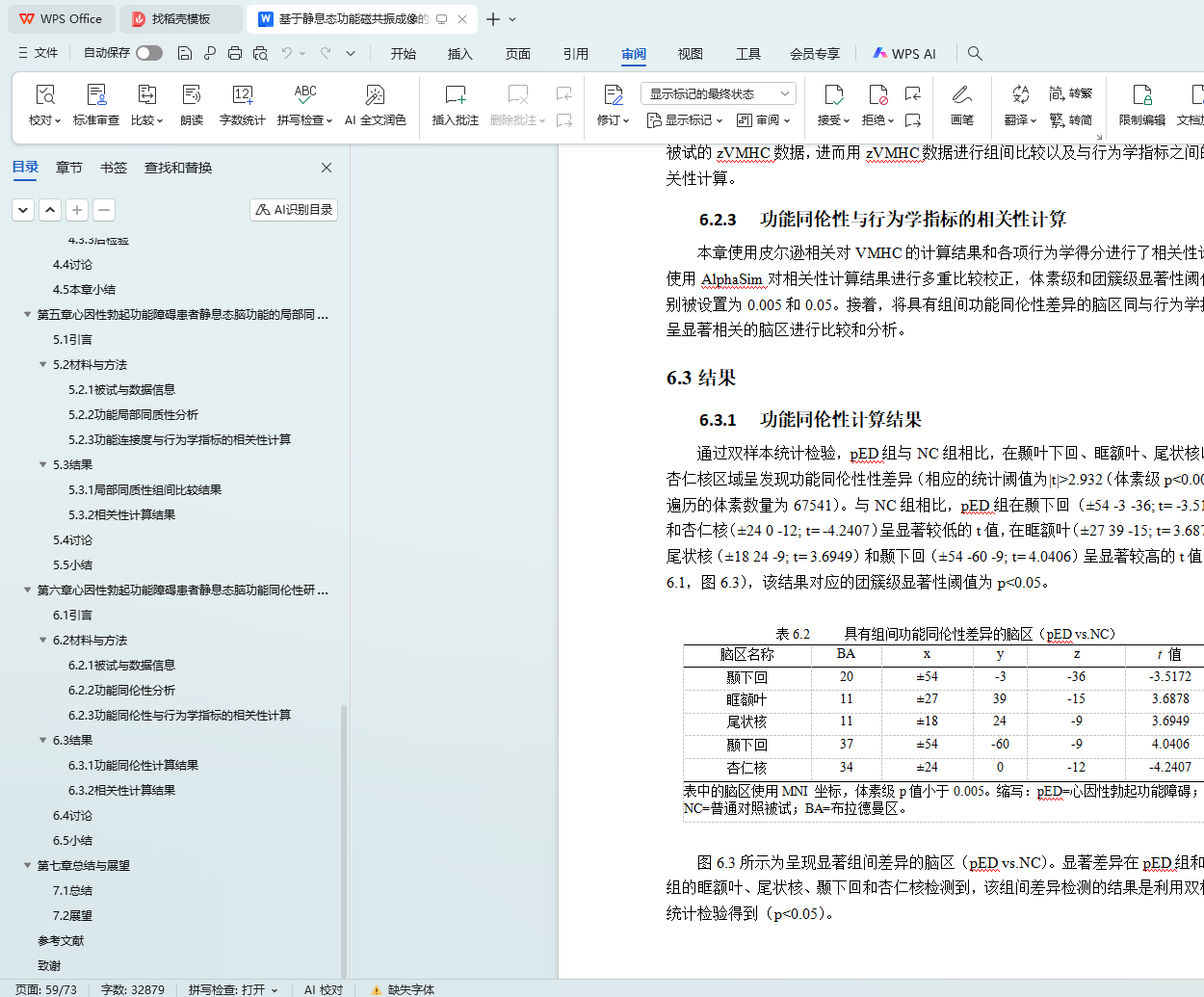
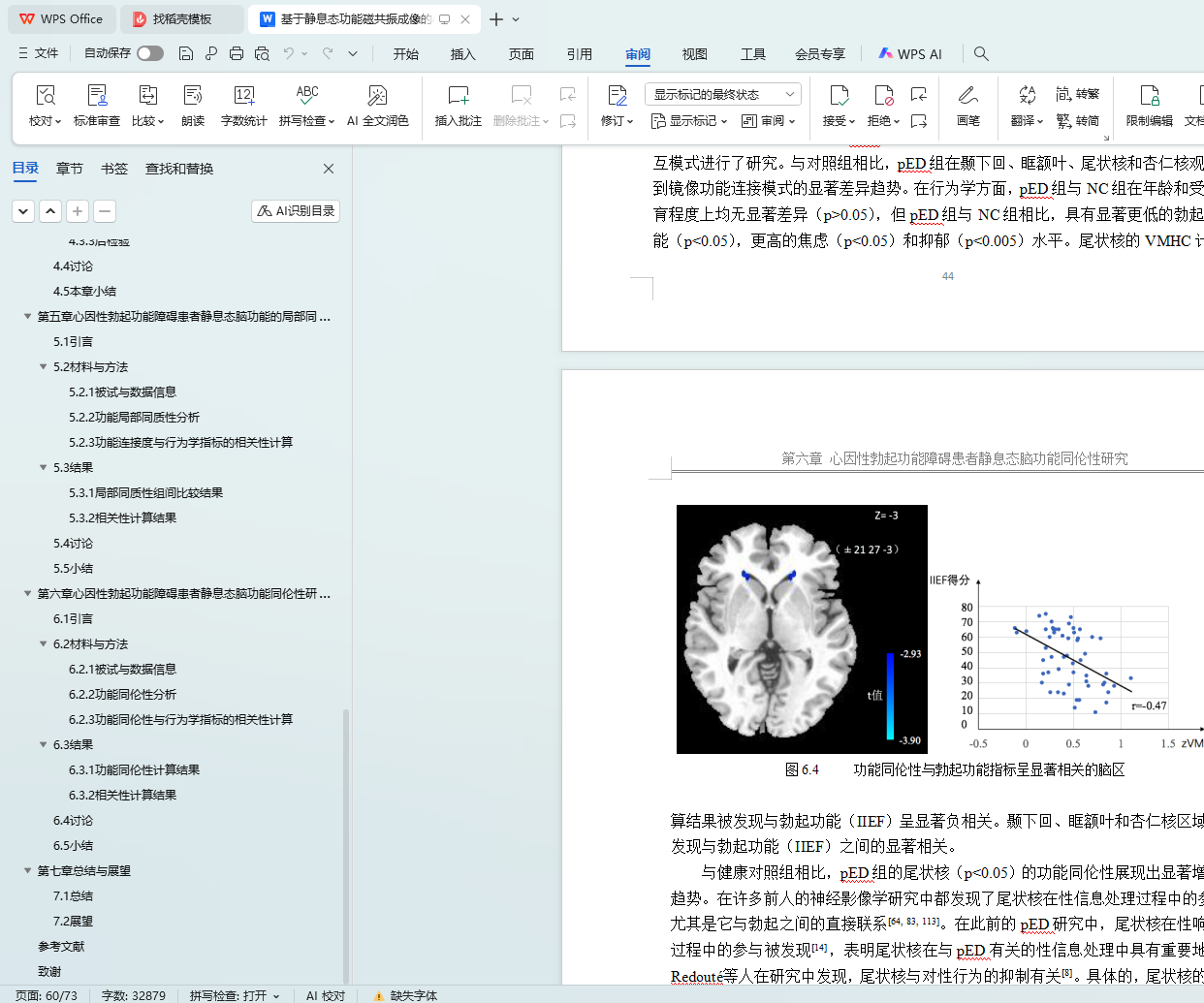
6.3.1 功能同伦性计算结果 39
6.3.2 相关性计算结果 40
6.4 讨论 40
6.5 小结 42
第七章 总结与展望 43
7.1 总结 43
7.2 展望 44
参考文献 45
致谢 53