目录
数字图像实验
1.实验目的:
2.论文详读:
3 The Operator
3.1减少能量方法
3.2图像能量函数
4 Discrete Image Resizing
4.1离散图像大小变化的长宽比
4.2最优接缝顺序的再定位
4.3图像放大
return
break
continue
1.实验目的:
阅读Seam Carving for Content-Aware Image Resizing论文,使用python复现论文中的算法并加入到pygame模块中,使其成为一个可交互的兼顾展示过程的demo。
2.论文详读:
这里从原文章出发,文章中介绍算法的部分从第三段开始

Figure 1: A seam is a connected path of low energy pixels in an image. On the left is the original image with one horizontal and one vertical seam. In the middle the energy function used in this example is shown (the magnitude of the gradient), along with the vertical and horizontal path maps used to calculate the seams. By automatically carving out seams to reduce image size, and inserting seams to extend it, we achieve content-aware resizing. The example on the top right shows our result of extending in one dimension and reducing in the other, compared to standard scaling on the bottom right
图1:接缝是图像中低能量像素的连通路径。左边是原始图像,有一个水平和一个垂直接缝。在中间显示了这个例子中使用的能量函数(梯度的大小),以及用于计算接缝的垂直和水平路径图。通过自动切割接缝来减少图像的大小,并插入接缝来扩展图像,我们实现了内容感知的大小调整。右上方的示例显示了我们在一个维度上扩展而在另一个维度上减小的结果,而右下方则是标准缩放的结果
3 The Operator
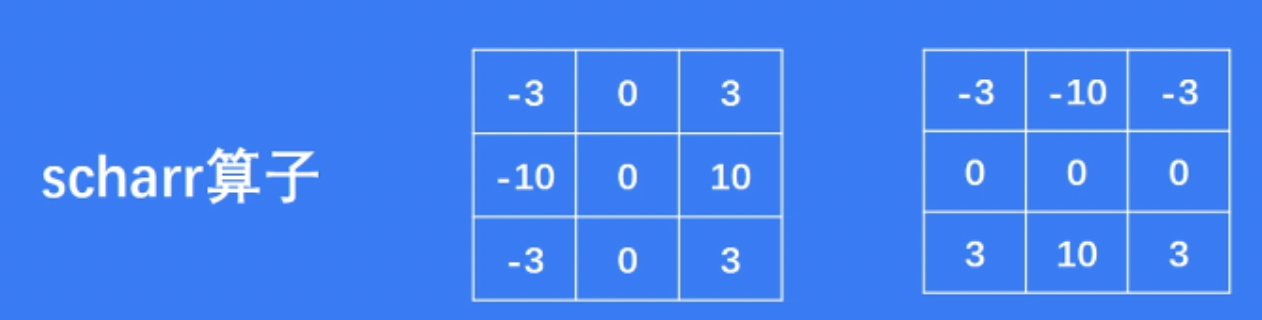
Our approach to content-aware resizing is to remove pixels in a ju- dicious manner. Therefor, the question is how to chose the pixels to be removed? Intuitively, our goal is to remove unnoticeable pixels that blend with their surroundings. This leads to the following sim- ple energy function that was used in many figures in this paper such as Figures 1, 6, 5, 8, 11, 12, 13 (we explore other energy functions in subsection 3.2):
我们的方法是内容感知的大小调整是删除像素在一个不利的方式。因此,问题是如何选择要删除的像素?直观地说,我们的目标是去除与周围环境混合的不明显的像素。这就产生了以下简单的能量函数,在本文的许多图中都使用了这个函数,如图1、6、5、8、11、12、13(我们在3.2小节中探索了其他的能量函数):