摘 要
能源、环境是当今人类生存和发展所要解决的紧迫问题。传统的化石燃料虽能解决能源短缺的问题,却给环境造成了很大的破坏,而风能具有无污染、可再生、低成本等优点,所以其受到世界各国的重视。
可靠、高效的风力发电系统的研发己经成为新能源技术领域的热点。然而,因为风能具有不稳定性、能量密度低和随机性等特点,同时风电厂通常位于偏远地区甚至海上,自然条件比较恶劣,因此要求其控制系统必须能够实现自动化运行,并且要求控制系统有高可靠性。所以对风力发电机组尤其是大型风电机组的控制技术的深入研究就具有相当重要的意义。
本文首先在对风力发电原理,风电机组研究的基础上从变桨距风力机空气动力学研究入手,分析了变桨距控制的基本规律,再结合目前国内主流的变桨距控制技术分别设计出了液压变桨距控制,电动变桨距控制的方案,最后在此基础上提出了一种较为理想的控制策——半桨主动失速控制。
关键词:风力发电,变桨距控制,伺服系统
Abstract
Energy and environment is the human survival and development of the pressing problems which should be solved. The traditional fossil fuel can solve the energy shortage, but give environment caused the most damage, and wind have clean, renewable and low cost, so its advantages by world attention.
Reliable and efficient wind power generation system research and development have already become the hot new energy technologies. However, because the wind is instability, energy density characteristics such as low and randomness, and wind power plant are usually located in remote areas and even at sea, natural condition is poor, so ask its control system must be able to realize automatic operation, and asked for the control system had high reliability. So for WTG especially large wind generator control technology research is of vital significance.
This paper firstly in the principle of wind power generation, based on the study of the wind generator from getting away from a wind turbine propeller air dynamics research, analyses from the basic control variable OARS, coupled with the current domestic law change from the mainstream of the OARS were designed control technology from control hydraulic change propeller, electric control scheme of variable propeller from last, based on this, advances a more ideal control strategy - half oar active stall control.
Keywords: Wind power, From control variable oar ,Servo system
目 录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 风能 1
1.2 风能发电的历史与现状 2
1.3 风力发电技术的发展 3
1.4 风力发电的前景 4
1.5 本章小结 5
第二章 风力发电机组概述 6
2.1 风力发电的原理 6
2.2 风力发电机组的组成 6
2.3 风电机组的分类 7
2.3.1 按功率控制方式分类 8
2.3.2 按发电机控制方式分类的风力机组 8
2.4 风力发电控制系统简介 9
2.4.1 变桨距系统 10
2.4.2 偏航系统 11
2.4.3 制动系统 11
2.5 本章小结 12
第三章 风力发电变桨距控制系统简介 13
3.1 风力发电的空气动力学基础 13
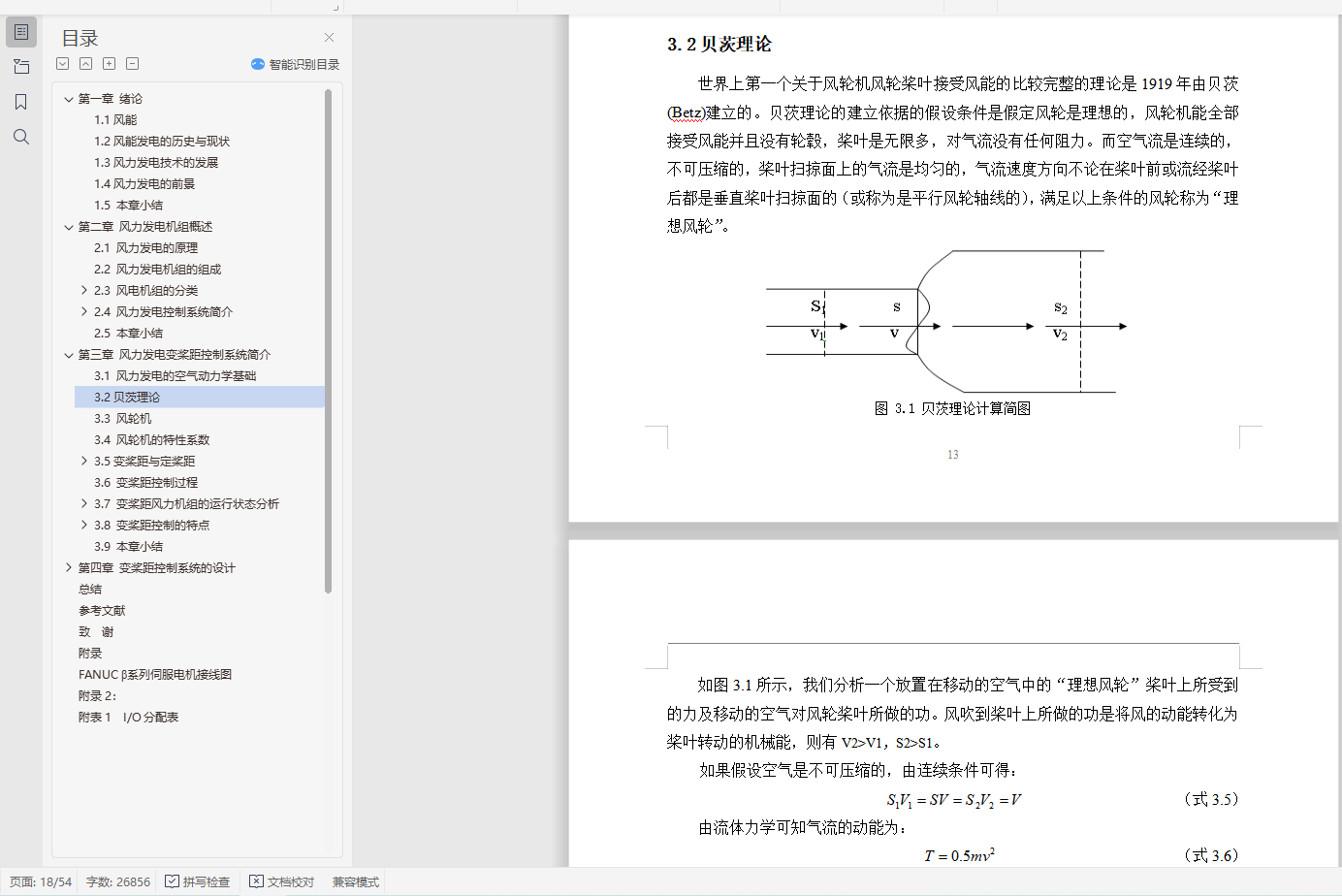
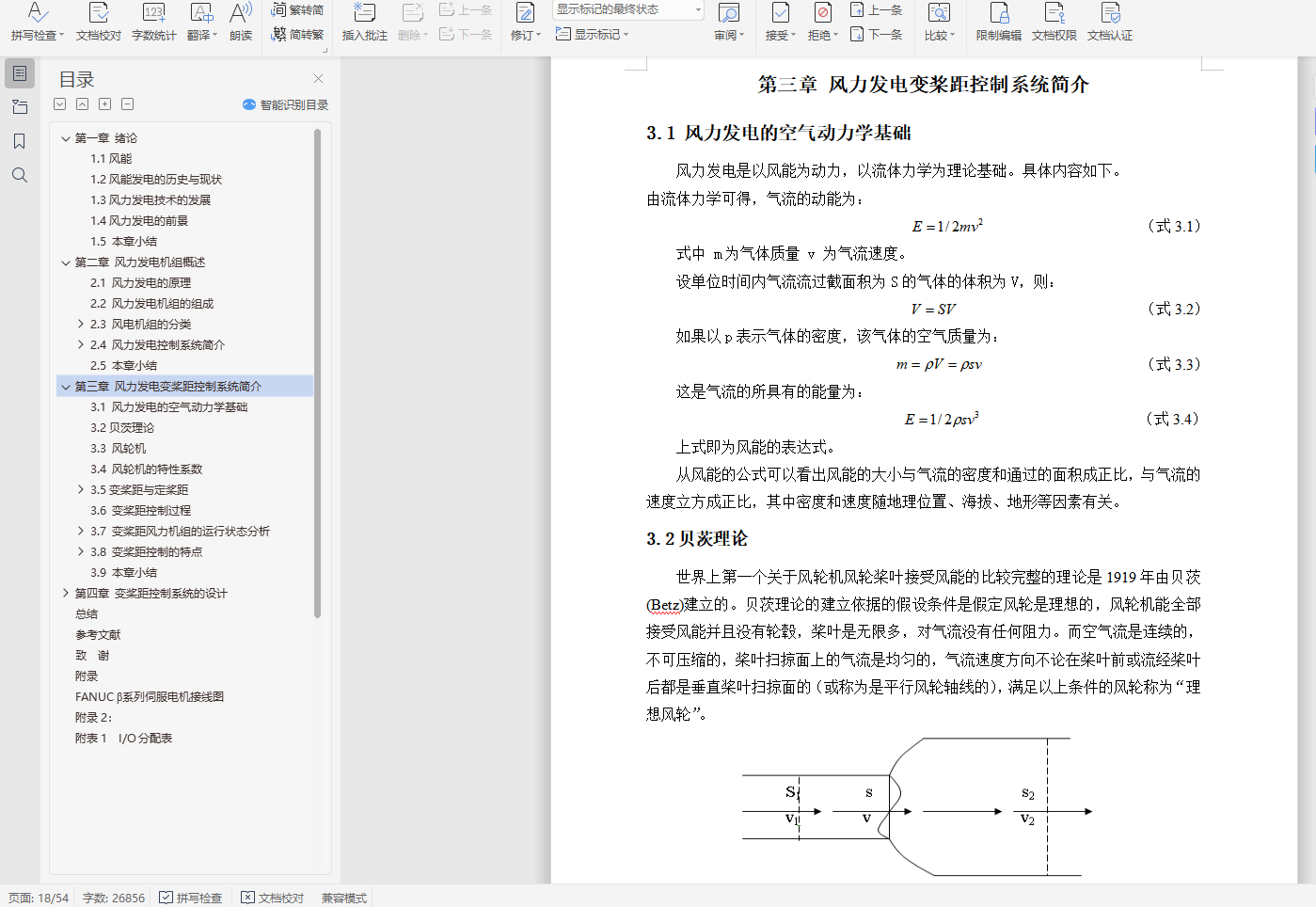
3.2 贝茨理论 13
3.3 风轮机 15
3.4 风轮机的特性系数 15
3.5 变桨距与定桨距 16
3.5.1 定桨距 16
3.5.2 变桨距 17
3.5.3 定桨距与变桨距的比较 17
3.6 变桨距控制过程 18
3.7 变桨距风力机组的运行状态分析 19
3.7.1 启动状态 19
3.7.2 欠功率状态 19
3.7.3 额定功率状态 20
3.8 变桨距控制的特点 20
3.8.1 输出功率特性 20
3.8.2 风能利用率 20
3.8.3 额定功率 21
3.8.4 启动与制动性能 21
3.8.5 对机械部件的影响 21
3.9 本章小结 21
第四章 变桨距控制系统的设计 22
4.1 所涉及设备介绍 23
4.1.1 GE PAC SysteRX3i控制器简介 23
4.1.2 PAC Systems RX3i性能 24
4.1.3 PACSystems RX3i模块简介 24
4.1.4 运动模块DSM324i介绍 25
4.1.5 伺服电机选型 27
4.2 方案设计 28
4.3 液压变桨距控制系统设计 28
4.3.1 液压变桨距控制系统 28
4.3.2 液压变桨距结构 28
4.3.3 变桨控制系统的设计 29
4.4 液压变桨距控制系统评估 33
4.5 电动变桨距控制系统设计 33
4.5.1 独立变桨距控制分析 34
4.5.2 统一变桨控制系统 38
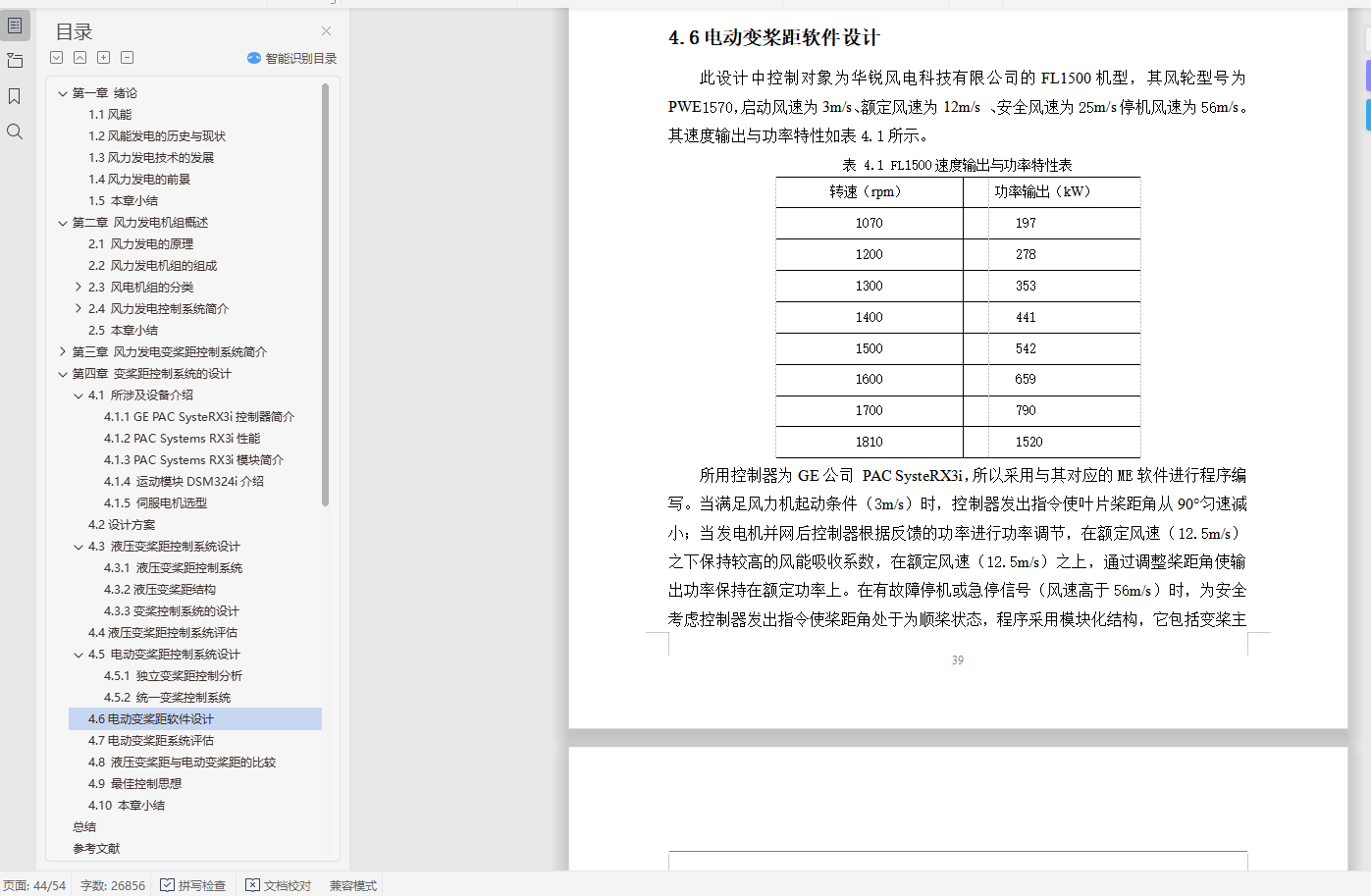
4.6 电动变桨距软件设计 39
4.7 电动变桨距系统评估 41
4.8 液压变桨距与电动变桨距的比较 42
4.9 最佳控制思想 42
总结 43
参考文献 44
致谢 44
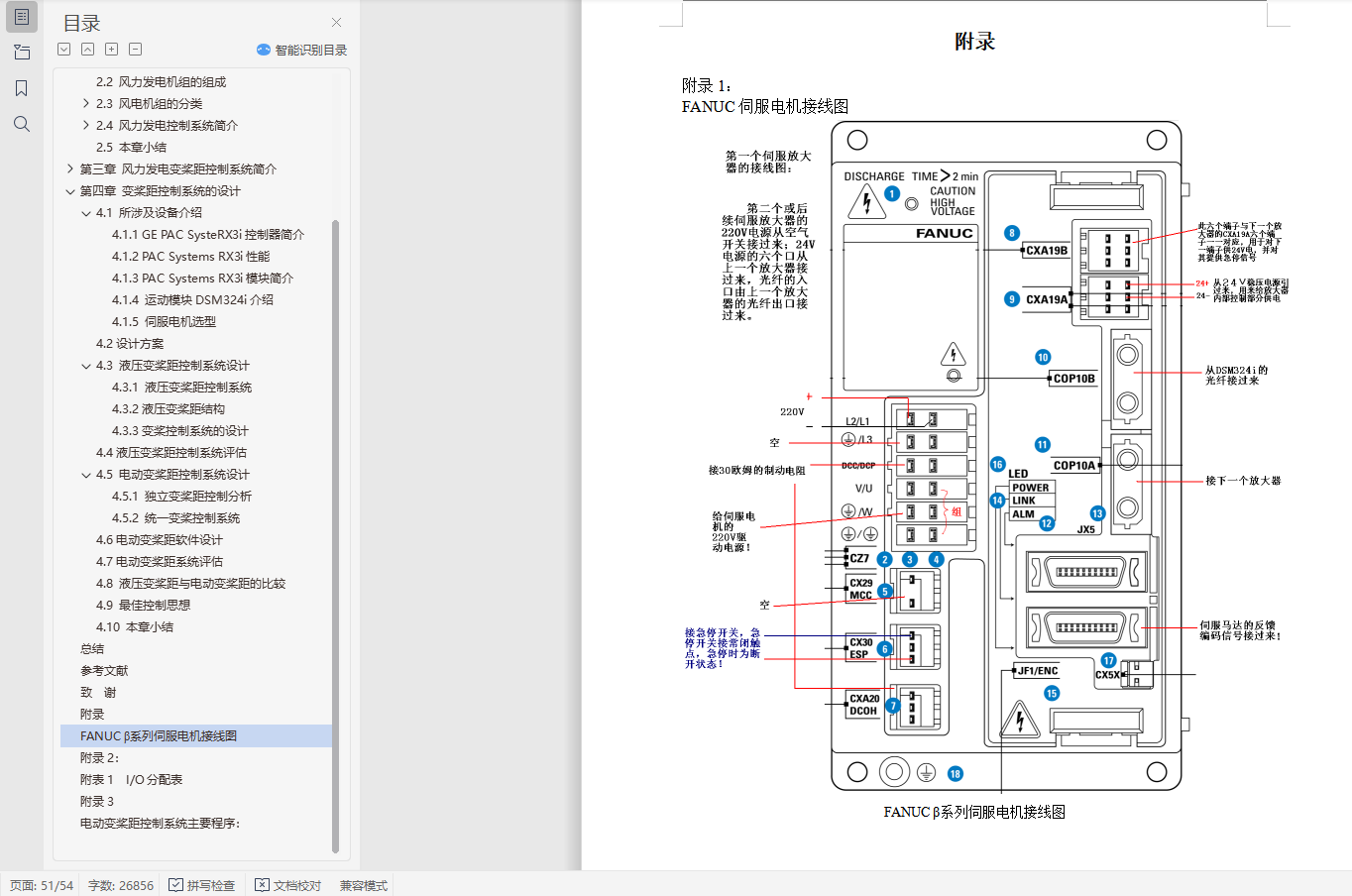
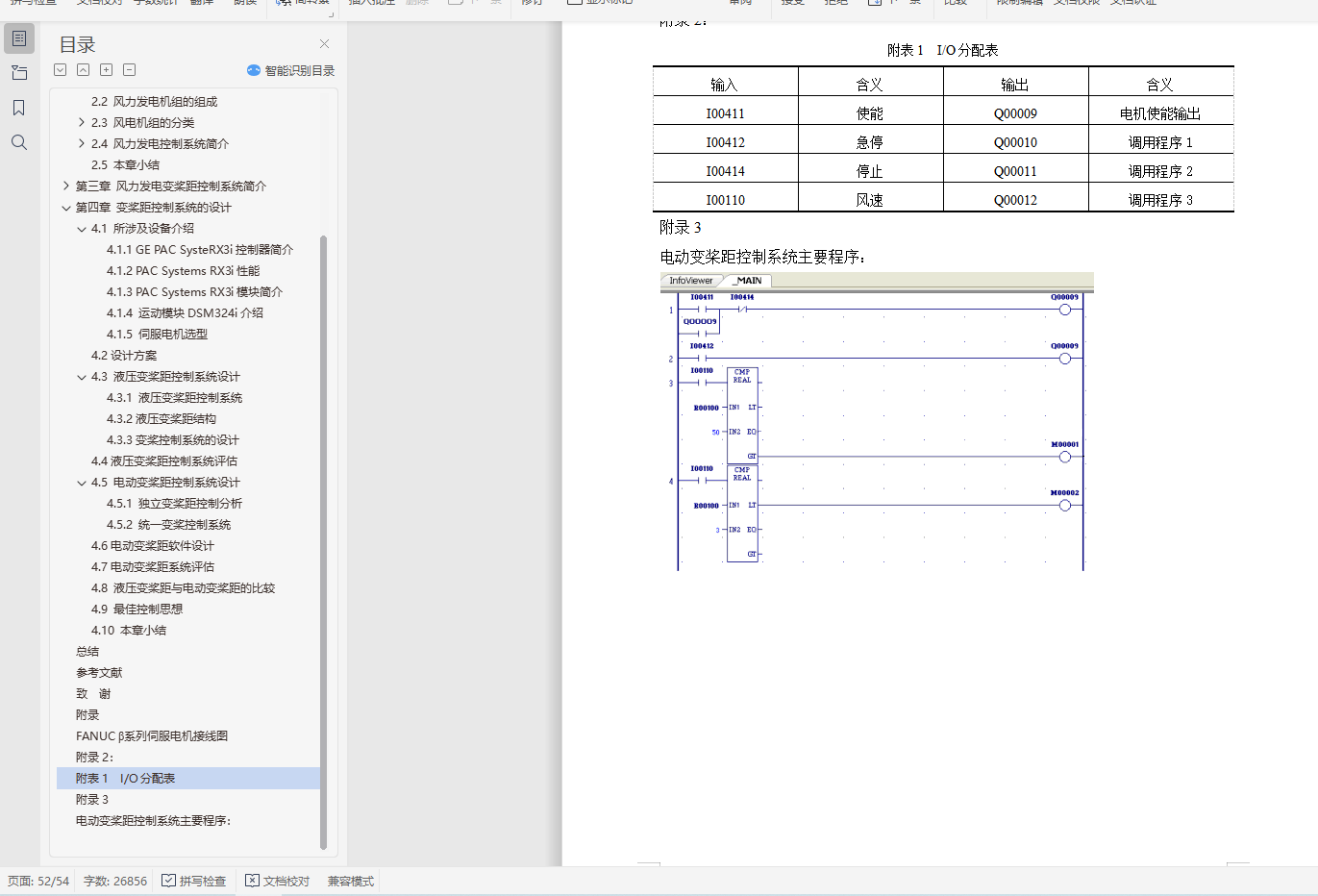
附录 45