目录
0摘要…………………………………………-3-
1引言……………………………………….-6-
第一章 设计方案的确定 - 9 -
一 总体设计方案的确定 - 9 -
二 机械部分的改造设计与计算 - 10 -
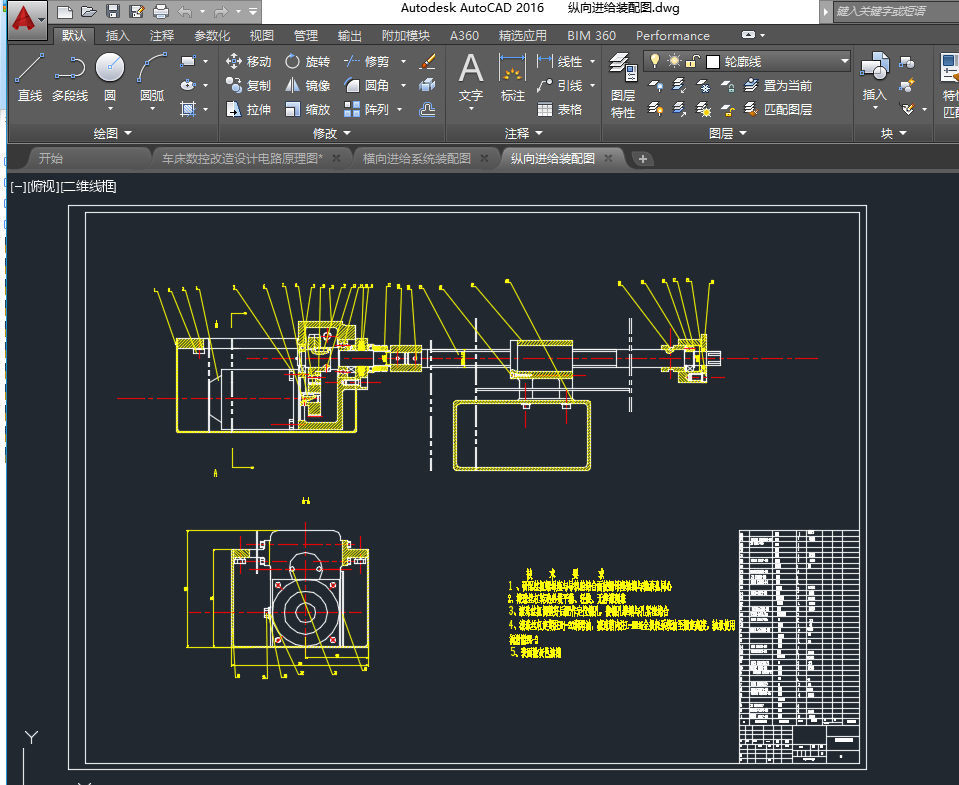
(一)纵向进给系统的设计选型 - 10 -
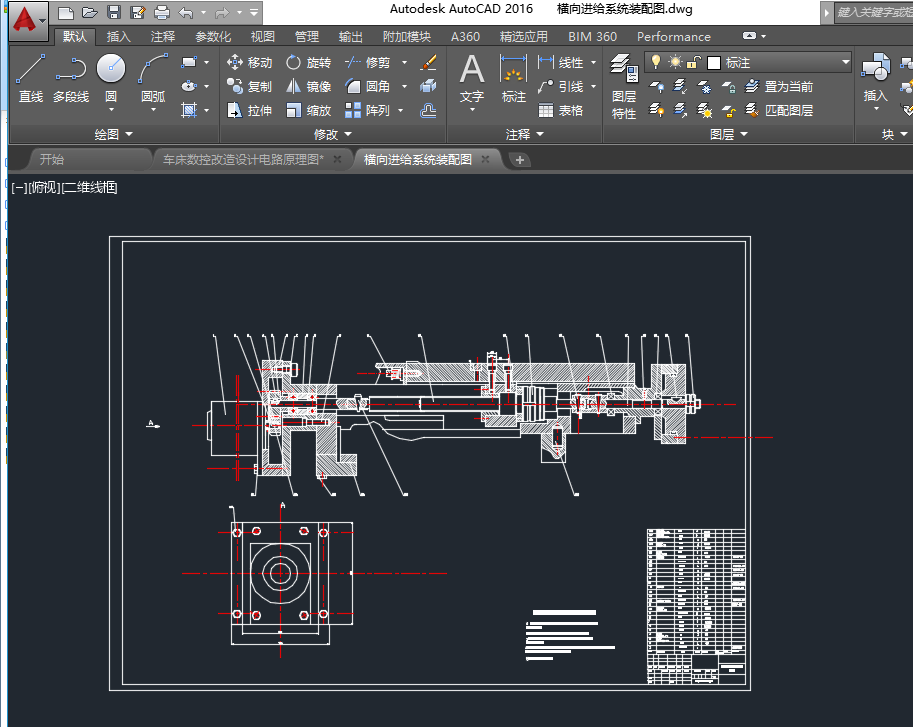
(二) 横向进给系统的设计与计算 - 15 -
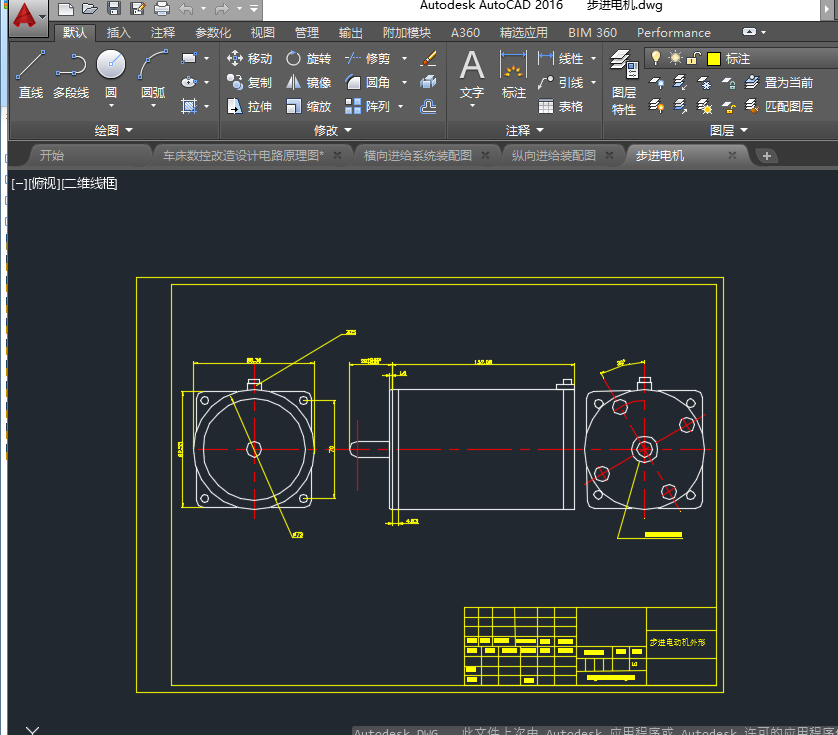
第二章 步进电动机的选择 - 19 -
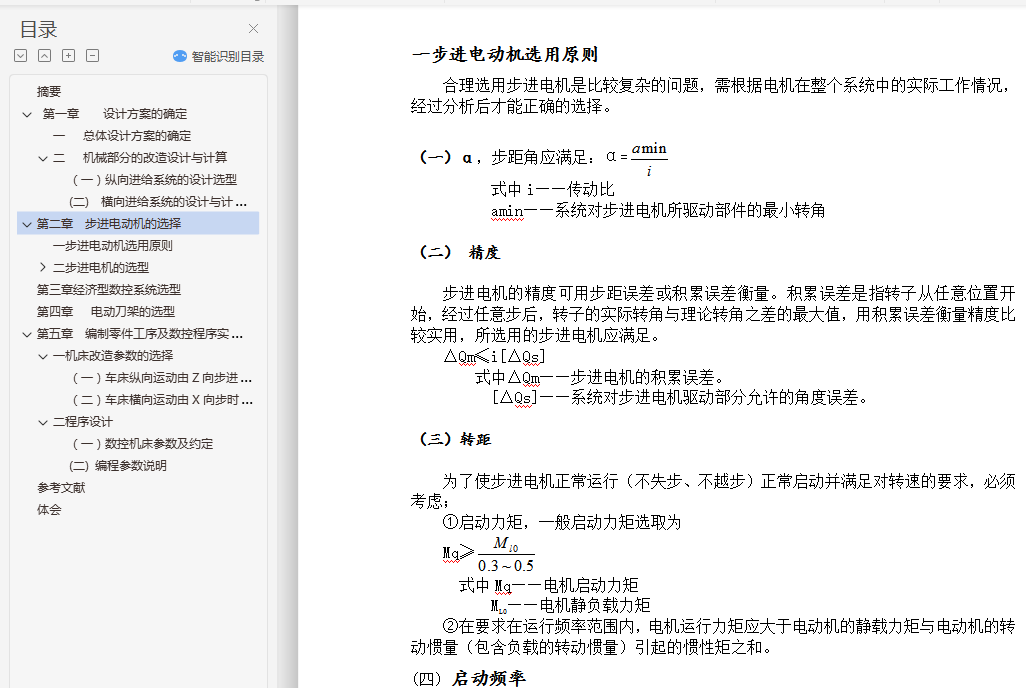
一步进电动机选用原则 - 19 -
二步进电机的选型 - 20 -
(一)C6140纵向进给系流步进电机的确定 - 20 -
(二)C6140横向进给系流步进电机的确定 - 20 -
(三)110BF003型直流步进电机主要技术参数 - 20 -
(四)110BF004型直流步进电机主要技术参数 - 21 -
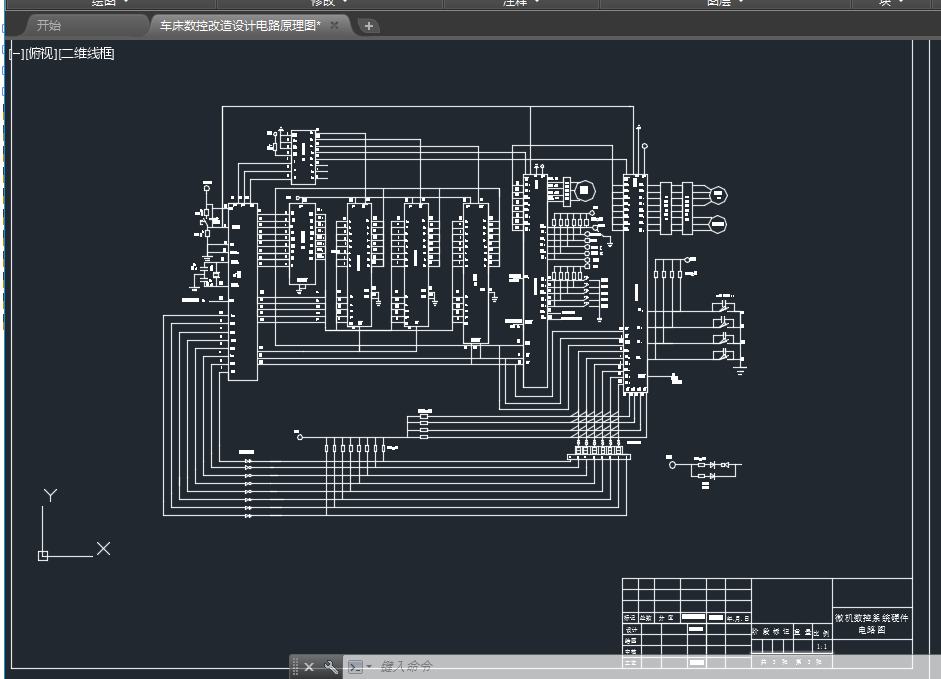
第三章经济型数控系统选型 - 21 -
第四章 电动刀架的选型 - 22 -
第五章 编制零件工序及数控程序实例 - 23 -
一机床改造参数的选择 - 23 -
(一)车床纵向运动由Z向步进电动机控制 - 23 -
(二)车床横向运动由X向步时电动机控制 - 23 -
二程序设计 - 23 -
(一)数控机床参数及约定 - 23 -
(二) 编程参数说明 - 23 -
参考文献 - 27 -
体会 - 28 -
摘要
1947年,Parsons公司的John Parsons着手进行一项实验,他想用空间数据控制机床加工飞机零件。1949年,Parsons公司与美国空军签定了制造第一台数控机床的合同。1951年, 美国麻省理工学院承担了这一项目。1952年,麻省理工学院(MIT)使用实验室制造的控制器和辛辛那提立式主轴展示三轴联动获得成功,这标志着数控时代的到来。到了1955年,几经改进之后,数空技术开始应用于生产。
早期的NC机床能运行穿孔卡和穿孔带,两者中以穿孔带更为通用。但是,鉴于更换、编辑纸带费时费力,后来便采用计算机作为编程的辅助工具。计算机在数控中的应用有两种形式:一是计算机辅助编程语言,二是实施直接数字控制(DNC),有了计算机辅助编程语言,程序员可用一套通用“混杂英语”命令编写NC程序,然后由计算机将其释译为机器码并制成穿孔带。直接数字控制是指用一台计算机对一台或多台数控机床实施部分或整体控制。虽然有些公司运用DNC已获得成功,但是,扩大计算机容量、购买软件、协调DNC系统等花费使这种系统并不适合所有公司,而只适用于一些大公司。
最近,一种叫做分布式数字控制的新型DNC系统已经开发出来,它用计算机网络来协调多台DNC机床的运行。这种方式最终有可能用来协调整个工厂的运转。这种分布式数字控制方法解决了协调直接数字控制系统时遇到的一些难题。在此基础上,人们还开发出另一种分布式数字控制系统,其整个NC程序可从主机直接传输到机床控制器。另外,该系统也可在必要时将程序从主机传输到车间的个人电脑(PC),然后再传输到机床控制器
工业机器人是在生产环境中用以提高生产效率的工具,它能做常规乏味的装配线工作,或能做那些对于工人来说是危险的工作,例如,第一代工业机器人是用来在核电站中更换核燃料棒,如果人去做这项工作,将会遭受有害放射线的辐射。工业机器人亦能工作在装配线上将小元件装配到一起,如将电子元件安放在电路印制板,这样,工人就能从这项乏味的常规工作中解放出来。机器人也能按程序要求用来拆除炸弹,辅助残疾人,在社会的很多应用场合下履行职能。
机器人可以认为是将手臂末端的工具、传感器和(或)手爪移到程序指定位置的一种机器。当机器人到达位置后,它将执行某种任务。除了编程以及系统的开停之外,一般来说这些工作可以在无人干预下完成。
关键字:加工精度,设计方案,分配,参数
ABSTRACT
In 1947 , John Parsons of the Parsons Corporation, began experimenting with the idea of using three-axis curvature data to control machine tool motion for the production of aircraft components . In 1949 , Parsons was awarded a U. S. Air Force contract to build what was to become the first numerical control machine . In 1951 , the project was assumed by Massachusetts Institute of Technology . In 1952 , numerical control arrived when MIT demonstrated that simultaneous three-axis movements were possible using a laboratory-built controller and a Cincinnati Hydrotel vertical spindle . By 1955 , after further refinements , numerical control became available to industry .
Early NC machines ran off punched cards and tape , with tape becoming the more common medium . Due to time and effort required to change or edit tape , computers were later introduced as aids in programming . Computer involvement came in two forms : computer aided programming languages and direct numerical control (DNC) . Computer aided programming language allowed a part programmer to develop an NC program using a set of universal “pidgin English” commands , which the computer then translated into machine codes and punched into the tape . Direct numerical control involved using a computer as a partial or complete controller of one or more numerical control machines . Although some companies have been reasonably successful at implementing DNC , the expense of computer capability and software and problems associated with coordinating a DNC system renders such systems economically unfeasible for all but the largest companies .
Recently a new tape of DNC system called distributive numerical control has been developed . It employs a network of computers to coordinate the operation of a number of CNC machines . Ultimately , it may be possible to coordinate an entire factory in this manner . Distributive numerical control solves some of the problems that exist in coordinating a direct numerical control system. There is another type of distributive numerical control that is a spin-off of the system previously explained . In this system , the NC program is transferred in its entirety from a host computer directly to the machine’s controller . Altemately , the program can be transferred from a host computer to a personal computer(PC) on the shop floor where it will be stored until it is needed . The program will then be transferred from the PC to the machine controller .
The industrial robot is a tool that is used in the manufacturing environment to increase productivity. It can be used to do routine and tedious assembly line jobs, or it can perform jobs that might be hazardous to the human worker. For example, one of the first industrial robots was used to replace the nuclear fuel rods in nuclear power plants. A human doing this job might be exposed to harmful amounts of radiation. The industrial robot can also operate on the assembly line, putting together small components, such as placing electronic components on a printed circuit board. Thus, the human worker can be relieved of the routine operation of this tedious task. Robots can also be programmed to defuse bombs, to serve the handicapped, and to perform functions in numerous applications in our society.
The robot can be thought of as a machine that will move an end-of-arm tool, sensor, and/or gripper to a preprogrammed location. When the robot arrives at this location, it will perform some sort of task. This task could be welding, sealing, machine loading, machine unloading, or a host of assembly jobs. Generally, this work can be accomplished without the involvement of a human being, except for programming and for turning the system on and off.
Key Words: Accuracy of Process,Project Design,Allotment,Parameter